什么是OCR识别
OCR是指对文本资料进行扫描后对图像文件进行分析处理,获取文字及版面信息的过程。用Opencv进行OCR识别时,通常分为两步:扫描、识别。
如何进行OCR识别
整体流程
1.读取图像
2.预处理(灰度--二值)
3.边缘检测
4.轮廓检测
5.轮廓近似
6.透视变换
7.OCR识别
8.展示结果
具体实现
Step1:边缘检测
1.读取图像
import cv2
import numpy as np
# 读取输入
image = cv2.imread('receipt.jpg')
#坐标也会相同变化
ratio = image.shape[0] / 500.0
orig = image.copy()
image = resize(orig, height = 500)
将输入的图像resize成高为500的等比例缩小的图像,所以之后所获取的关键点的坐标也是基于resize后的图像得到的,故在这里我们需要先知道图片resize的比例,称为ratio.
同时,为了方便,在这里写了一个函数进行resize操作,如下:
def resize(image,width=None,height=None,inter=cv2.INTER_AREA):
dim=None
(h,w)=image.shape[:2]
if width is None and height is None:
return image
if width is None:
r=height/float(h)
dim=(int(w*r),height)
else:
r=width/float(w)
dim=(width,int(h*r))
resized=cv2.resize(image,dim,interpolation=inter)
return resized
2.预处理
#预处理
#灰度转换
gray=cv2.cvtColor(image,cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
#高斯滤波--去噪点
gray=cv2.GaussianBlur(gray,(5,5),0)
#边缘检测
edged=cv2.Canny(gray,75,200)
imshow("canny",edged);

Step2:获取轮廓
#轮廓检测--面积最大的轮廓就是需要的
cnts,hierarchy=cv2.findContours(edged.copy(),cv2.RETR_LIST,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cnts=sorted(cnts,key=cv2.contourArea,reverse=True)[:5]
#遍历轮廓
for c in cnts:
#计算轮廓近似
peri=cv2.arcLength(c,True)
approx=cv2.approxPolyDP(c,0.02*peri,True)
#4个点的时候就拿出来
if len(approx)==4:
screenCnt=approx
break
#显示结果
print("STEP2:获取轮廓")
cv2.drawContours(image,[screenCnt],-1,(0,0,255),2,LINE_AA)
imshow("outline",image);

Step3:透视变换
透视变换的基本原理
首先引入两个函数完成透视变换的操作。
(1)order_points(pts)函数:将上一步得到的轮廓的四个顶点按照左上,右上,右下,左下的顺序排序。
其原理为:首先计算每个点所包含的两个坐标的和,最小的为左上角的点,最大的为右下角的点。然后计算每个点所包含的两个坐标的差,最小的为右上角的点,最大的为左下角的点。
def order_points(pts):
# 一共4个坐标点
rect = np.zeros((4, 2), dtype = "float32")
# 按顺序找到对应坐标0123分别是 左上,右上,右下,左下
# 计算左上,右下
s = pts.sum(axis = 1)
rect[0] = pts[np.argmin(s)]
rect[2] = pts[np.argmax(s)]
# 计算右上和左下
diff = np.diff(pts, axis = 1)
rect[1] = pts[np.argmin(diff)]
rect[3] = pts[np.argmax(diff)]
return rect
(2)four_point_transform(image, pts):透视变换。
def four_point_transform(image, pts):
# 获取输入坐标点
rect = order_points(pts)
(tl, tr, br, bl) = rect
# 计算输入的w和h值
widthA = np.sqrt(((br[0] - bl[0]) ** 2) + ((br[1] - bl[1]) ** 2))
widthB = np.sqrt(((tr[0] - tl[0]) ** 2) + ((tr[1] - tl[1]) ** 2))
maxWidth = max(int(widthA), int(widthB))
heightA = np.sqrt(((tr[0] - br[0]) ** 2) + ((tr[1] - br[1]) ** 2))
heightB = np.sqrt(((tl[0] - bl[0]) ** 2) + ((tl[1] - bl[1]) ** 2))
maxHeight = max(int(heightA), int(heightB))
# 变换后对应坐标位置(-1只是为了防止有误差出现,不-1也可以。)
dst = np.array([
[0, 0],
[maxWidth - 1, 0],
[maxWidth - 1, maxHeight - 1],
[0, maxHeight - 1]], dtype = "float32")
# 计算变换矩阵
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(rect, dst)
warped = cv2.warpPerspective(image, M, (maxWidth, maxHeight))
# 返回变换后结果
return warped
# 透视变换
warped = four_point_transform(orig, screenCnt.reshape(4, 2) * ratio)
# 二值处理
warped = cv2.cvtColor(warped, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ref = cv2.threshold(warped, 100, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)[1]
cv2.imwrite('scan.jpg', ref)
# 展示结果
print("STEP 3: 变换")
cv2.imshow("Scanned", ref)
cv2.waitKey(0)
变换后的结果:

Step4:OCR识别
1.下载
https://digi.bib.uni-mannheim.de/tesseract/
选择一个版本进行下载
2.安装
下载完成后打开一路next安装完成
3.环境变量配置
将刚刚安装的目录添加到环境变量中
(可以在命令行窗口(cmd)中输入tesseract -v进行测试,会输出版本号。)
4.OCR识别测试
在命令行窗口中输入tesseract scan.jpg result,会将刚才扫描的图片上的信息写入result.txt文件中。
5.在python中实现
- 5.1 先安装pytesseract---pip install pytesseract
- 5.2 在库文件夹中找到pytesseract文件夹里的pytesseract.py文件,打开,修改里面tesseract_cmd一行为绝对路径。
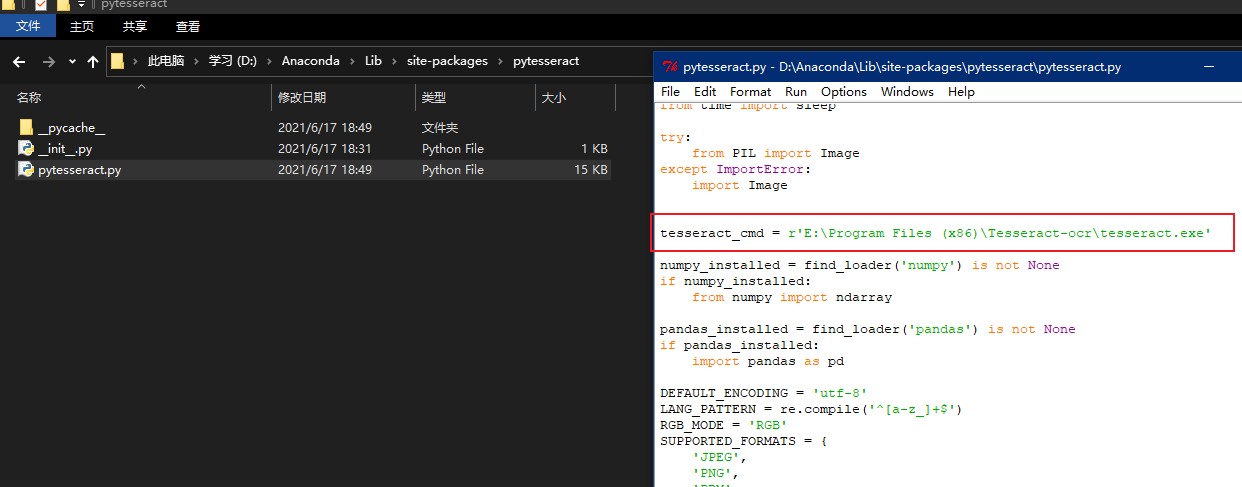
6.在python中引入相关的库
from PIL import Image
import pytesseract
import cv2
import os
7.执行识别操作
preprocess = 'blur' #thresh
image = cv2.imread('scan.jpg')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
if preprocess == "thresh":
gray = cv2.threshold(gray, 0, 255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
if preprocess == "blur":
gray = cv2.medianBlur(gray, 3)
filename = "{}.png".format(os.getpid())
cv2.imwrite(filename, gray)
text = pytesseract.image_to_string(Image.open(filename))
print(text)
os.remove(filename)
8.最终效果
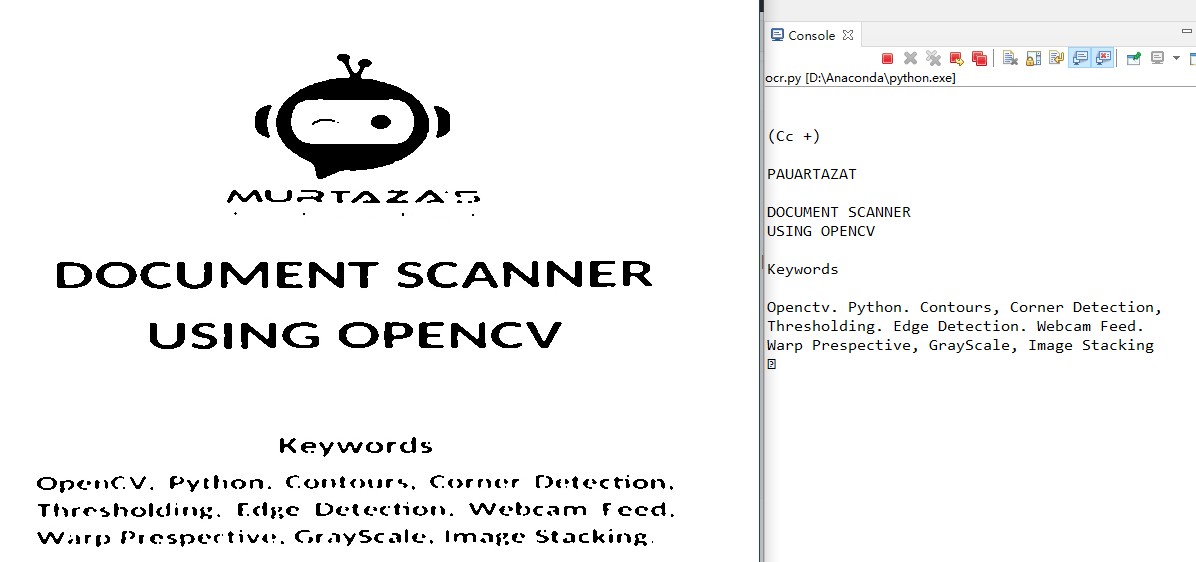
完整代码
#ocr_demo.py 输入参数:--image D:imagepaper.jpg
import cv2
import argparse
import numpy as np
import imutils
ap=argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("-i","--image",required=True,help="path to input image")
args=vars(ap.parse_args())
def resize(image,width=None,height=None,inter=cv2.INTER_AREA):
dim=None
(h,w)=image.shape[:2]
if width is None and height is None:
return image
if width is None:
r=height/float(h)
dim=(int(w*r),height)
else:
r=width/float(w)
dim=(width,int(h*r))
resized=cv2.resize(image,dim,interpolation=inter)
return resized
def order_point(pts):
#一共4个坐标点
rect=np.zeros((4,2),dtype="float32")
#按顺序找到对应坐标,左上,右上,右下,左下
#计算左上,右下
s=pts.sum(axis=1)
rect[0]=pts[np.argmin(s)]
rect[2]=pts[np.argmax(s)]
#计算右上和左下
diff=np.diff(pts,axis=1)
rect[1]=pts[np.argmin(diff)]
rect[3]=pts[np.argmax(diff)]
return rect
def four_point_transform(image,pts):
#获取输入的坐标点
rect=order_point(pts)
