好文:https://blog.csdn.net/javazejian/article/details/56267036
通过一个实例来理解
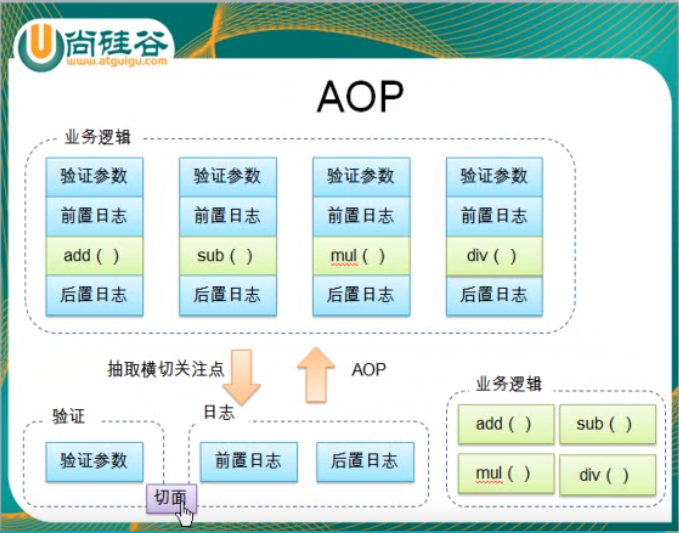
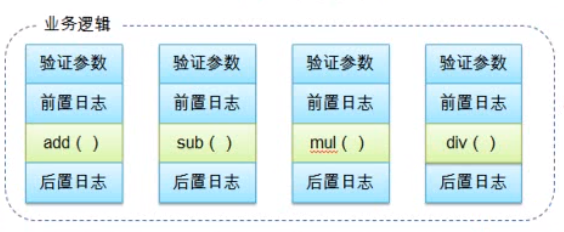
1. 需求:实现算术计算器,可以加减乘除,同时记录日志
2. 实现方式:
① 高度耦合(直接pass)
② 自己实现动态代理
③ 利用Spring AOP框架
二. 自己实现动态代理
1. 定义接口及实现类:
-- 接口:ArithmeticCalculator
public interface ArithmeticCalculator { int add(int i, int j); int sub(int i, int j); int mul(int i, int j); int div(int i, int j); }
-- 接口的实现类
public class ArithmeticCalculatorImpl implements ArithmeticCalculator{ public int add(int i, int j) { int result = i + j; System.out.println("[add] " + i + " + " + j + " = " + result); return result; } public int sub(int i, int j) { int result = i - j; System.out.println("[sub] " + i + " - " + j + " = " + result); return result; } public int mul(int i, int j) { int result = i * j; System.out.println("[mul] " + i + " * " + j + " = " + result); return result; } public int div(int i, int j) { int result = i / j; System.out.println("[div] " + i + " / " + j + " = " + result); return result; } }
-- 返回动态代理类
关键代码已经标红,利用JDK的Proxy类,加入参数,返回代理类
try-catch-finally分别对应四种通知
public class ArithmeticCalculatorLoggingProxy { private ArithmeticCalculator target; public ArithmeticCalculatorLoggingProxy(ArithmeticCalculator target) { this.target = target; } public ArithmeticCalculator getLoggingProxy() { ArithmeticCalculator proxy = null; //代理对象由哪一个类加载器加载 ClassLoader loader = target.getClass().getClassLoader(); //代理对象的类型 Class[] interfaces = new Class[] {ArithmeticCalculator.class}; //调用代理对象的目标方法,并执行的代理方法 InvocationHandler h = new InvocationHandler() { //proxy: 一般不用proxy中的方法,容易死循环 //method: 目标类中的方法 //args: 目标类方法的参数 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) { Object result = null; try { System.out.println("这是前置通知..."); result = method.invoke(target, args); System.out.println("这是返回通知,方法正常执行时执行..."); } catch(Exception e) { System.out.println("这是异常通知,方法异常时执行..."); e.printStackTrace(); } finally { System.out.println("这是后置通知,不论是否异常,都会执行"); } return result; } }; proxy = (ArithmeticCalculator) Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader, interfaces, h); return proxy; } }
-- 调用
public class App { public static void main( String[] args ) { ArithmeticCalculator target = new ArithmeticCalculatorImpl(); ArithmeticCalculator proxy = new ArithmeticCalculatorLoggingProxy(target).getLoggingProxy(); proxy.add(1, 3); System.out.println(); proxy.div(4, 2); } }
-- 结果(后置通知的执行顺序好像和spring aop不太一样)

三 通过Spring AOP + AspectJ注解方式
-- 配置文件(利用context和aop命名空间)
<!-- 配置bean自动扫描 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.spring_1.aop"></context:component-scan> <!-- 配置aspectj起作用 --> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
-- 接口,实现类同前,需要注意,实现类要加到spring容器中

-- 日志切面类
需要注意,用@Component 加入到Spring IOC容器中, 用 @Aspect 让AspectJ自动扫描
@Component @Aspect public class LogginAspect { /** * 定义一个方法,用于声明切入点表达式,一般的,方法中不需要其他代码 */ @Pointcut("execution(* com.atguigu.spring_1.aop.ArithmeticCalculator.*(..))") public void declareJointPointExpression() {}; /** * 前置通知 */ @Before("declareJointPointExpression()") public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint) { // JoinPoint:链接点可以访问到方法的具体信息 String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); List<Object> args = Arrays.asList(joinPoint.getArgs()); System.out.println("前置通知: method " + methodName + " begin with arguments:" + args +""); } /** * 后置通知: 不论是否有异常,都会如期执行 * 但是无法访问到方法的返回值 */ @After("declareJointPointExpression()") public void afterMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint) { String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); System.out.println("后置通知: method " + methodName + " end"); } /** * 返回通知:只有正常执行时,才可以执行 * 能够访问到方法的返回值 */ @AfterReturning(value="declareJointPointExpression()", returning="result") public void afterReturningMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) { String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); System.out.println("返回通知: method " + methodName + " end with result: " + result +""); } /** * 异常通知:抛出异常时执行 */ @AfterThrowing(value="declareJointPointExpression()", throwing="ex") public void afterThrowingMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint, Exception ex) { String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); System.out.println("异常通知: method " + methodName + " throw an exception " + ex +""); } }
-- 调用
public class App { public static void main( String[] args ) { ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("aop.xml"); ArithmeticCalculator target = ctx.getBean(ArithmeticCalculator.class); target.add(1, 3); System.out.println(); target.div(4, 2); } }
-- 结果

四)四种通知的执行顺序
没有异常:前置通知->目标方法->后置通知->返回通知
有异常: 前置通知->目标方法->后置通知->异常通知
五)后置通知和返回通知的区别
-- 后置通知(@After)不能访问到目标方法的结果,而返回通知(@AfterReturning)则可以
六)切面等基本概念的理解