首先先拿官网的一张图说一下:
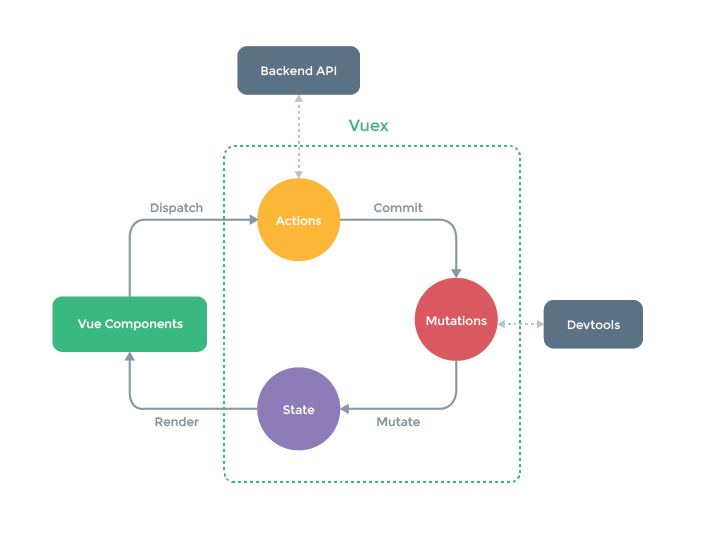
这张图够简单清晰了,首先呢,vuex是用来管理全局变量的一个玩意,然后呢vuex里面有几个大的属性,名字称为Actions,Mutations,State,还有一个Getters,图片没画出来。
vuex是用来管理全局变量的,它有一套流程;
(1)首先State里面定义了所有变量,用来保存数据状态,里面的数据是响应式的,作用相当于组件里的data方法;
(2)Getters,就像它的词义一样,用来获取值的,功能和computed差不多;
(3)Mutations是用来定义函数的地方,它定义的函数,整个vue组件都可以调用。官方告诉我们不要直接修改State里的变量,虽然直接修改也可以起作用,但是直接修改值,vue专门的debug软件检测不到,不理于调式,所以所有调用Mutations里面的方法都是通过this.$store.commit('方法名',参数)提交给Mutations,再由Mutations内部一些处理,最终改变State里的值;它参数有个专用名词,payload;
(4)Actions里面也可以定义函数,里面的函数整个vue组件也可以调用,但是它和Mutations不一样的地方是,Mutations不能响应异步函数操作,所以所有异步函数的定义都是在Actions里面定义的,正如上面的backend API,获取后端值时就是一个异步,需要通知Actions,告诉它我们使用了它里面的异步方法。通过this.$store.dispatch('函数名',参数)来提交给Actions;
另外再记录一下:Getters(),Mutations()里面定义的函数第一个参数都是state,通过state可以获取state里面的变量,,Actions()的参数和前面两个不一样,它的参数叫context,即上下文的意思,他这个参数其实是一个对象,功能很强大,拥有store对象的所有功能,所以context也可以使用context.commit()来提交函数给Mutations,作用和store.commit(),初次学习把context看成一个store就好了。
例子1:state:
state:{ cartList:[],//变量1 isShow:true//变量2 },
与data定义变量一样。
例子2:Mutation定义函数,组件调用
state: { count: 1 }, mutations: { increment (state) { // 变更状态 state.count++ } }
//组件调用vuex里面的方法 this.$store.commit('increment')//利用commit通知有人调用了它的方法
例子3:actions定义函数与组件调用vuex里其定义的方法:
//actions里面定义的所有函数都要通过commit提交给mutations actions: { incrementAsync ({ commit }) { setTimeout(() => { commit('increment') }, 1000) } }
//区别于mutations,actions通过dispatch,即分发的意思,通知actions,有人调用了它的方法 this.$store.dispatch('incremnetAsync');//然后内部actions再commit提交给mutations,
还记的我上面提到的actions里面的参数是context吗,那这里为什么写commit,其实你看一下下面就知道了:
//actions里面定义的所有函数都要通过commit提交给mutations actions: { incrementAsync (context) { setTimeout(() => { context.commit('increment') }, 1000) } }
因为commit是context的一个属性,context相当于store对象;所以当你只使用到commit,你可以直接{commit}作为参数传入,但是一定要有大括号括起来,因为actions的第一个参数本来是context,它是一个对象,所以你一定要用大括号,指出你也是传入一个对象。
最后:vuex所有对state的操作最后都要通过commit提交给mutations;getter则不用,因为getter本身没有对state操作,他只是返回state里面变量的计算结果而已。
忘记补上getter的例子了,补上:
例子4:getters定义与组件调用
vuex里面定义:
state: { todos: [ { id: 1, text: '...', done: true }, { id: 2, text: '...', done: false } ] }, getters: { doneTodos: state => { return state.todos.filter(todo => todo.done) } }
组件调用:
this.$store.getters.doneTodos
--------------------------第二次更新:
混入简单写法,组件再也不用写这么长this.$store.XXX来调用vuex里面的方法了:
使用map,即映射的意思:
有四个map函数:1、mapGetters、2、mapState3、mapMutations、4、mapActions
在组件引入的方式:
//要用哪个就引入哪个 import { mapActions } from 'vuex' import { mapMutations } from 'vuex' import { mapGetters } from 'vuex' import { mapState } from 'vuex' //全部引入也可 import { mapState,mapGetters,mapMutations ,mapActions } from 'vuex'
(1)getters和State里面的东西需要写到computed中:
1、state
state:{ cartList:[],//变量1 isShow:true//变量2 },
之前写法:
通过:this.$store.state.isShow来获取值。
现在:
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
computed: mapState([
// 映射 this.isShow 为this.$ store.state.isShow
'isShow',
])
//在组件中需要调用该值的地方直接:this.isShow就可以拿到该值
2、getters
state: { todos: [ { id: 1, text: '...', done: true }, { id: 2, text: '...', done: false } ] }, getters: { doneTodos: state => { return state.todos.filter(todo => todo.done) }
anotherGetter :state =>{
.................
