Introduction
In this tutorial, we will learn how to call a Web Service using SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol).
Prerequisites
Web Service, SOAP envelope, WSDL (Web Service Definition Language)
What is SOAP?
SOAP is a protocol specification for exchanging structured information in the implementation of Web Services in computer networks. It relies on Extensible Markup Language (XML) for its message format, and usually relies on other Application Layer protocols, most notably Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), for message negotiation and transmission. The following is the structure of SOAP Envelope: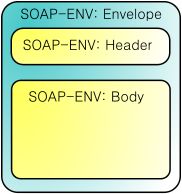
Step 1:
First create a "New Android Project". Name it "WebServiceDemo" like below.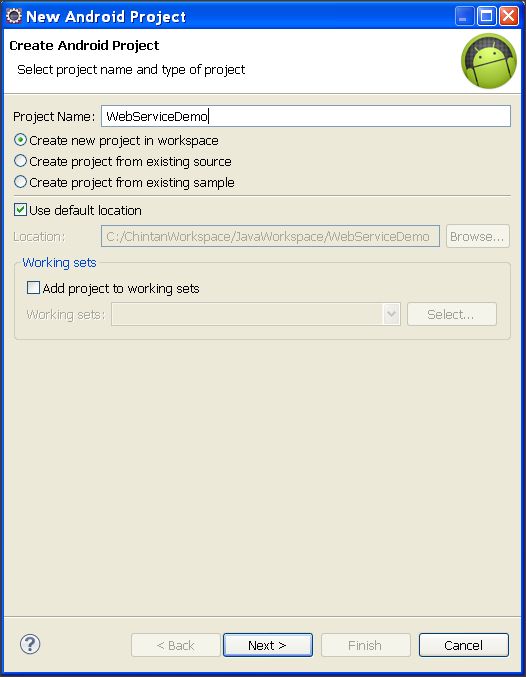