(tl,tr,br,bl)=rect
#计算输入的w和h值
#w---x的平方+y的平方开根号 取比较大的那个
widthA=np.sqrt(((br[0]-bl[0])**2)+((br[1]-bl[1])**2))
widthB=np.sqrt(((tr[0]-tl[0])**2)+((tr[1]-tl[1])**2))
maxWidth=max(int(widthA),int(widthB))
#h同理
heightA=np.sqrt(((tr[0]-br[0])**2)+((tr[1]-br[1])**2))
heightB=np.sqrt(((tl[0]-bl[0])**2)+((tl[1]-bl[1])**2))
maxHeight=max(int(heightA),int(heightB))
#变换后对应坐标的位置
dst=np.array([[0,0],[maxWidth-1,0],[maxWidth-1,maxHeight-1],[0,maxHeight-1]],dtype="float32")
#dst=np.array([[0,0],[500,0],[666,500],[0,666]],dtype="float32")
#计算变换矩阵
#2维----3维---2维
M=cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(rect,dst)
warped=cv2.warpPerspective(image,M,(maxWidth,maxHeight))
return warped
#读取图片
image=cv2.imread(args["image"])
ratio=image.shape[0]/500.0
orig=image.copy()
image=resize(orig,height=500)
#预处理
gray=cv2.cvtColor(image,cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
gray=cv2.GaussianBlur(gray,(5,5),0)
#边缘检测
edged=cv2.Canny(gray,75,200)
imshow("canny",edged);
#轮廓检测
cnts,hierarchy=cv2.findContours(edged.copy(),cv2.RETR_LIST,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cnts=sorted(cnts,key=cv2.contourArea,reverse=True)[:5]
#遍历轮廓
for c in cnts:
#计算轮廓近似
peri=cv2.arcLength(c,True)
approx=cv2.approxPolyDP(c,0.02*peri,True)
#4个点的时候就拿出来
if len(approx)==4:
screenCnt=approx
break
#显示结果
print("STEP2:获取轮廓")
cv2.drawContours(image,[screenCnt],-1,(0,0,255),2,LINE_AA)
imshow("outline",image);
#cv.Circle(img, center, radius, color, thickness=1, lineType=8, shift=0) → None
#透视变换
wraped=four_point_transform(orig,screenCnt.reshape(4,2)*ratio)
#二值处理
wraped=cv2.cvtColor(wraped,cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
ref=cv2.threshold(wraped,100,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)[1]
cv2.imwrite("scan.jpg",ref)
#展示结果
print("STEP3:变换")
imshow("Original",resize(orig,width=500))
imshow("Scanned",ref)
waitKey()
#ocr.py
from PIL import Image
import pytesseract
import cv2
import os
from cv2 import waitKey
preprocess='blur'
image=cv2.imread("scan.jpg")
gray=cv2.cvtColor(image,cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
if preprocess=="thresh":
gray=cv2.threshold(gray,0,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY|cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
if preprocess=="blur":
gray=cv2.medianBlur(gray,3)
filename="{}.png".format(os.getpid())
cv2.imwrite(filename,gray)
text=pytesseract.image_to_string(Image.open(filename))
print(text)
os.remove(filename)
cv2.imshow("Image",image)
cv2.imshow("output",gray)
waitKey()