k-近邻算法原理
简单地说,K-近邻算法采用测量不同特征值之间的距离方法进行分类。
- 优点:精度高(计算距离)、对异常值不敏感(单纯根据距离进行分类,会忽略特殊情况)、无数据输入假定(不会对数据预先进行判定)。
- 缺点:时间复杂度高、空间复杂度高。
- 适用数据范围:数值型和标称型。
工作原理
存在一个样本数据集合,也称作训练样本集,并且样本集中每个数据都存在标签,即我们知道样本集中每一数据 与所属分类的对应关系。输人没有标签的新数据后,将新数据的每个特征与样本集中数据对应的 特征进行比较,然后算法提取样本集中特征最相似数据(最近邻)的分类标签。一般来说,我们 只选择样本数据集中前K个最相似的数据,这就是K-近邻算法中K的出处,通常K是不大于20的整数。 最后 ,选择K个最相似数据中出现次数最多的分类,作为新数据的分类。
回到前面电影分类的例子,使用K-近邻算法分类爱情片和动作片。有人曾经统计过很多电影的打斗镜头和接吻镜头,下图显示了6部电影的打斗和接吻次数。假如有一部未看过的电影,如何确定它是爱情片还是动作片呢?我们可以使用K-近邻算法来解决这个问题。

首先我们需要知道这个未知电影存在多少个打斗镜头和接吻镜头,上图中问号位置是该未知电影出现的镜头数图形化展示,具体数字参见下表。

即使不知道未知电影属于哪种类型,我们也可以通过某种方法计算出来。首先计算未知电影与样本集中其他电影的距离,如图所示

现在我们得到了样本集中所有电影与未知电影的距离,按照距离递增排序,可以找到K个距 离最近的电影。假定k=3,则三个最靠近的电影依次是California Man、He's Not Really into Dudes、Beautiful Woman。K-近邻算法按照距离最近的三部电影的类型,决定未知电影的类型,而这三部电影全是爱情片,因此我们判定未知电影是爱情片。
欧几里得距离(Euclidean Distance)
欧氏距离是最常见的距离度量,衡量的是多维空间中各个点之间的绝对距离。公式如下:

在scikit-learn库中使用k-近邻算法
一个最简单的例子
身高、体重、鞋子尺码数据对应性别
import numpy as np import pandas as pd from pandas import DataFrame,Series
feature = np.array([[170,75,41],[166,65,38],[177,80,43],[179,80,43],[170,60,40],[160,55,38]]) target = np.array(['男','女','男','男','女','女'])
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=3)
knn.fit(feature,target)
knn.score(feature,target)
knn.predict(np.array([[180,70,43]])) array(['男'], dtype='<U1')
预测电影类型案例
# 预测电影类型案例 data = pd.read_excel('../../my_films.xlsx') data name Action lens Love lens target 0 前任3 4 10 Action 1 西游记 16 2 Action 2 战狼2 18 3 Action 3 失恋33天 2 13 Love 4 宝贝计划 4 2 Comedy 5 捉妖记 10 10 Action 6 乡村爱情 3 4 Comedy 7 阳光的快乐生活 2 3 Comedy 8 后来的你们 2 11 Love 9 大话西游 18 2 Action 10 速度与激情8 3 19 Love 11 一路向北 5 17 Love
# 取出模型特征数据 feature = data[['Action lens','Love lens']] # 取出模型目标数据 target = data['target'] # 实例化模型对象 knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=3) # 对模型进行训练 knn.fit(feature,target) knn.score(feature,target)
# 进行分类预测 knn.predict(np.array([[90,33]])) # 90 Action lens 33 Love lens array(['Comedy'], dtype=object)
预测年收入是否大于50K美元
读取adult.txt文件,最后一列是年收入,并使用KNN算法训练模型,然后使用模型预测一个人的年收入是否大于50
df = pd.read_csv('../data/adults.txt') df.head()
| age | workclass | final_weight | education | education_num | marital_status | occupation | relationship | race | sex | capital_gain | capital_loss | hours_per_week | native_country | salary | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 39 | State-gov | 77516 | Bachelors | 13 | Never-married | Adm-clerical | Not-in-family | White | Male | 2174 | 0 | 40 | United-States | <=50K |
| 1 | 50 | Self-emp-not-inc | 83311 | Bachelors | 13 | Married-civ-spouse | Exec-managerial | Husband | White | Male | 0 | 0 | 13 | United-States | <=50K |
| 2 | 38 | Private | 215646 | HS-grad | 9 | Divorced | Handlers-cleaners | Not-in-family | White | Male | 0 | 0 | 40 | United-States | <=50K |
| 3 | 53 | Private | 234721 | 11th | 7 | Married-civ-spouse | Handlers-cleaners | Husband | Black | Male | 0 | 0 | 40 | United-States | <=50K |
| 4 | 28 | Private | 338409 | Bachelors | 13 | Married-civ-spouse | Prof-specialty | Wife | Black | Female | 0 | 0 | 40 | Cuba | <=50K |
获取年龄、教育程度、职位、每周工作时间作为机器学习数据
获取薪水作为对应结果
# 提取出职位 job_array = df['occupation'].unique() job_array
array(['Adm-clerical', 'Exec-managerial', 'Handlers-cleaners',
'Prof-specialty', 'Other-service', 'Sales', 'Craft-repair',
'Transport-moving', 'Farming-fishing', 'Machine-op-inspct',
'Tech-support', '?', 'Protective-serv', 'Armed-Forces',
'Priv-house-serv'], dtype=object)
# 将职位转换为数值 dic = {} for i in range(15): key = job_array[i] value = i dic[key] = value
# 将职业映射成数值 df['occupation'] = df['occupation'].map(dic)
# 提取特征数据和目标数据 feature = df[['occupation','age','education_num','hours_per_week']] target = df['salary']
# 训练数据和测试数据 x_train = feature[:32551] y_train = target[:32551] x_test = feature[-10:] y_test = target[-10:]
# 生成knn knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=10) knn.fit(x_train,y_train) knn.score(x_train,y_train)
0.8192375042241405
print('预测值:',knn.predict(x_test)) print('真实值:',y_test)
保存训练模型
from sklearn.externals import joblib joblib.dump(knn,'./job_knn.m') k = joblib.load('./job_knn.m') k
KNN实现数字识别
import numpy as np # bmp 图片后缀 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt %matplotlib inline from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifie
提炼样本数据
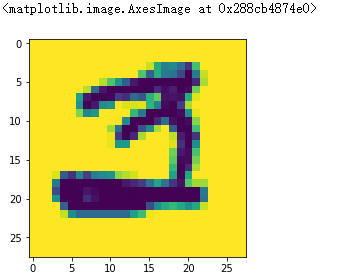
img_arr = plt.imread('./data/3/3_100.bmp') plt.imshow(img_arr)
all_imgs_list = [] target_list = [] for i in range(10): for j in range(500): img_path = './data/'+str(i)+'/'+str(i)+'_'+str(j+1)+'.bmp' img_arr = plt.imread(img_path) all_imgs_list.append(img_arr) target_list.append(i)
# 此时的是一个三维数组 feature = np.array(all_imgs_list) feature.shape (5000, 28, 28) #feature是一个三维数组(执行降维操作) feature = feature.reshape(5000,28*28) feature.shape (5000, 784) # 目标模型 target = np.array(target_list)
将样本打乱
np.random.seed(3) np.random.shuffle(feature) np.random.seed(3) np.random.shuffle(target)
获取训练数据和测试数据
x_train = feature[:4950] y_train = target[:4950] x_test = feature[-50:] y_test = target[-50:] # 实例化模型对象,训练 knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=30) knn.fit(x_train,y_train) knn.score(x_train,y_train) 0.9195959595959596 print('测试模型预测分类:',knn.predict(x_test)) print('测试的真实数据:',y_test) 预测分类: [4 5 7 9 7 5 7 6 8 6 1 1 3 4 8 4 1 0 1 2 0 5 8 6 5 9 3 9 1 8 9 6 4 1 5 0 8 7 7 1 5 3 5 5 6 1 1 3 6 3] 真实数据: [4 5 7 9 7 5 7 6 8 6 4 1 3 4 8 4 2 0 1 2 0 5 8 6 5 9 3 9 1 8 9 6 4 1 5 2 8 7 7 2 5 3 5 5 6 1 1 3 6 3]
对图片进行识别
#外部图片的识别 img_arr = plt.imread('./数字.jpg') plt.imshow(img_arr)
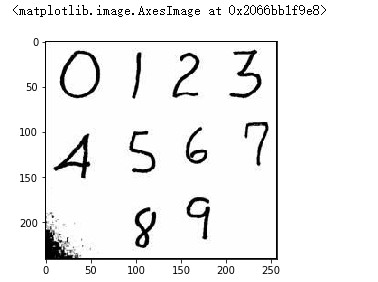
# 切上面的图,将5切出来 five_arr = img_arr[90:155,80:135] plt.imshow(five_arr)
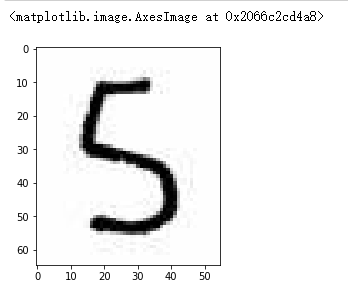
#five数组是三维的,需要进行降维,舍弃第三个表示颜色的维度 five_arr = five_arr.mean(axis=2)
five_arr.shape
(65, 55)
# 实现图片的等比压缩 import scipy.ndimage as ndimage five = ndimage.zoom(five_arr,zoom = (28/65,28/55)) five.shape (28, 28)
# 使用模型对图片进行解析 knn.predict(five.reshape(1,784)) array([5])
#保存模型 #knn 模型,算法 from sklearn.externals import joblib joblib.dump(knn,'数字识别.m') # 加载模型 knn_digits = joblib.load('./数字识别.m') knn_digits.predict(data_pre_test.reshape(1,-1))