1. Select- subquery子查询
子查询:是将一条查询语句嵌套在另一条查询语句之中。
2. 案例
需求:查询获得代课天数最多的那个老师的信息。
思路:先获得最多的代课天数是多少天,然后再判断哪个老师的代课天数和最大值是一样的。MySQL允许将上面的查询结果,作为一个值来使用。
即:
var1 = Select max(days) from teacher_class;/* 保存起来 */
Select t_name,gender from teacher_class where days = var1;
Select t_name,gender from teacher_class where days = ( Select max(days) from teacher_class );
3. 子查询详解:
上面2中使用到就是子查询,子查询需要使用括号括起来。
(1)子查询的分类:
分类标准:
• 子查询使用的结构:exists型,where型,from型
• 子查询返回值形式:(1)单一值 (2)一列 (3)多列 (4)多行多列

(2)标量子查询:
获得一个值之后,使用关系运算符,进行判断。
= > < <= >= !=
比如:Select t_name,gender from teacher_class where days < ( Select max(days) from teacher_class );

(3)列子查询:
获得一列 ,通常是多个行的一列值。
需求:获得所有带过0228班的讲师信息。
思路:先获得0228班讲师的姓名,再利用这姓名查询其所有的班记录。
select t_name from teacher_class where c_name ='php0228';
select t_name,c_name,days from teacher_class where t_name in ( select t_name from teacher_class where c_name ='php0228' );
注意:
• 返回一列。
• 使用in / not in
• 还可以使用其他的集合操作符:
Any(集合):集合中的任何一个
= any(集合):等于集合中的任何一个即可。等同与in
all(集合):集合中所有的元素。
!=all(集合):不等于集合中的任何一个即可。等同与 not in
Some(集合):集合中的一些
--> 使用 in

--> 使用 any
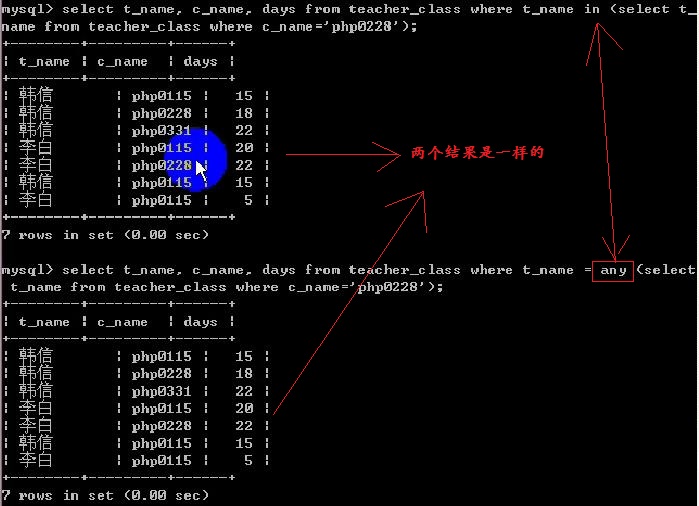
--> 使用 !=any
!=any不等于集合中的任意一个就可以(注意不是要求和集合中所有的元素不相等),只要与集合中的一些元素不相等即可。
注意 !=any不是 not in

总结:
• = any ----- in
• != all ----- not in
• Some 和 any 同义词
(4)行子查询:
使用 limit 1

行子查询案例:
在参与比较的时候,使用括号可以构建一行(field1, field2)
select t_name, gender,c_name from teacher_class where (gender,c_name) = (select distinct gender,c_name from teacher_class where t_name='李白' and c_name='php0115');

这时候要求查询结果返回一行,如下:
select t_name, gender,c_name from teacher_class where (gender,c_name) = (select distinct gender,c_name from teacher_class where t_name='李白' and c_name='php0115' limit 1);
(5)表子查询:
通常用在from型语句中。
select * from (select t_name ,c_name,days from teacher_class where days > 15);

在from子句中内,要求使用一个表,而不是一个结构,应该给这个查询结果起名,别名。
select * from (select t_name ,c_name,days from teacher_class where days > 15) as temp;

在上面的基础上,添加查询条件,如下:
select * from (select t_name ,c_name,days from teacher_class where days > 15) as temp where t_name like '李%';

再次添加查询条件:
select teacher from (select t_name as teacher ,c_name,days from teacher_class where days > 15) as temp where teacher like '李%';
