题目地址
https://buuoj.cn/challenges#CrackRTF
题解
IDA打开,F5反编译,双击进入main_0,代码如下,注释是我以自己的理解写的
1 int __cdecl main_0() 2 { 3 DWORD v0; // eax 4 DWORD v1; // eax 5 CHAR String; // [esp+4Ch] [ebp-310h] 6 int v4; // [esp+150h] [ebp-20Ch] 7 CHAR String1; // [esp+154h] [ebp-208h] 8 BYTE pbData; // [esp+258h] [ebp-104h] 9 10 memset(&pbData, 0, 0x104u); 11 memset(&String1, 0, 0x104u); 12 v4 = 0; 13 printf("pls input the first passwd(1): "); 14 scanf("%s", &pbData); 15 if ( strlen((const char *)&pbData) != 6 ) 16 { 17 printf("Must be 6 characters! "); 18 ExitProcess(0); 19 } 20 v4 = atoi((const char *)&pbData); // 将输入字符串转整型赋给v4 21 if ( v4 < 100000 ) // 不能小于100000 22 ExitProcess(0); 23 strcat((char *)&pbData, "@DBApp"); // 将输入字符串和"@DBApp"拼接赋给pbData 24 v0 = strlen((const char *)&pbData); 25 sub_40100A(&pbData, v0, &String1); // 用SHA1算法,将pbData哈希,并赋给String1 26 if ( !_strcmpi(&String1, "6E32D0943418C2C33385BC35A1470250DD8923A9") )// 相同则返回0 27 { 28 printf("continue... "); 29 printf("pls input the first passwd(2): "); 30 memset(&String, 0, 0x104u); 31 scanf("%s", &String); 32 if ( strlen(&String) != 6 ) 33 { 34 printf("Must be 6 characters! "); 35 ExitProcess(0); 36 } 37 strcat(&String, (const char *)&pbData); // 将第二次输入字符串和pbData拼接赋给String 38 memset(&String1, 0, 0x104u); 39 v1 = strlen(&String); 40 sub_401019((BYTE *)&String, v1, &String1); // 用MD5算法,将String哈希,并赋给String1 41 if ( !_strcmpi("27019e688a4e62a649fd99cadaafdb4e", &String1) )// 相同则返回0 42 { 43 if ( !sub_40100F(&String) ) 44 { 45 printf("Error!! "); 46 ExitProcess(0); 47 } 48 printf("bye ~~ "); 49 } 50 } 51 return 0; 52 }
进入第25行的sub_40100A函数,再进入sub_401230,代码如下,注释是按我的理解写的
1 int __cdecl sub_401230(BYTE *pbData, DWORD dwDataLen, LPSTR lpString1) 2 { 3 int result; // eax 4 DWORD i; // [esp+4Ch] [ebp-28h] 5 CHAR String2; // [esp+50h] [ebp-24h] 6 char v6[20]; // [esp+54h] [ebp-20h] 7 DWORD pdwDataLen; // [esp+68h] [ebp-Ch] 8 HCRYPTHASH phHash; // [esp+6Ch] [ebp-8h] 9 HCRYPTPROV phProv; // [esp+70h] [ebp-4h] 10 11 if ( !CryptAcquireContextA(&phProv, 0, 0, 1u, 0xF0000000) )// 使用默认的CSP得到指向key contanier的handle 12 return 0; // 失败则return 0 13 if ( CryptCreateHash(phProv, 0x8004u, 0, 0, &phHash) )// 使用CALG_SHA1算法,无密钥 MAC。