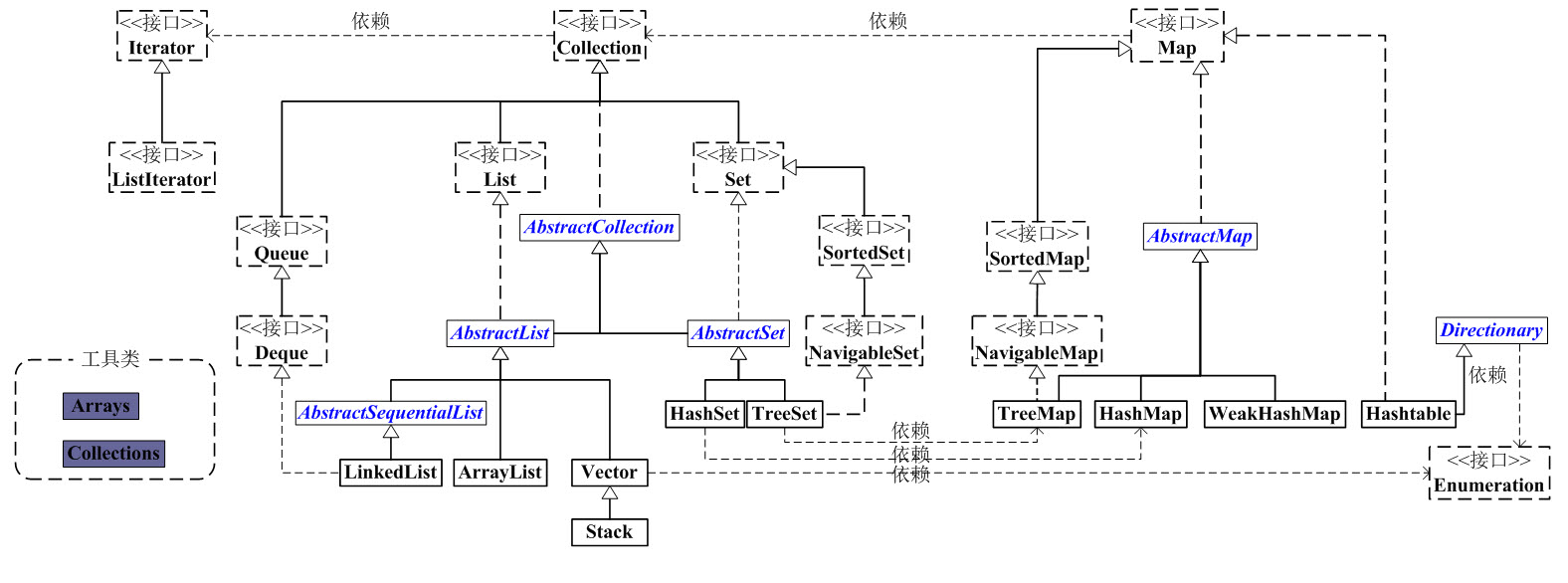
一、总体框架
Java集合是java提供的工具包,包含了常用的数据结构:集合、链表、队列、栈、数组、映射等。Java集合工具包位置是java.util.* 。
Java集合主要可以划分为4个部分:List列表、Set集合、Map映射、工具类(Iterator迭代器、Enumeration枚举类、Arrays和Collections)。
Java集合工具包框架图(如下):
大致说明:
看上面的框架图,先抓住它的主干,即Collection和Map。
1 、Collection是一个接口,是高度抽象出来的集合,它包含了集合的基本操作和属性。Collection包含了List和Set两大分支。
(1) List是一个有序的队列,每一个元素都有它的索引。第一个元素的索引值是0。List的实现类有LinkedList, ArrayList, Vector, Stack。
(2)Set是一个不允许有重复元素的集合。Set的实现类有HastSet和TreeSet。HashSet依赖于HashMap,它实际上是通过HashMap实现的;TreeSet依赖于TreeMap,它实际上是通过TreeMap实现的。
2、 Map是一个映射接口,即key-value键值对。Map中的每一个元素包含一个key和key对应的value,每一个key是唯一的。
(1)AbstractMap是个抽象类,它实现了Map接口中的大部分API。而HashMap,TreeMap,WeakHashMap都是继承于AbstractMap。
(2)Hashtable虽然继承于Dictionary,但它实现了Map接口。
3、接下来,再看Iterator。它是遍历集合的工具,即我们通常通过Iterator迭代器来遍历集合。我们说Collection依赖于Iterator,是因为Collection的实现类都要实现iterator()函数,返回一个Iterator对象。其中,ListIterator是专门为遍历List而存在的。
4、再看Enumeration,它是JDK 1.0引入的抽象类。作用和Iterator一样,也是遍历集合;但是Enumeration的功能要比Iterator少。在上面的框图中,Enumeration只能在Hashtable, Vector, Stack中使用。
5、最后,看Arrays和Collections。它们是操作数组、集合的两个工具类。
(来源:http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3308498.html)
二、List
List中ArrayList又最为常用。看ArrayList的使用例子:
package chapter11;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class TestArrayList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ArrayList<String> cityList=new ArrayList<String>();
cityList.add("London");
cityList.add("Denver");
cityList.add("Paris");
cityList.add("Miami");
cityList.add("Seoul");
cityList.add("Tokyo");
System.out.println("List size is "+cityList.size()+
"
Is Miami in the list? "+cityList.contains("Miami")+
"
The location of Denver in the list? "+cityList.indexOf("Denver")+
"
Is the list empty? "+cityList.isEmpty());
cityList.add(2, "Xian");
cityList.remove("Miami");
cityList.remove(1);
System.out.println(cityList.toString());
for(int i=cityList.size()-1;i>=0;i--){
System.out.print(cityList.get(i)+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
三、Set
1、Set不能存储相同的元素,同时因为其是一个抽象的接口,所以不能直接实例化一个set对象。(Set s = new Set() 是错误的 )
2、Set的两个实现是HashSet和TreeSet。他们都是单列集合,元素不可重复。HashSet无序,TreeSet会将里面的元素默认排序。
3、TreeSet的应用实例
Set<Integer> set = new TreeSet<>();
int a = 1;
int b = 8;
int c = 3;
set.add(a);
set.add(b);
set.add(c);
//遍历集合set ,利用foreach遍历
for (Integer value : set) {
System.out.print(value+" "); //输出结果:1 3 8
}
//利用Iterator实现遍历
Iterator<Integer> value =set.iterator();
while (value.hasNext()) {
int c= value.next();
System.out.print(c+" "); //输出结果:1 3 8
}
四、Map
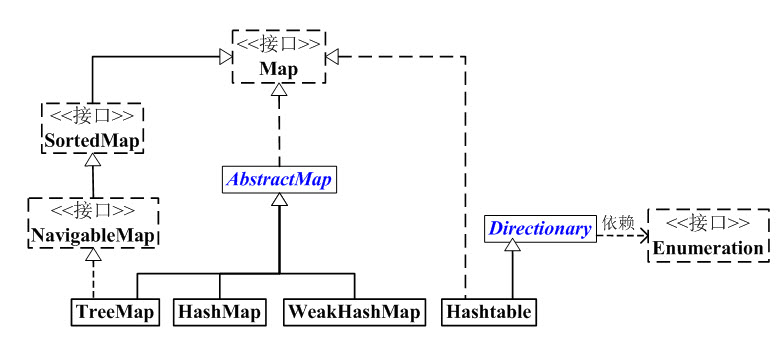
1、
如上图:
(1) Map 是映射接口,Map中存储的内容是键值对(key-value)。Map映射中不能包含重复的键;每个键最多只能映射到一个值。
(2) AbstractMap 是继承于Map的抽象类,它实现了Map中的大部分API。其它Map的实现类可以通过继承AbstractMap来减少重复编码。
(3) SortedMap 是继承于Map的接口。SortedMap中的内容是排序的键值对,排序的方法是通过比较器(Comparator)。
(4) NavigableMap 是继承于SortedMap的接口。相比于SortedMap,NavigableMap有一系列的导航方法;如"获取大于/等于某对象的键值对"、“获取小于/等于某对象的键值对”等等。
(5) TreeMap 继承于AbstractMap,且实现了NavigableMap接口;因此,TreeMap中的内容是“有序的键值对”!
(6) HashMap 继承于AbstractMap,但没实现NavigableMap接口;因此,HashMap的内容是“键值对,但不保证次序”!
