MapReduce 最优路径算法
实验目的
1.了解Dijkstra算法
2.学习使用mapreduce计算最短路径
实验原理
最优路径算法是无向图中满足通路上所有顶点(除起点、终点外)各异,所有边也各异的的通路。应用在公路运输中,可以提供起点和终点之间的最短路径,节省运输成本。可以大大提高交通运输效率。
本实验采用Dijkstra算法,迪杰斯特拉算法是由荷兰计算机科学家狄克斯特拉于1959 年提出的,因此又叫狄克斯特拉算法。是从一个顶点到其余各顶点的最短路径算法,解决的是有向图中最短路径问题。迪杰斯特拉算法主要特点是以起始点为中心向外层层扩展,直到扩展到终点为止。
算法伪代码如下:
Dijkstra(G,w, s)
d[s] ← 0
for all vertex v ∈ V do
d[v] ← ∞
Q ← {V }
while Q != ∅ do
u ←ExtractMin(Q)
for all vertex v ∈ u.AdjacencyList do
if d[v] > d[u] + w(u, v) then
d[v] ← d[u] + w(u, v)
Dijkstra算法关键的一点是优先队列Q,它保存了全局的从源点出发最近的结点。而map-reduce则无法做到这一点。
基于map-reduce的并行算法跟Dijkstra算法有点类似,它也基于Dijkstra的迭代思想,伪代码如下:
class Mapper
method Map(nid n, node N)
d ← N.Distance
Emit(nid n,N) //Pass along graph
structure [1]
for all nodeid m ∈ N.AdjacencyList do
Emit(nid m, d+w) //Emit distances to
reachable nodes [2]
class Reducer
method Reduce(nid m, [d1, d2, . . .])
dmin←∞
M ← ∅
for all d ∈ counts [d1, d2, . . .] do
if IsNode(d) then
M ← d //Recover graph
structure
else if d < dmin then //Look for shorter
distance
dmin ← d
M.Distance← dmin //Update shortest
distance
Emit(nid m, node M)
它每次迭代执行一个map-reduce job,并且只遍历一个节点。在Map中,它先输出这个节点的完整邻接节点数据,即[1]。然后遍历该节点的邻接节点,并输出该节点ID及权重。在Reduce中,对当前节点m,遍历map的输出权重,若比当前的路径值小,则更新。最后输出该节点的路径值及完整邻接节点数据,作为下一次迭代的输入。
实现上有个细节需要注意的是,map的输出有两种类型的数据:邻接节点数据和权重数据,这可以通过一个包装类,并设置一个dataType变量来实现。
当遍历完所有的节点之后,迭代就终止了。
实验环境
Linux Ubuntu 14.04
jdk-7u75-linux-x64
Hadoop 2.6.0-cdh5.4.5
实验内容
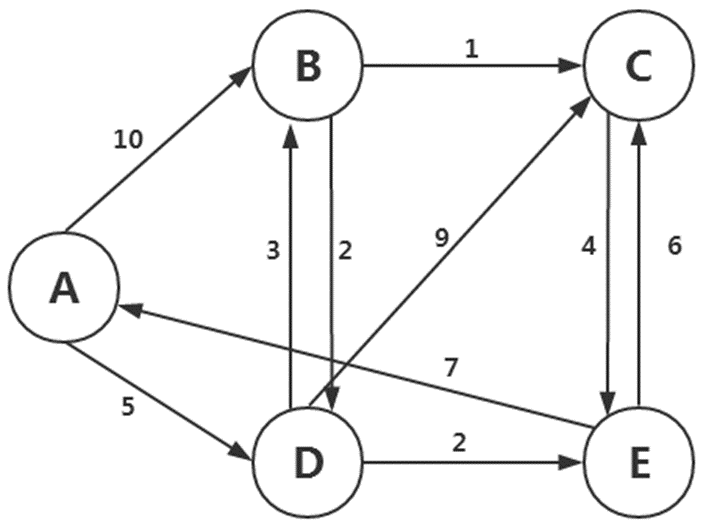
原始数据:
A(B,10) (D,5)
B(C,1) (D,2)
C(E,4)
D(B,3) (C,9) E,2)
E(A,7) (C,6)
如图,A为初始节点,A到B的距离为10,A到D的距离为5。
B到C的距离为1,B到D的距离为3
Map阶段:
从初始A节点开始,将节点到其他相连节点的距离列举出来,然后传递给reduce,找到距离最短的。
从初始A节点开始,找到B和D,然后再找B和D的相邻节点,依次类推,这个就是广度优先搜索。
从A节点出发,A节点不能直接到达节点默认的距离为inf,表示距离无穷大。
A能到达的节点有:A本身(距离为0),B(距离为10),D(距离为5)
则可以表示为:
A 0(B,10) (D,5)
B 10
D 5
Reduce阶段:
找到所有存在的距离中最短的,并更新记录中的最短距离。
如A节点到C节点有两种路径:
A=>B=>C,距离为:10+1=11
A=>D=>B=>C,距离为5+3+1=9
则A节点到C节点的最短距离为9
实验步骤
1.首先,我们来准备实验需要用到的数据,切换到/data/mydata目录下,使用vim编辑一个data.txt文件
- cd /data/mydata
- vim data.txt
2.将如下数据写入其中(注意数据之间以\t分割)
- A (B,10) (D,5)
- B (C,1) (D,2)
- C (E,4)
- D (B,3) (C,9) (E,2)
- E (A,7) (C,6)
3.切换到/apps/hadoop/sbin目录下,开启Hadoop相关进程
- cd /apps/hadoop/sbin
- ./start-all.sh
4.输入JPS查看一下相关进程是否已经启动。
- jps
5.在HDFS的根下创建一个input目录,并将data.txt文件上传到HDFS上的input文件夹下
- hadoop fs -mkdir /input
- hadoop fs -put /data/mydata/data.txt /input
6.打开Eclipse,创建一个Map/Reduce项目
7.设置项目名为mr_sf并点击Finish
8.创建一个包,名为mr_mindistance
9.创建一个类,名为RunJob,作用为计算最短路径。
10.下面开始编写Runjob类的代码
完整代码为:
- package mr_mindistance;
- import java.io.IOException;
- import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
- import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
- import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
- import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
- import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
- import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
- import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
10. import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
11. import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.KeyValueTextInputFormat;
12. import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
13. import org.apache.hadoop.util.StringUtils;
14. public class RunJob {
- 15. static enum eInf {
- 16. COUNTER
- 17. }
- 18. public static void main(String[] args) {
- 19. Configuration conf = new Configuration();
- 20. //设置主机地址及端口号
- 21.
- 22. conf.set("fs.defaultFS", "hdfs://localhost:9000");
- 23. try {
- 24. FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf);
- 25. int i = 0;
- 26. long num = 1;
- 27. long tmp = 0;
- 28. while (num > 0) {
- 29. i++;
- 30. conf.setInt("run.counter", i);
- 31. Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
- 32. job.setJarByClass(RunJob.class);
- 33. job.setMapperClass(ShortestPathMapper.class);
- 34. job.setReducerClass(ShortestPathReducer.class);
- 35. job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
- 36. job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
- 37. //key value 的格式 第一个item为key,后面的item为value
- 38. job.setInputFormatClass(KeyValueTextInputFormat.class);
- 39. //设置输入、输出路径
- 40.
- 41. if (i == 1)
- 42. FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path("/input/"));
- 43. else
- 44. FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path("/output/" + (i - 1)));
- 45. Path outPath = new Path("/output/" + i);
- 46. if (fs.exists(outPath)) {
- 47. fs.delete(outPath, true);
- 48. }
- 49. FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outPath);
- 50. boolean b = job.waitForCompletion(true);
- 51. if (b) {
- 52. num = job.getCounters().findCounter(eInf.COUNTER).getValue();
- 53. if (num == 0) {
- 54. System.out.println("共执行了" + i + "次,完成最短路径计算");
- 55. }
- 56. }
- 57. }
- 58. } catch (Exception e) {
- 59. e.printStackTrace();
- 60. }
- 61. }
- 62. public static class ShortestPathMapper extends Mapper<Text, Text, Text, Text> {
- 63. protected void map(Text key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
- 64. int conuter = context.getConfiguration().getInt("run.counter", 1);
- 65. Node node = new Node();
- 66. String distance = null;
- 67. String str = null;
- 68. // 第一次计算,填写默认距离 A:0 其他:inf
- 69. if (conuter == 1) {
- 70. if (key.toString().equals("A") || key.toString().equals("1")) {
- 71. distance = "0";
- 72. } else {
- 73. distance = "inf";
- 74. }
- 75. str = distance + "\t" + value.toString();
- 76. } else {
- 77. str = value.toString();
- 78. }
- 79. context.write(key, new Text(str));
- 80. node.FormatNode(str);
- 81. // 没走到此节点 退出
- 82. if (node.getDistance().equals("inf"))
- 83. return;
- 84. // 重新计算源点A到各点的距离
- 85. for (int i = 0; i < node.getNodeNum(); i++) {
- 86. String k = node.getNodeKey(i);
- 87. String v = new String(
- 88. Integer.parseInt(node.getNodeValue(i)) + Integer.parseInt(node.getDistance()) + "");
- 89. context.write(new Text(k), new Text(v));
- 90. }
- 91. }
- 92. }
- 93. public static class ShortestPathReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> {
