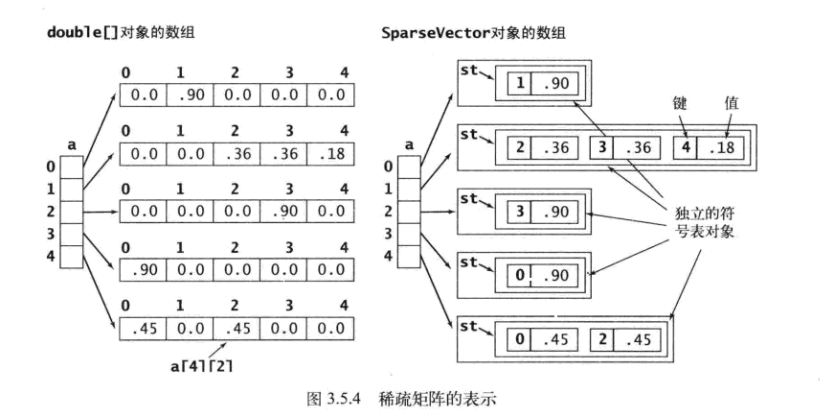
大数据下,数据大都比较稀疏,用矩阵存储的数据是稀疏的,大多数项是0。
算法四中介绍用稀疏矩阵的形式来存储数组
点乘的稀疏向量代码
public double dot(double[] that) { double sum = 0.0; for (int i : st.keys()) sum += that[i] * this.get(i); return sum; }
public double dot(SparseVector that) { double sum = 0.0; // iterate over the vector with the fewest nonzeros if (this.st.size() <= that.st.size()) { for (int i : this.st.keys()) if (that.st.contains(i)) sum += this.get(i) * that.get(i); } else { for (int i : that.st.keys()) if (this.st.contains(i)) sum += this.get(i) * that.get(i); } return sum; }
完整代码:
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.ST; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class SparseVector { private int d; // dimension private ST<Integer, Double> st; // the vector, represented by index-value pairs /** * Initializes a d-dimensional zero vector. * @param d the dimension of the vector */ public SparseVector(int d) { this.d = d; this.st = new ST<Integer, Double>(); } /** * Sets the ith coordinate of this vector to the specified value. * * @param i the index * @param value the new value * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless i is between 0 and d-1 */ public void put(int i, double value) { if (i < 0 || i >= d) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal index"); if (value == 0.0) st.delete(i); else st.put(i, value); } /** * Returns the ith coordinate of this vector. * * @param i the index * @return the value of the ith coordinate of this vector * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless i is between 0 and d-1 */ public double get(int i) { if (i < 0 || i >= d) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal index"); if (st.contains(i)) return st.get(i); else return 0.0; } /** * Returns the number of nonzero entries in this vector. * * @return the number of nonzero entries in this vector */ public int nnz() { return st.size(); } /** * Returns the dimension of this vector. * * @return the dimension of this vector * @deprecated Replaced by {@link #dimension()}. */ @Deprecated public int size() { return d; } /** * Returns the dimension of this vector. * * @return the dimension of this vector */ public int dimension() { return d; } /** * Returns the inner product of this vector with the specified vector. * * @param that the other vector * @return the dot product between this vector and that vector * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the lengths of the two vectors are not equal */ public double dot(SparseVector that) { if (this.d != that.d) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Vector lengths disagree"); double sum = 0.0; // iterate over the vector with the fewest nonzeros if (this.st.size() <= that.st.size()) { for (int i : this.st.keys()) if (that.st.contains(i)) sum += this.get(i) * that.get(i); } else { for (int i : that.st.keys()) if (this.st.contains(i)) sum += this.get(i) * that.get(i); } return sum; } /** * Returns the inner product of this vector with the specified array. * * @param that the array * @return the dot product between this vector and that array * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the dimensions of the vector and the array are not equal */ public double dot(double[] that) { double sum = 0.0; for (int i : st.keys()) sum += that[i] * this.get(i); return sum; } /** * Returns the magnitude of this vector. * This is also known as the L2 norm or the Euclidean norm. * * @return the magnitude of this vector */ public double magnitude() { return Math.sqrt(this.dot(this)); } /** * Returns the Euclidean norm of this vector. * * @return the Euclidean norm of this vector * @deprecated Replaced by {@link #magnitude()}. */ @Deprecated public double norm() { return Math.sqrt(this.dot(this)); } /** * Returns the scalar-vector product of this vector with the specified scalar. * * @param alpha the scalar * @return the scalar-vector product of this vector with the specified scalar */ public SparseVector scale(double alpha) { SparseVector c = new SparseVector(d); for (int i : this.st.keys()) c.put(i, alpha * this.get(i)); return c; } /** * Returns the sum of this vector and the specified vector. * * @param that the vector to add to this vector * @return the sum of this vector and that vector * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the dimensions of the two vectors are not equal */ public SparseVector plus(SparseVector that) { if (this.d != that.d) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Vector lengths disagree"); SparseVector c = new SparseVector(d); for (int i : this.st.keys()) c.put(i, this.get(i)); // c = this for (int i : that.st.keys()) c.put(i, that.get(i) + c.get(i)); // c = c + that return c; } /** * Returns a string representation of this vector. * @return a string representation of this vector, which consists of the * the vector entries, separates by commas, enclosed in parentheses */ public String toString() { StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(); for (int i : st.keys()) { s.append("(" + i + ", " + st.get(i) + ") "); } return s.toString(); } /** * Unit tests the {@code SparseVector} data type. * * @param args the command-line arguments */ public static void main(String[] args) { SparseVector a = new SparseVector(10); SparseVector b = new SparseVector(10); a.put(3, 0.50); a.put(9, 0.75); a.put(6, 0.11); a.put(6, 0.00); b.put(3, 0.60); b.put(4, 0.90); StdOut.println("a = " + a); StdOut.println("b = " + b); StdOut.println("a dot b = " + a.dot(b)); StdOut.println("a + b = " + a.plus(b)); } }
运行结果:
a = (3, 0.5) (9, 0.75) b = (3, 0.6) (4, 0.9) a dot b = 0.3 a + b = (3, 1.1) (4, 0.9) (9, 0.75)