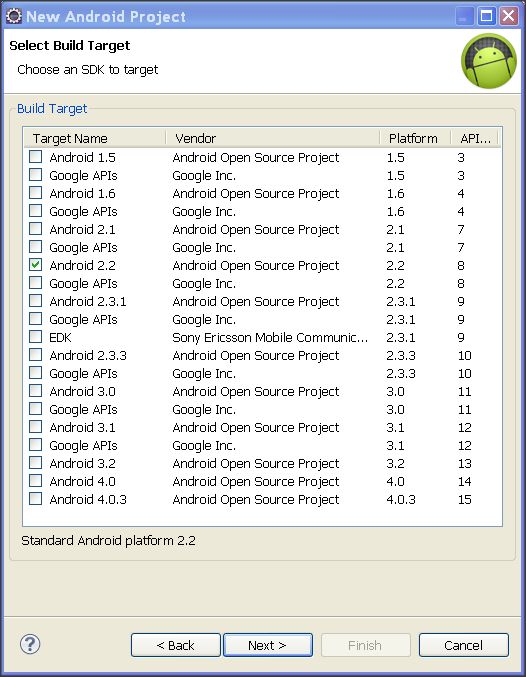
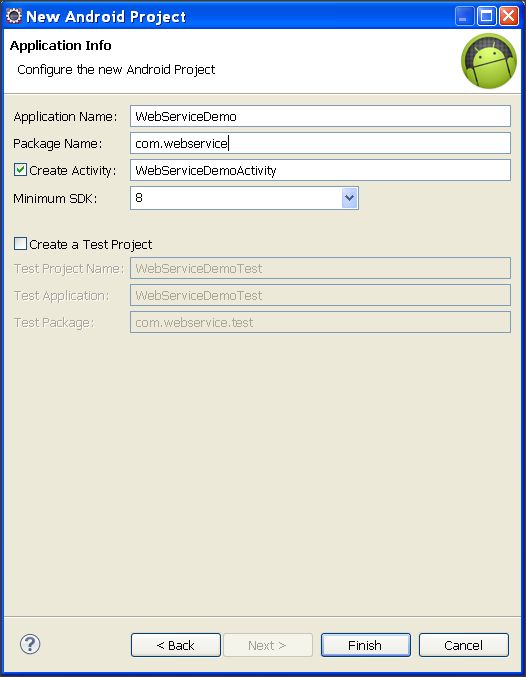
Step 2:
Now right-click on your "WebServiceDemo" project and select "New -> Folder"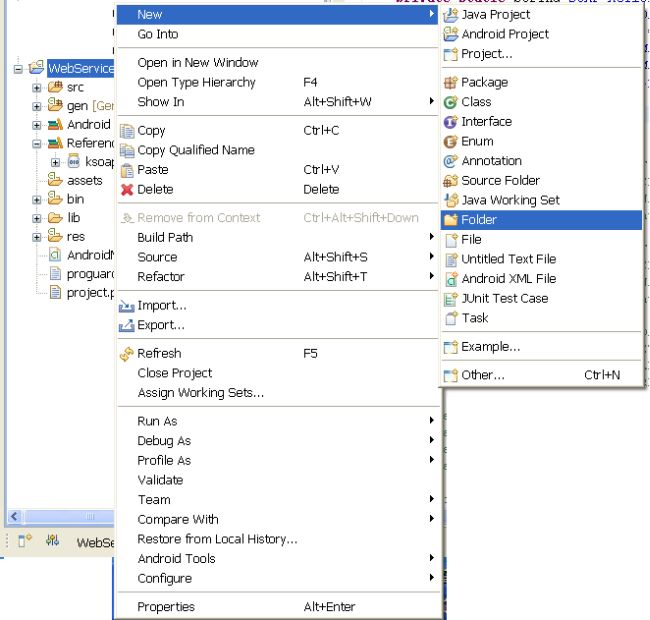
Now, give it a name it "lib". We need to add a SOAP library into this directory.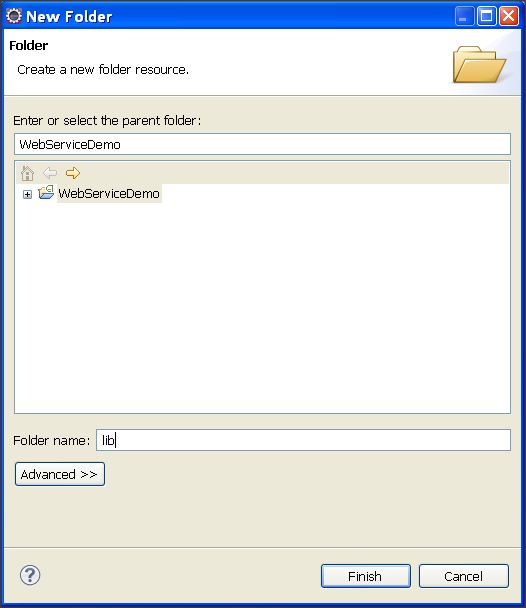
Step 3:
Now download the attached library named "ksoap2-android-assembly-2.6.0-jar-with-dependencies.jar". Copy that file and paste it into the "lib" directory.
After copying, do the following steps:
- Right-click on the project.
- Go "Build Path -> Configure Build Path"
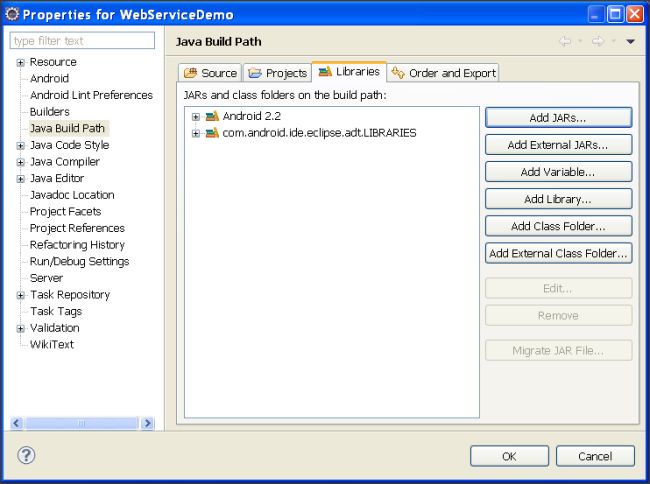
- Now, click on "Add Jars" and select ".jar" file from "project -> lib" directory.
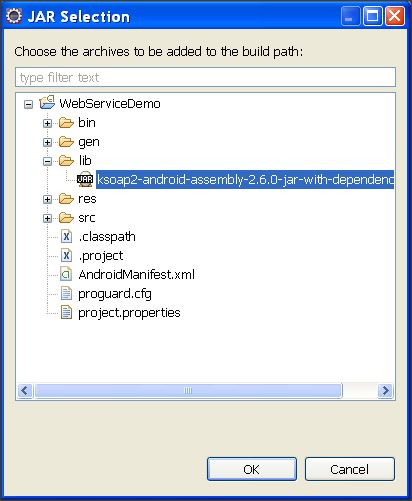
- Click on "Ok" to finish the procedure of adding library to Android application.
