1. Bundle 和 Intent:
Bundle只是一个信息的载体 将内部的内容以键值对组织 ,Intent负责Activity之间的交互自己是带有一个Bundle的。Intent.putExtras(Bundle bundle)直接将Intent的内部Bundle设置为参数里的bundle,Intent.getExtras()直接可以获取Intent带有的Bundle.
Intent携带了Bundle数据,Bundle是一种数据包裹(打包数据),利用Intent机制通过Bundle数据进行不同Activity通信。
两个activity之间的通讯可以通过bundle类来实现,做法就是:
(1)新建一个bundle类
Bundle mBundle = new Bundle();
(2)bundle类中加入数据(key -value的形式,另一个activity里面取数据的时候,就要用到key,找出对应的value)
mBundle.putString("Data", "data from TestBundle");
(3)新建一个intent对象,并将该bundle加入这个intent对象
Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setClass(TestBundle.this, Target.class); intent.putExtras(mBundle);
完整代码如下:
AndroidManifest.xml如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.tencent.test" android:versionCode="1" android:versionName="1.0"> <application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name"> <activity android:name=".TestBundle" android:label="@string/app_name"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> <activity android:name=".Target"></activity> </application> <uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="7" /> </manifest>
两个类如下:intent从TestBundle类发起,到Target类。
类1:TestBundle类:
import android.app.Activity; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; import android.view.View.OnClickListener; import android.widget.Button; public class TestBundle extends Activity { private Button button1; private OnClickListener cl; public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.main); button1 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button1); cl = new OnClickListener(){ @Override public void onClick(View arg0) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setClass(TestBundle.this, Target.class); Bundle mBundle = new Bundle(); mBundle.putString("Data", "data from TestBundle");//压入数据 intent.putExtras(mBundle); startActivity(intent); } }; button1.setOnClickListener(cl); } }
类2: Target
import android.app.Activity; import android.os.Bundle; public class Target extends Activity{ public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.target); <span style="color:#ff6600;">Bundle bundle = getIntent().getExtras(); </span> //得到传过来的bundle String data = bundle.getString("Data");//读出数据 setTitle(data); } }
布局文件main.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/hello" /> <Button android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/button" android:id = "@+id/button1" /> </LinearLayout>
target.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/target" /> </LinearLayout>
String.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <string name="hello">Hello World, TestBundle!</string> <string name="app_name">测试Bundle用法</string> <string name="button">点击跳转</string> <string name="target">来到target activity</string> </resources>
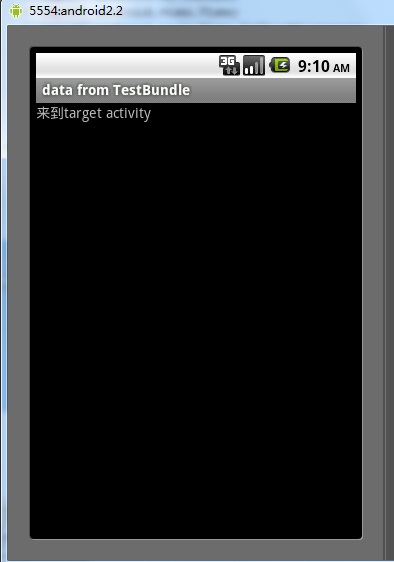
结果:
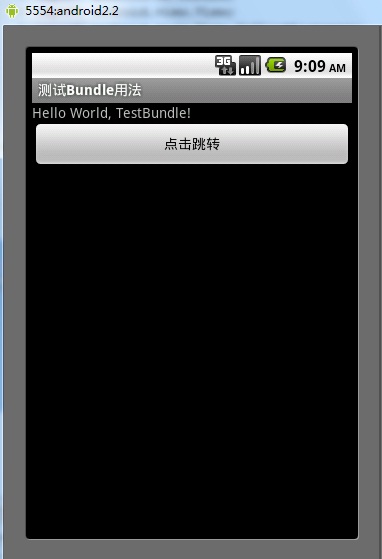
跳转结果: