排序算法
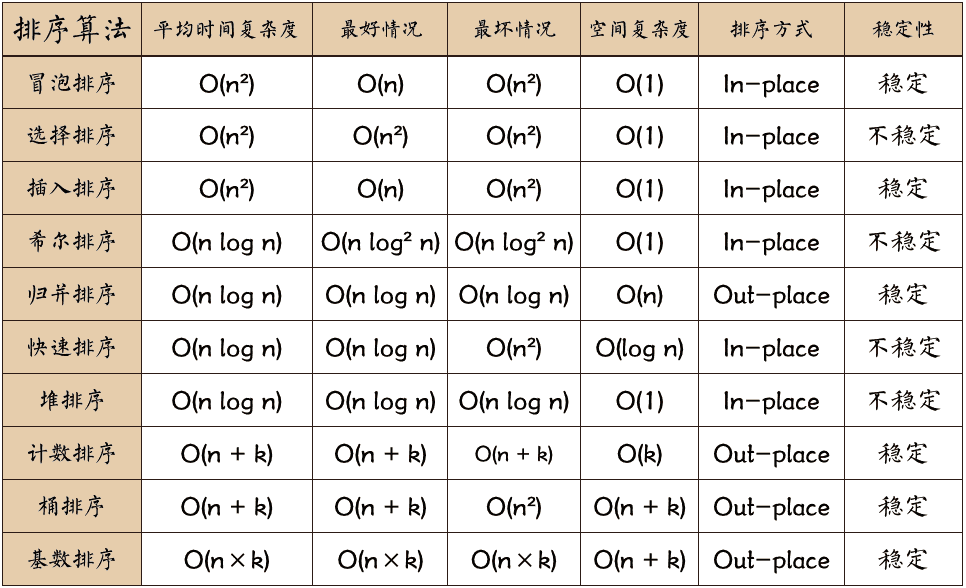
冒泡排序
public static void BubbleSort(int[] datas) {
int length = datas.length;
for (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < length - i - 1; j++) {
if (datas[j] > datas[j + 1]) {
int temp = datas[j];
datas[j] = datas[j + 1];
datas[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
选择排序
public static void SelectSort(int[] datas) {
int length = datas.length;
// 做第i趟排序,n个数只需要(n-1)次排序,找到最小的数与第一个数交换,找到第二小的数与第二个数交换...
for (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) {
int k = i;
for (int j = k + 1; j < length; j++) {
if (datas[j] < datas[k]) { // 选最小的记录
k = j; // 记下目前找到的最小值所在的位置
}
}
// 在内层循环结束,也就是找到本轮循环的最小的数以后,再进行交换
if (i != k) { // 交换datas[i]和datas[k]
int temp = datas[i];
datas[i] = datas[k];
datas[k] = temp;
}
}
}
插入排序
public static void InsertSort(int[] datas) {
int i, j;
int target;
int n = datas.length;
for (i = 1; i < n; i++) {
j = i;
target = datas[i];
while (j > 0 && target < datas[j - 1]) {
datas[j] = datas[j - 1];
j--;
}
datas[j] = target;
}
}
快速排序
import java.util.Arrays;
public class 快速排序 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 4, 3, 5, 1, 2 };
System.out.println("排序前: " + Arrays.toString(arr));
QuickSort(arr, 0, 4);
System.out.println("排序后:" + Arrays.toString(arr));
}
// 快速排序递归算法
public static void QuickSort(int[] data, int L, int R) {
int i = L;
int j = R;
int pivot = data[(L + R) / 2];// 分割点,分割点左边的数都比分割点小,右边的数都比分割点大
while (i <= j) {
while (pivot > data[i]) {
i++;// 找到左边比分割点大的数
}
while (pivot < data[j]) {
j--;// 找到右边比分割点小的数
}
// 交换左右两边的数
if (i <= j) {
int temp = data[i];
data[i] = data[j];
data[j] = temp;
i++;
j--;
}
}
// 一次交换完后,分割点相当于已经排序好了
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data));
// 递归左边
if (L < j) {
QuickSort(data, L, j);
}
// 递归右边
if (R > i) {
QuickSort(data, i, R);
}
}
}
归并排序
1、归并排序思想
归并排序是建立在归并操作上的一种有效的排序算法,它过程为:比较a[i]和a[j]的大小,若a[i]≤a[j],则将第一个有序表中的元素a[i]复制到r[k]中,并令i和k分别加上1;否则将第二个有序表中的元素a[j]复制到r[k]中,并令j和k分别加上1,如此循环下去,直到其中一个有序表取完,然后再将另一个有序表中剩余的元素复制到r中从下标k到下标t的单元。
2、实现原理
- 1、申请空间,使其大小为两个已经排序序列之和,该空间用来存放合并后的序列;
- 2、设定两个指针变量,最初位置分别指向两个已经排好序的数组序列的起始位置;
- 3、比较两个指针所指向的元素,选择相对小的元素放入到申请的合并空间里,并移动此指针到下一位置;
- 4、继续重复步骤3直到某一指针达到序列尾;
- 5、当一个指针到达一个序列尾时,将另一序列剩下的所有元素直接复制到合并序列尾。
3、Java 实现
package Java算法;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 参考:https://blog.csdn.net/jianyuerensheng/article/details/51262984
* @author bin
*
*/
public class 归并排序 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {5,4,2,1,3,7,9,8,0,6};
sort(a,0,a.length-1);
System.out.println("最后排序的结果为:"+Arrays.toString(a));
}
public static void mergeSort(int[] a,int low,int mid,int high){
int i = low; // 左指针
int j = mid + 1; //右指针
