正文从这开始~
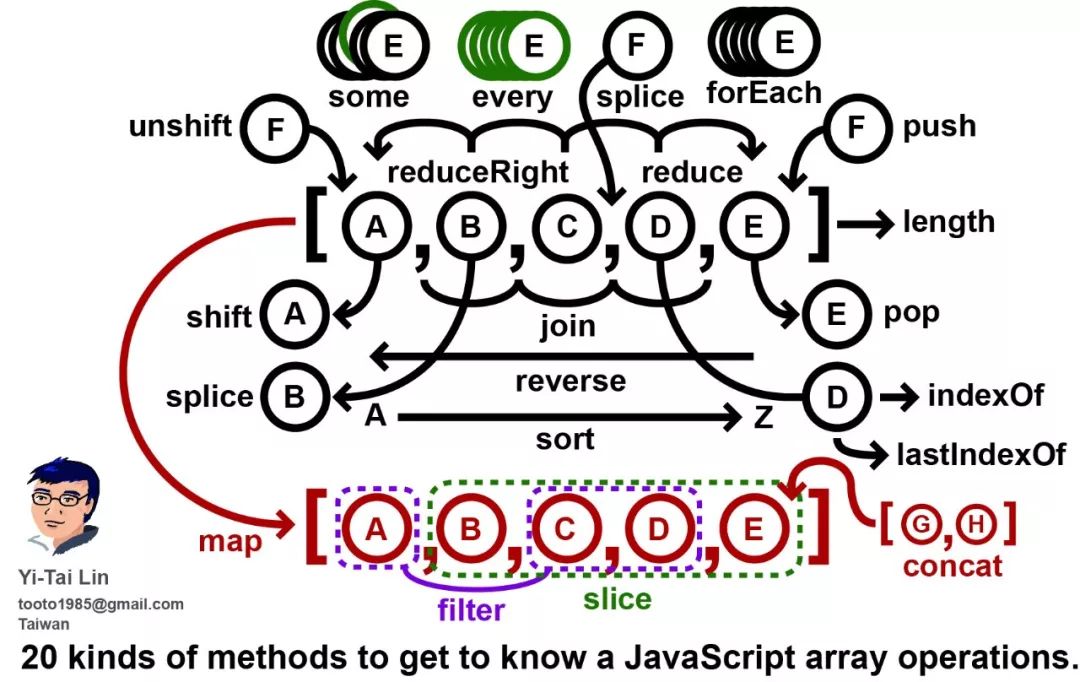
ECMAScript 5.1 中提供的数组方法
其中部分方法,ECMAScript 3 就出现了,但是本文不再细分。
ECMA-262/5.1 规范:https://www.ecma-international.org/ecma-262/5.1/#sec-15.4
判断是否是数组
Array.isArray ( arg )
// false or true不支持此方法的IE9-等浏览器可以这样处理:
Object.prototype.toString.call(obj) === '[object Array]';转换方法
toString
数组的 valueOf 会默认调用 toString 方法,所以他们的返回值一样,都是逗号分隔每一项组成的字符串
var months = ['Jan', 'Feb', 'Mar', 'Apr'];
months.toString(); // "Jan,Feb,Mar,Apr"toLocaleString
调用数组每一项的 toLocaleString 方法,有时和 toString 方法的结果是一样的。有时也不同,比如 Date 对象元素组成的数组里,返回的结果会不同。
join
a.join(); // 'Wind,Rain,Fire'
a.join(', '); // 'Wind, Rain, Fire'
a.join(' + '); // 'Wind + Rain + Fire'
a.join(''); // 'WindRainFire'如果数组中的某一项的值是 null 或者 undefined,那么该值在 join()、toLocale-String()、toString() 和 valueOf() 方法返回的结果中以空字符串表示
对应的逆向方法是 String.split()
栈方法
pop 删除数组的最后一项
操作原数组,返回删除项
var a = [1, 2, 3];
var b = a.pop();
console.log(a); // [1, 2]
console.log(b); // 3push 在数组末尾添加新元素
操作的原数组,返回数组长度
var a = [1, 2, 3];
var b = a.push(4, 5);
console.log(a); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
console.log(b); // 5队列方法
shift 删除数组的第一项
操作的原数组,返回删除项
var a = [1, 2, 3];
var b = a.shift();
console.log(a); // [2, 3]
console.log(b); // 1unshift 数组的前面添加新元素
操作的原数组,返回数组长度
var a = [1, 2, 3];
var b = a.unshift(4, 5);
console.log(a); // [4, 5, 1, 2, 3]
console.log(b); // 5重排序方法
reverse 反转数组项的顺序
操作原数组,返回数组
var a = ['one', 'two', 'three'];
var b= a.reverse();
console.log(a); // ['three', 'two', 'one']
console.log(b); // ['three', 'two', 'one']sort 排序
按照 Unicode code 位置排序,默认升序
var fruit = ['cherries', 'apples', 'bananas'];
fruit.sort(); // ['apples', 'bananas', 'cherries']
var scores = [1, 10, 21, 2];
scores.sort(); // [1, 10, 2, 21]