创建一个指向CSP hash object的handle 14 { 15 if ( CryptHashData(phHash, pbData, dwDataLen, 0) )// 将首地址为pbData,长度为dwDataLen的部分加到phHash的hash object上 16 { 17 CryptGetHashParam(phHash, 2u, (BYTE *)v6, &pdwDataLen, 0);// 哈希值的长度为2u,长度为pdwDataLen的数据存到v6里 18 *lpString1 = 0; 19 for ( i = 0; i < pdwDataLen; ++i ) 20 { 21 wsprintfA(&String2, "%02X", (unsigned __int8)v6[i]);// 以2位16进制格式(不足2位则前面补0)的格式赋给String2 22 lstrcatA(lpString1, &String2); // 将String2拼接到lpString1后面 23 } 24 CryptDestroyHash(phHash); // 销毁hash object 25 CryptReleaseContext(phProv, 0); // 释放CSP和key container 26 result = 1; 27 } 28 else 29 { 30 CryptDestroyHash(phHash); 31 CryptReleaseContext(phProv, 0); 32 result = 0; 33 } 34 } 35 else 36 { 37 CryptReleaseContext(phProv, 0); 38 result = 0; 39 } 40 return result; 41 }
其中第13行的第二个参数0x8004u说明了算法是SHA1,可以参考https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/windows/win32/api/wincrypt/nf-wincrypt-cryptcreatehash和https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/windows/win32/seccrypto/alg-id
同理,回到main_0中,第40行用的哈希算法是MD5,可以自己进入验证。
回到main_0,可以看出输入的第一个字符串与”@DBApp”拼接进行SHA1,得到的结果需要与提供的一致。而且输入一定是6位,纯数字(atoi函数),且大于100000,那么可以写脚本爆破。Python代码如下:
1 import hashlib 2 t = "@DBApp" 3 hash1 = "6E32D0943418C2C33385BC35A1470250DD8923A9".lower() 4 hash2 = "27019e688a4e62a649fd99cadaafdb4e" 5 Aan="QWERTYUIOPLKJHGFDSAZXCVBNMmnbvcxzasdfghjklpoiuytrewq1234567890" 6 for i in range(100001,1000000): 7 pwd1 = str(i)+t 8 h1 = hashlib.sha1(pwd1.encode('utf-8')).hexdigest() 9 if h1==hash1: 10 print(i) 11 break
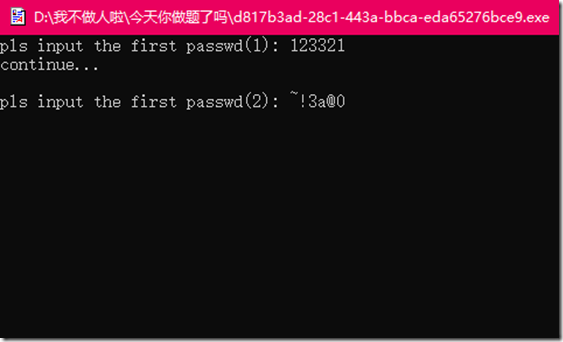
跑完结果是123321
然后对于第二个输入,本想故技重施,但是发现除了必须为6位外,没有输入限制,使得爆破不行了(我尝试过)后面我就去看了别人的Wp,发现重点在第43行的sub_40100F,进入,再进入sub_4014D0,代码如下:
1 char __cdecl sub_4014D0(LPCSTR lpString) 2 { 3 LPCVOID lpBuffer; // [esp+50h] [ebp-1Ch] 4 DWORD NumberOfBytesWritten; // [esp+58h] [ebp-14h] 5 DWORD nNumberOfBytesToWrite; // [esp+5Ch] [ebp-10h] 6 HGLOBAL hResData; // [esp+60h] [ebp-Ch] 7 HRSRC hResInfo; // [esp+64h] [ebp-8h] 8 HANDLE hFile; // [esp+68h] [ebp-4h] 9 10 hFile = 0; 11 hResData = 0; 12 nNumberOfBytesToWrite = 0; 13 NumberOfBytesWritten = 0; 14 hResInfo = FindResourceA(0, (LPCSTR)0x65, "AAA"); 15 if ( !hResInfo ) 16 return 0; 17 nNumberOfBytesToWrite = SizeofResource(0, hResInfo); 18 hResData = LoadResource(0, hResInfo); 19 if ( !hResData ) 20 return 0; 21 lpBuffer = LockResource(hResData); // 将数据指针给lpBuffer 22 sub_401005(lpString, (int)lpBuffer, nNumberOfBytesToWrite); 23 hFile = CreateFileA("dbapp.rtf", 0x10000000u, 0, 0, 2u, 0x80u, 0); 24 if ( hFile == (HANDLE)-1 ) 25 return 0; 26 if ( !WriteFile(hFile, lpBuffer, nNumberOfBytesToWrite, &NumberOfBytesWritten, 0) ) 27 return 0; 28 CloseHandle(hFile); 29 return 1; 30 }
然后进入22行的sub_401005,再进入sub_401420,代码如下:
1 // lpString是String,a2是lpBuffer,a3是lpBuffer指向数据的长度 2 unsigned int __cdecl sub_401420(LPCSTR lpString, int a2, int a3) 3 { 4 unsigned int result; // eax 5 unsigned int i; // [esp+4Ch] [ebp-Ch] 6 unsigned int v5; // [esp+54h] [ebp-4h] 7 8 v5 = lstrlenA(lpString); // String的长度,12 9 for ( i = 0; ; ++i ) 10 { 11 result = i; 12 if ( i >= a3 ) 13 break; 14 *(_BYTE *)(i + a2) ^= lpString[i % v5]; // lpBuffer指向数据的每一位与String的每一位循环异或,结果给lpBuffer指向数据 15 } 16 return result; 17 }
第14行进行循环异或,并赋给lpBuffer,我们再回到sub_4014D0的第23行,发现WriteFile的第二个参数就是lpBuffer。也就是说,要将lpBuffer指向的数据写入RTF文件。那么RTF文件的开头肯定是RTF文件头,而这个文件头就是由lpBuffer起初指向的数据,即”AAA”的数据,与我们第二次输入的字符串(String的前6位)进行异或得到。又因为异或的逆运算就是异或,所以我们只需要将RTF文件头前6位与”AAA”的数据前六位异或,就能得到我们第二次输入的6位字符串。
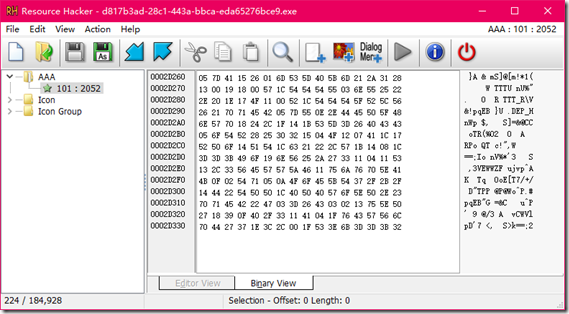
首先要得到”AAA”的数据,用Resource Hacker工具打开即可。
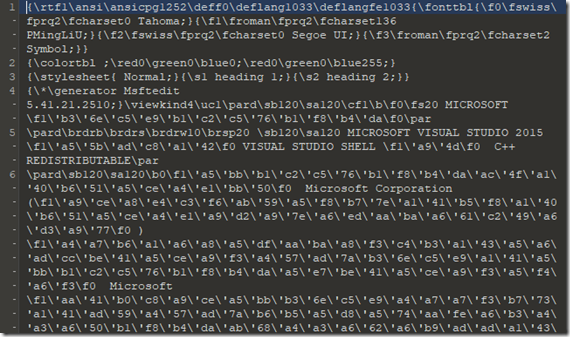
然后用010editor随便打开电脑里的一个.rtf文件,查看其文件头前6位
然后写脚本将他们异或,就能得到第二次要输入的6位字符串,脚本代码如下:
1 AAA = [0x05,0x7D,0x41,0x15,0x26,0x01] 2 a = '' 3 for i in AAA: 4 a += chr(int(i)) 5 rtf = "{\rtf1" # \转义 6 for i in range(0,6): 7 print(chr(ord(a[i])^ord(rtf[i])),end='')
得到第二次要输入的字符串~!3a@0
现在两次输入的字符串都有了,双击运行题目文件,依次输入两个字符串
运行后,在题目文件所在文件夹会找到一个rtf文件,双击打开,得到flag。
参考
windows的各种API去官网看
https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/windows/win32/api/wincrypt/nf-wincrypt-cryptacquirecontexta