(7) Hashtable 虽然不是继承于AbstractMap,但它继承于Dictionary(Dictionary也是键值对的接口),而且也实现Map接口;因此,Hashtable的内容也是“键值对,也不保证次序”。但和HashMap相比,Hashtable是线程安全的,而且它支持通过Enumeration去遍历。
(8) WeakHashMap 继承于AbstractMap。它和HashMap的键类型不同,WeakHashMap的键是“弱键”。
(来源:http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3308931.html)
2、以TreeMap为例,介绍用法
public class SortDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("---------------- 默认排序结果-----------------");
createDefaultSortTreeMap();
System.out.println("---------------- 自定义排序结果-----------------");
createDefinitionSortTreeMap();
}
public static void createDefaultSortTreeMap() {
TreeMap<String, String> map = new TreeMap<String, String>();
init(map);
print(map);
}
public static void createDefinitionSortTreeMap() {
TreeMap<String, String> map = new TreeMap<String, String>(new Comparator<String>() {
@Override
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
return o2.compareTo(o1);
}
});
init(map);
print(map);
}
public static void init(Map<String, String> map) {
map.put("c", "1");
map.put("a", "1");
map.put("bb", "1");
map.put("b", "1");
}
public static void print(Map<String, String> map) {
Iterator<Entry<String, String>> it = map.entrySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
Entry<String, String> entry = it.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " : " + entry.getValue());
}
}
结果:
---------------- 默认排序结果-----------------
a : 1
b : 1
bb : 1
c : 1
---------------- 自定义排序结果-----------------
c : 1
bb : 1
b : 1
a : 1
注释:TreeMap 默认排序规则:按照key的字典顺序来排序(升序)。当然,也可以自定义排序规则:要实现Comparator接口。
(来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/chenmo-xpw/p/4922641.html)
五、List、Set、Map集合的遍历方法
1、List集合遍历
public class TraversingList {
/**
* @author zhuxun describe: 定一个List集合并遍历
*/
/** 定义一个List集合 */
public List<String> getList() {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("ZhuXun");
list.add("Jack Ma");
list.add("Kobe");
list.add("Andy Lau");
return list;
}
/** 遍历list集合 */
public void traversingList(List<String> list) {
// 方法一:通过下标遍历
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
// 方法二:Iterator迭代器遍历
Iterator<String> itr = list.iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
String str = itr.next();
System.out.println(str);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TraversingList test = new TraversingList();
List<String> list = test.getList();// 获得List集合
test.traversingList(list);// 遍历List集合并输出
}
}
2、Set集合遍历
public class TraversingSet {
/**
* @author zhuxun describe: 定一个Set集合并遍历
*/
/** 定义一个Set集合 */
public Set<String> getSet() {
Set<String> set = new HashSet<String>();
set.add("ZhuXun");
set.add("Jack Ma");
set.add("Kobe");
set.add("Andy Lau");
return set;
}
/** 遍历Set集合 */
public void traversingSet(Set<String> set) {
// 方法一:Iterator迭代器遍历
Iterator<String> itr = set.iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
String str = itr.next();
System.out.println(str);
}
// 方法二:通过增强型for循环遍历
// 注:Set集合中不存在下标,因此无法通过下标遍历,对于Java编译器而言,方法一和方法二是等价的
for (String str : set) {
System.out.println(str);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TraversingSet test = new TraversingSet();
Set<String> set = test.getSet();// 获得Set集合
test.traversingSet(set);// 遍历Set集合并输出
}
}
3、Map集合遍历
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
public class TestMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
map.put(1, "a");
map.put(2, "b");
map.put(3, "ab");
map.put(4, "ab");
map.put(4, "ab");// 和上面相同 , 会自己筛选,不会重复存储
System.out.println(map.size());
// 第一种:通过Map.keySet遍历key和value
for (Integer in : map.keySet()) {
//map.keySet()返回的是所有key的值
String str = map.get(in);//得到每个key多对用value的值
System.out.println(in + " " + str);
}
// 第二种:通过Map.entrySet使用iterator遍历key和value
Iterator<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> it = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry = it.next();
System.out.println("key= " + entry.getKey() + " and value= " + entry.getValue());
}
// 第三种:通过Map.entrySet遍历key和value,推荐,尤其是容量大时
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
//Map.entry<Integer,String> 映射项(键-值对) 有几个方法:用上面的名字entry
//entry.getKey() ;entry.getValue(); entry.setValue();
//map.entrySet() 返回此映射中包含的映射关系的 Set视图。
System.out.println("key= " + entry.getKey() + " and value= "
+ entry.getValue());
}
// 第四种:通过Map.values()遍历所有的value,但不能遍历key
for (String v : map.values()) {
System.out.println("value= " + v);
}
}
}
(来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/blest-future/p/4628871.html)