// because '10' is mix of two characters '1' and '0' so '10' is before '2' in Unicode code point order.排序后 undefined 会被放在数组末尾
之前写过一篇排序方法的深入解读,感兴趣请点击这里
深入浅出 JavaScript 的 Array.prototype.sort 排序算法:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000010648740
操作方法
concat 合并数组
返回新数组
var arr1 = ['a', 'b', 'c'];
var arr2 = ['d', 'e', 'f'];
var arr3 = arr1.concat(arr2);
console.log(arr3);
// expected output: ["a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f"]
var arr4 = arr1.concat(1, [4, [5, 6]]);
console.log(arr4);
//猜猜这个的结果?
// 输出: ['a', 'b', 'c', 1, 4, [5, 6]]
//如果传入的是数组,取的是其值。但是数组中的数组,是保留的。slice 基于当前数组创建新数组
返回新数组
传入两个参数 起始位置(包含) 结束位置(不包含),虎头蛇尾,有始无终。
只传一个参数默认截取到数组末尾, 会认为是开始位置
传递的参数中有一个负数,则用数组长度加上该数来确定位置。长度为 5 的数组 slice(-2,-1) 与 slice(3, 4) 结果相同。
结束位置小于起始位置,则返回空数组
var a = ['1', '2', '3', '4'];
var sliced = a.slice(1, 3);
console.log(a); // ['1', '2', '3', '4']
console.log(sliced); // ['2', '3']splice
可以实现 删除、插入(元素个数大于要删除的元素个数)、替换(删除一个,再添加一个)
返回被删除元素组成的数组,如果没有被删除元素,返回空数组
参数: 起始位置(包含)、要删除的元素个数、元素
var myFish = ['angel', 'clown', 'mandarin', 'sturgeon'];
myFish.splice(2, 0, 'drum');
// ["angel", "clown", "drum", "mandarin", "sturgeon"]
myFish.splice(2, 1);
// ["angel", "clown", "mandarin", "sturgeon"]
myFish.splice(-1, 0, 'drum');
//["angel", "clown", "mandarin", "drum", "sturgeon"]区别于 concat 如果插入数组,就会插入数组,而不是将数组拆开。
myFish.splice(2, 1, ["hello", "world"]);
// ["angel", "clown", ["hello", "world"], "sturgeon"]位置方法
indexOf 和 lastIndexOf 都接受两个参数:查找的值、查找起始位置
不存在,返回 -1 ;存在,返回位置。indexOf 是从前往后查找, lastIndexOf是从后往前查找。
indexOf
var a = [2, 9, 9];
a.indexOf(2); // 0
a.indexOf(7); // -1
if (a.indexOf(7) === -1) {
// element doesn't exist in array
}lastIndexOf
var numbers = [2, 5, 9, 2];
numbers.lastIndexOf(2); // 3