}
} })
之前写法:
this.$store.getters.doneTodos
this.$store.getters.anotherGetter
现在:
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
computed: {
// 使用对象展开运算符将 getter 混入 computed 对象中
...mapGetters([
'doneTodos',
'anotherGetter',
// ...
])
}
}
直接:this.anotherGetter
(2)actionss和mutationss里面的东西需要写到methods中:
1.mutations
mutations: { increment (state, payload) { state.count += payload.amount } incrementBy (state, payload) { state.count += payload.amount } }
以前:
this.$store.commit('xxxxx')
现在:
组件中引入
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
methods: {
...mapMutations([
'increment', // 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
// `mapMutations` 也支持载荷:
'incrementBy' // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
...mapMutations({
add: 'increment' // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
})
}
}
2、actions同理
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
methods: {
...mapActions([
'increment', // 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
// `mapActions` 也支持载荷:
'incrementBy' // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
...mapActions({
add: 'increment' // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
})
}
}
--------------------------第三次更新:
vuex模块化分及引入使用的语法格式:
首先建好大仓库store文件夹:
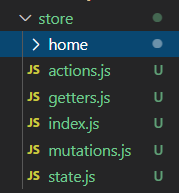
store文件夹:内容分为:action.js , getter.js, index.js, mutations.js, state.js与其他子模块,例如上面的home文件夹。
同样home文件夹里面建好同父模块一样的js文件:

(1)初始化语法
父模块内容:
index.js
import 'es6-promise/auto'
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
//模块化
import state from './state'
import mutations from './mutations'
import actions from './actions'
import getters from './getters'
//引入子模块
import home from './home/index'
//1.安装插件
Vue.use(Vuex)
//2.创建store对象
// es6对象写法
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state,//相当于data,不过作用范围是全局的,数据能够实时变化
getters,//相当于computed,不过也是全局的
mutations,//相当于methods,不过不能实现异步方法,在组件中需要调用this.$store.commit('方法名',payload)把函数操作提交到此处,、payload为参数
actions,//用于处理异步函数,接收一个context参数,此参数也是一个函数,可以使用store的全部方法,可以通过context.commit来提交方法到mutation当中,action中的函数使用dispatch来提交,就如同mutation的commit一样
modules:{
home//子模块
}
})
//3.挂载vue实例上
export default store
state.js
export default{
articleList:[]
}
export default{
openEnterDialog(state){
state.is_showConfirmEnterDialog = true//控制未登录前进入某权限页面弹框是否显示
},
closeEnterDialog(state){
state.is_showConfirmEnterDialog = false//控制未登录前进入某权限页面弹框是否显示
}
}
父模块其他状态拆开写法与上面一样。
子模块iindex.js
//模块化
import state from './state'
import mutations from './mutations'
import actions from './actions'
import getters from './getters'
// login子模块
export default{
namespaced: true,//声明子模块命名空间,以便父亲调用
state,//相当于data,不过作用范围是全局的,数据能够实时变化
getters,//相当于computed,不过也是全局的
mutations,//相当于methods,不过不能实现异步方法,在组件中需要调用this.$store.commit('方法名',payload)把函数操作提交到此处,、payload为参数
actions,//用于处理异步函数,接收一个context参数,此参数也是一个函数,可以使用store的全部方法,可以通过context.commit来提交方法到mutation当中,action中的函数使用dispatch来提交,就如同mutation的commit一样
}
子模块其它状态语法格式同父模块,除了index,js有点特殊外
(2)全局使用
父模块注入语法:
mutation
...mapMutations(['openEnterDialog','closeEnterDialog']),//注入方法

action如上语法一样;
state语法注入:
computed:{
...mapState(['is_showConfirmEnterDialog'])
},
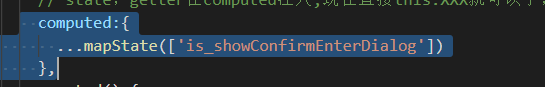
getter同state注入
子模块注入语法:
mutations注入:
...mapMutations({
'changeArticleItem':'home/changeArticleItem'
}),
state注入:
...mapState({
articleList:state => state.home.articleList
})
---------------------------下面是一点杂记-----------------------------------------------------------------------
import 'es6-promise/auto' import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' //模块化 import mutations from './mutations' import actions from './actions' import getters from './getters' //1.安装插件 Vue.use(Vuex) //2.创建store对象 const state = { showPublicNav:true } // es6对象写法 const store = new Vuex.Store({ state,//相当于data,不过作用范围是全局的,数据能够实时变化 getters,//相当于computed,不过也是全局的 mutations,//相当于methods,不过不能实现异步方法,在组件中需要调用this.$store.commit('方法名',payload)把函数操作提交到此处,、payload为参数 actions,//用于处理异步函数,接收一个context参数,此参数也是一个函数,可以使用store的全部方法,可以通过context.commit来提交方法到mutation当中,action中的函数使用dispatch来提交,就如同mutation的commit一样 }) //3.挂载vue实例上 export default store