int k = 0;
int[] nums = new int[high-low+1]; //临时数组
// 把较小的数先移到新数组中
while(i<=mid&&j<=high){
if(a[i]<a[j]){
nums[k++] = a[i++];
}else{
nums[k++] = a[j++];
}
}
// 把左边剩余的数移入数组
while(i<=mid){
nums[k++] = a[i++];
}
// 把右边边剩余的数移入数组
while(j<=high){
nums[k++] = a[j++];
}
// 把新数组中的数覆盖nums数组
for(int m =0;m<nums.length;m++){
a[m+low] = nums[m];
}
}
public static void sort(int[] a,int low,int high){
int mid = (low+high)/2;
if(low<high){
sort(a,low,mid); //左边有序
sort(a,mid+1,high); //右边有序
mergeSort(a,low,mid,high); //左右归并
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
}
}
4、算法分析
归并排序是速度仅次于快速排序的算法,为稳定排序算法,一般用于对总体无序,但是各子项相对有序的数列,其时间和空间复杂度信息如下:
时间复杂度
对长度为n的文件,需进行FLOOR(logn) 趟二路归并,每趟归并的时间为O(n),故其时间复杂度无论是在最好情况下还是在最坏情况下均是O(nlgn)。
空间复杂度
需要一个辅助向量来暂存两有序子文件归并的结果,故其辅助空间复杂度为O(n),显然它不是就地排序。
排序稳定性
归并排序是一种稳定的排序。
二分查找
思想: 1、二分查找又称折半查找,它是一种效率较高的查找方法。 2、二分查找要求: (1)必须采用顺序存储结构 (2)必须按关键字大小有序排列 3、原理:将数组分为三部分,依次是中值(所谓的中值就是数组中间位置的那个值)前,中值,中值后;将要查找的值和数组的中值进行比较,若小于中值则在中值前 面找, 若大于中值则在中值后面找,等于中值时直接返回。然后依次是一个递归过程,将前半部分或者后半部分继续分解为三部分。 4、实现:二分查找的实现用递归和循环两种方式
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* 二分查找 */
/* 循环算法 */
int BinarySearch( int *array, int key, int low, int high )
{
int mid;
while ( low <= high )
{
mid = (low + high) / 2;
if ( key == array[mid] )
{
return(mid);
}else if ( key < array[mid] )
{
high = mid - 1;
}else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return(-1);
}
/* 递归算法 */
int BinarySearch2( int *array, int key, int low, int high )
{
if ( low > high )
{
return(-1);
} else {
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
if ( array[mid] == key )
{
return(mid);
} else if ( array[mid] > key )
{
BinarySearch2( array, key, low, mid - 1 );
} else {
BinarySearch2( array, key, mid + 1, high );
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n, i, key, position;
int *array;
printf( "请输入有序数组的大小:" );
scanf( "%d", &n );
array = (int *) malloc( sizeof(int) * n );
printf( "请按升序输入数据:
" );
for ( i = 0; i < n; i++ )
{
scanf( "%d", &array[i] );
}
printf( "请输入想要查找的数:" );
scanf( "%d", &key );
position = BinarySearch2( array, key, 0, n - 1 );
if ( position != -1 )
{
printf( "%d的位置为:%d
", key, position );
}else {
printf( "%d不存在
", key );
}
}
public class BinarySearch {
public static int search(int[] nums, int target) {
if(nums==null||nums.length==0){
return -1;
}
int length = nums.length;
int low = 0,high = length-1;
int mid;
while(low<=high){
mid = low + (high-low)/2;
if(nums[mid] == target){
return mid;
}else if(nums[mid] < target){
low = mid + 1;
}else{
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {-1,0,3,5,9,12};
int index = search(nums,9);
System.out.println(index);
}
}
点击查看结果
```
4
```
参考链接