numbers.lastIndexOf(7); // -1
numbers.lastIndexOf(2, 3); // 3
numbers.lastIndexOf(2, 2); // 0
numbers.lastIndexOf(2, -2); // 0
numbers.lastIndexOf(2, -1); // 3迭代方法
ECMAScript 5 提供了5个迭代方法,他们的参数都是
给定的函数(当前元素、位置、数组)
可选的,执行回调是的 this 值
every
对数组的每一项都运行给定的函数,每一项都返回 ture,则返回 true
function isBigEnough(element, index, array) {
return element < 10;
}
[2, 5, 8, 3, 4].every(isBigEnough); // truesome
对数组的每一项都运行给定的函数,任意一项都返回 ture,则返回 true
function isBiggerThan10(element, index, array) {
return element > 10;
}
[2, 5, 8, 1, 4].some(isBiggerThan10); // false
[12, 5, 8, 1, 4].some(isBiggerThan10); // truefilter
对数组的每一项都运行给定的函数,返回 结果为 ture 的项组成的数组
var words = ["spray", "limit", "elite", "exuberant", "destruction", "present", "happy"];
var longWords = words.filter(function(word){
return word.length > 6;
});
// Filtered array longWords is ["exuberant", "destruction", "present"]map
对数组的每一项都运行给定的函数,返回每次函数调用的结果组成一个新数组
var numbers = [1, 5, 10, 15];
var doubles = numbers.map(function(x) {
return x * 2;
});
// doubles is now [2, 10, 20, 30]
// numbers is still [1, 5, 10, 15]forEach 数组遍历
const items = ['item1', 'item2', 'item3'];
const copy = [];
items.forEach(function(item){
copy.push(item)
});缩小方法
reduce、reduceRight 一个是从前往后遍历,一个是从后往前遍历,比上面的五个迭代方法回调函数多了一个参数:上一项的值
回调函数参数 上一项、当前元素、位置、数组
reduce
var numbers = [0, 1, 2, 3];
var result = numbers.reduce(function(accumulator, currentValue) {
return accumulator + currentValue;
});
console.log(result);
// expected output: 6reduceRight
var flattened = [[0, 1], [2, 3], [4, 5]].reduceRight(function(a, b) {
return a.concat(b);
}, []);
// flattened is [4, 5, 2, 3, 0, 1]小总结
队列方法和栈方法操作的都是原数组,增加数组元素的时候,返回值是数组长度;删除数组元素的时候,返回值是被删除的元素。
哪些方法改变了原数组?
栈方法:push、pop
队列方法:shift、unshift
重排序方法:reverse、sort
哪些方法返回的是数组?