- 94. protected void reduce(Text arg0, Iterable<Text> arg1, Context arg2) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
- 95. String min = null;
- 96. int i = 0;
- 97. String dis = "inf";
- 98. Node node = new Node();
- 99. for (Text t : arg1) {
- i++;
- dis = StringUtils.split(t.toString(), '\t')[0];
- // 如果存在inf节点,表示存在没有计算距离的节点。
- // if(dis.equals("inf"))
- // arg2.getCounter(eInf.COUNTER).increment(1L);
- // 判断是否存在相邻节点,如果是则需要保留信息,并找到最小距离进行更新。
- String[] strs = StringUtils.split(t.toString(), '\t');
- if (strs.length > 1) {
- node.FormatNode(t.toString());
- }
- // 第一条数据默认是最小距离
- if (i == 1) {
- min = dis;
- } else {
- if (dis.equals("inf"))
- ;
- else if (min.equals("inf"))
- min = dis;
- else if (Integer.parseInt(min) > Integer.parseInt(dis)) {
- min = dis;
- }
- }
- }
- // 有新的最小值,说明还在进行优化计算,需要继续循环计算
- if (!min.equals("inf")) {
- if (node.getDistance().equals("inf"))
- arg2.getCounter(eInf.COUNTER).increment(1L);
- else {
- if (Integer.parseInt(node.getDistance()) > Integer.parseInt(min))
- arg2.getCounter(eInf.COUNTER).increment(1L);
- }
- }
- node.setDistance(min);
- arg2.write(arg0, new Text(node.toString()));
- }
- }
- }
11.创建一个Node类,作用为保存节点的信息
12.下面开始编写代码
完整代码为:
- package mr_mindistance;
- import org.apache.hadoop.util.StringUtils;
- public class Node {
- private String distance;
- private String[] adjs;
- public String getDistance() {
- return distance;
- }
- public void setDistance(String distance) {
- 10. this.distance = distance;
- 11. }
- 12. public String getKey(String str)
- 13. {
- 14. return str.substring(1, str.indexOf(","));
- 15. }
- 16. public String getValue(String str)
- 17. {
- 18. return str.substring(str.indexOf(",")+1, str.indexOf(")"));
- 19. }
- 20. public String getNodeKey(int num)
- 21. {
- 22. return getKey(adjs[num]);
- 23. }
- 24. public String getNodeValue(int num)
- 25. {
- 26. return getValue(adjs[num]);
- 27. }
- 28. public int getNodeNum()
- 29. {
- 30. return adjs.length;
- 31. }
- 32. public void FormatNode(String str)
- 33. {
- 34. if(str.length() == 0)
- 35. return ;
- 36. String[] strs = StringUtils.split(str, '\t');
- 37. adjs = new String[strs.length-1];
- 38. for(int i=0; i<strs.length; i++)
- 39. {
- 40. if(i == 0)
- 41. {
- 42. setDistance(strs[i]);
- 43. continue;
- 44. }
- 45. this.adjs[i-1]=strs[i];
- 46. }
- 47. }
- 48. public String toString()
- 49. {
- 50. String str = this.distance+"" ;
- 51. if(this.adjs == null)
- 52. return str;
- 53. for(String s:this.adjs)
- 54. {
- 55. str = str+"\t"+s;
- 56. }
- 57. return str;
- 58. }
- 59. public static void main(String[] args)
- 60. {
- 61. Node node = new Node();
- 62. node.FormatNode("1 (A,20) (B,30)");
- 63. System.out.println(node.distance+"|"+node.getNodeNum()+"|"+node.toString());
- 64. }
65. }
13.下面在Runjob类下,单击右键,选择Run As=>Run on Hadoop,运行程序,查看执行结果
可以在Console界面看到如下输出,证明程序执行成功,共进行了4次运算。

14.查看HDFS上的/output目录及最终计算结果(/ouput/下的1、2、3、4目录分别保存了4次执行程序的计算结果)
- hadoop fs -ls -R /output
- hadoop fs -cat /output/4/part-r-00000

通过分析结果,可以清楚地看到A点距离各点的最短距离。
至此,实验就已经结束了。