E. Analysis of Pathes in Functional Graph
You are given a functional graph. It is a directed graph, in which from each vertex goes exactly one arc. The vertices are numerated from 0 to n - 1.
Graph is given as the array f0, f1, ..., fn - 1, where fi — the number of vertex to which goes the only arc from the vertex i. Besides you are given array with weights of the arcs w0, w1, ..., wn - 1, where wi — the arc weight from i to fi.
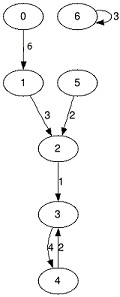
Also you are given the integer k (the length of the path) and you need to find for each vertex two numbers si and mi, where:
- si — the sum of the weights of all arcs of the path with length equals to k which starts from the vertex i;
- mi — the minimal weight from all arcs on the path with length k which starts from the vertex i.
The length of the path is the number of arcs on this path.
The first line contains two integers n, k (1 ≤ n ≤ 105, 1 ≤ k ≤ 1010). The second line contains the sequence f0, f1, ..., fn - 1 (0 ≤ fi < n) and the third — the sequence w0, w1, ..., wn - 1 (0 ≤ wi ≤ 108).
Print n lines, the pair of integers si, mi in each line.
7 3
1 2 3 4 3 2 6
6 3 1 4 2 2 3
10 1
8 1
7 1
10 2
8 2
7 1
9 3
4 4
0 1 2 3
0 1 2 3
0 0
4 1
8 2
12 3
5 3
1 2 3 4 0
4 1 2 14 3
7 1
17 1
19 2
21 3
8 1
#include<cstdio> #include<cmath> #include<map> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #define fi first #define se second using namespace std; typedef long long LL; typedef pair<LL,int>pii; const int N=1e5+5; LL ws[N][40],k; int f[N][40],wm[N][40],n; void bz() { for(int j=1;(1LL<<j)<=k;j++) for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { f[i][j]=f[f[i][j-1]][j-1]; ws[i][j]=ws[i][j-1]+ws[f[i][j-1]][j-1]; wm[i][j]=min(wm[i][j-1],wm[f[i][j-1]][j-1]); } } pii query(int u) { pii res; res.fi=0,res.se=1e8; for(int i=0;i<40;i++) if(k&(1LL<<i)) res.fi+=ws[u][i],res.se=min(wm[u][i],res.se),u=f[u][i]; return res; } int main() { scanf("%d%I64d",&n,&k); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%d",&f[i][0]); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%d",&wm[i][0]),ws[i][0]=wm[i][0]; bz(); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { pii ans=query(i); printf("%I64d %d ",ans.fi,ans.se); } return 0; }