重排序方法:reverse、sort
操作方法:splice、slice、concat
迭代方法中:filter、map
ECMAScript 6.0 新增的方法
ECMA-262/6.0 规范:https://www.ecma-international.org/ecma-262/6.0/#sec-array-objects
from
将类似数组的对象(array-like object)和可遍历(iterable)的对象转为真正的数组
const bar = ["a", "b", "c"];
Array.from(bar);
// ["a", "b", "c"]
Array.from('foo');
// ["f", "o", "o"]of
用于将一组值,转换为数组
这个方法的主要目的,是弥补数组构造函数 Array() 的不足。因为参数个数的不同,会导致 Array() 的行为有差异。
Array() // []
Array(3) // [, , ,]
Array(3, 11, 8) // [3, 11, 8]
Array.of(7); // [7]
Array.of(1, 2, 3); // [1, 2, 3]
Array(7); // [ , , , , , , ]
Array(1, 2, 3); // [1, 2, 3]copyWithin
将指定位置的元素复制到其他位置(会覆盖原有元素),返回当前数组。该方法会修改当前数组。
它接受三个参数。
-
target(必需):从该位置开始替换数据。
-
start(可选):从该位置开始读取数据,默认为0。如果为负值,表示倒数。
-
end(可选):到该位置前停止读取数据,默认等于数组长度。如果为负值,表示倒数。
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5].copyWithin(-2);
// [1, 2, 3, 1, 2]
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5].copyWithin(0, 3);
// [4, 5, 3, 4, 5]
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5].copyWithin(0, 3, 4);
// [4, 2, 3, 4, 5]
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5].copyWithin(-2, -3, -1);
// [1, 2, 3, 3, 4]fill
使用给定值,填充一个数组。
会抹除数组原有的元素
还可以接受第二个和第三个参数,用于指定填充的起始位置和结束位置。
var numbers = [1, 2, 3]
numbers.fill(1);
// results in [1, 1, 1]
['a', 'b', 'c'].fill(7, 1, 2)
// ['a', 7, 'c']find
找出第一个符合条件的数组元素,参数是一个回调函数,所有数组元素依次执行该回调函数,直到找出第一个返回值为 true 的元素,然后返回该元素。如果没有符合条件的元素,则返回 undefined。回调函数可以接受三个参数,依次为当前的值、当前的位置和原数组。
[1, 5, 10, 15].find(function(value, index, arr) {
return value > 9;
}) // 10
[1, 5, 2, 3].find(function(value, index, arr) {
return value > 9;
}) // undefinedfindIndex
findIndex 方法的用法与 find 方法非常类似,返回第一个符合条件的数组元素的位置,如果所有元素都不符合条件,则返回 -1。
[1, 5, 10, 15].findIndex(function(value, index, arr) {
return value > 9;
}) // 2ES6 提供三个新的方法—— entries(),keys()和 values() —— 用于遍历数组。它们都返回一个遍历器对象,可以用 for…of 循环进行遍历,唯一的区别是 keys() 是对键名的遍历、values() 是对键值的遍历,entries() 是对键值对的遍历。
for (let index of ['a', 'b'].keys()) {
console.log(index);
}
// 0
// 1
for (let elem of ['a', 'b'].values()) {
console.log(elem);
}
// 'a'
// 'b'
for (let [index, elem] of ['a', 'b'].entries()) {
console.log(index, elem);
}
// 0 "a"
// 1 "b"entries
var a = ['a', 'b', 'c'];
var iterator = a.entries();
console.log(iterator.next().value); // [0, 'a']
console.log(iterator.next().value); // [1, 'b']
console.log(iterator.next().value); // [2, 'c']keys
var arr = ['a', 'b', 'c'];
var iterator = arr.keys();
console.log(iterator.next()); // { value: 0, done: false }
console.log(iterator.next()); // { value: 1, done: false }
console.log(iterator.next()); // { value: 2, done: false }
console.log(iterator.next()); // { value: undefined, done: true }values
var a = ['w', 'y', 'k', 'o', 'p'];
var iterator = a.values();
console.log(iterator.next().value); // w
console.log(iterator.next().value); // y
console.log(iterator.next().value); // k
console.log(iterator.next().value); // o
console.log(iterator.next().value); // p更多使用方式,可以参考 阮一峰 ECMAScript 6入门:http://es6.ruanyifeng.com/#docs/array
ECMAScript 7.0 新增的方法
ECMA-262/7.0 规范:https://www.ecma-international.org/ecma-262/7.0/#sec-properties-of-the-array-prototype-object
includes
判断数组中是否存在该元素
参数:查找的值、起始位置
可以替换 ES5 时代的 indexOf 判断方式
indexOf 判断元素是否为 NaN,会判断错误
var a = [1, 2, 3];
a.includes(2); // true
a.includes(4); // falseECMA-262/8.0 规范:https://www.ecma-international.org/ecma-262/8.0/index.html#sec-array-objects
ES8 没增加数组方法