Step 4:
Next we need to create a layout of screen. To do so, go to "WebServiceDemo -> res -> layout -> main.xml"
Open this xml file in editing mode, and place below code.
Main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Fahrenheit"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/txtFar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<requestFocus />
</EditText>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Celsius"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/txtCel"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/linearLayout1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnFar"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="0.5"
android:text="Convert To Celsius" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnCel"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="0.5"
android:text="Convert To Fahrenheit" />
</LinearLayout>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnClear"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Clear" />
</LinearLayout>
This will create simple following screen.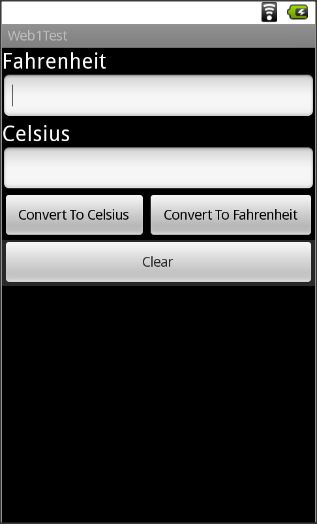
Step 5:
Now, find out any Web Service, make sure that you can view its WSDL file by writing "?wsdl" after that address.
For example, you have a web service like http://www.w3schools.com/webservices/tempconvert.asmx", so to view the WSDL file, simply write "?wsdl" after this address like:
http://www.w3schools.com/webservices/tempconvert.asmx?WSDL".
You are now done with the Web Service part from the internet. Now you need to extend some portion of the WSDL file. Open the first link in your browser, it will display 2 conversions for you:
-
CelsiusToFahrenheit
-
FahrenheitToCelsius
Select anyone of them, and you will see following screen: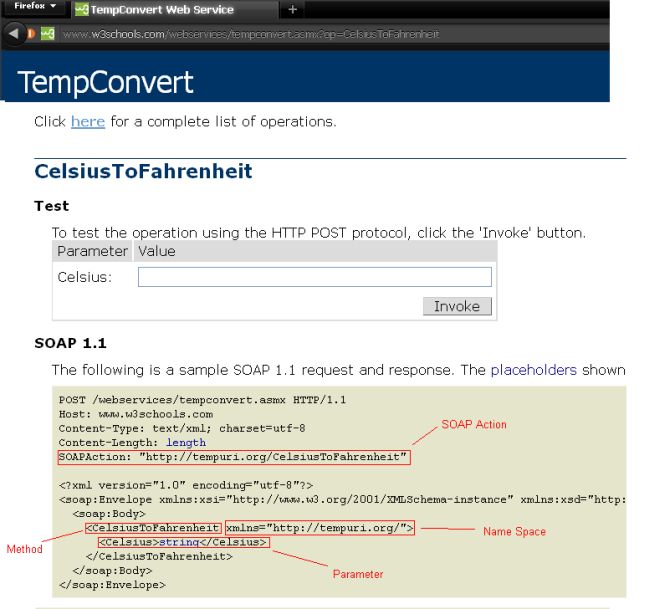
For CelsiusToFahrenheit:
-
SOAP_ACTION = "http://tempuri.org/CelsiusToFahrenheit";
-
NAMESPACE = "http://tempuri.org/";
-
METHOD_NAME = "CelsiusToFahrenheit";
-
URL = "http://www.w3schools.com/webservices/tempconvert.asmx?WSDL";
For FahrenheitToCelsius:
-
SOAP_ACTION = "http://tempuri.org/FahrenheitToCelsius";
-
NAMESPACE = "http://tempuri.org/";
-
METHOD_NAME = " FahrenheitToCelsius ";
-
URL = "http://www.w3schools.com/webservices/tempconvert.asmx?WSDL";
Step 6:
You need to understand some classes before proceeding to use a Web Service.
-
SoapObject (
A simple dynamic object that can be used to build SOAP calls without implementing KvmSerializable. Essentially, this is what goes inside the body of a SOAP envelope - it is the direct subelement of the body and all further sub elements. Instead of this class, custom classes can be used if they implement the KvmSerializable interface.
Constructor:
SoapObject (java.lang.String namespace, java.lang.String method)
-
SoapSerializationEnvelope
This class extends the SoapEnvelope with Soap Serialization functionality.
Constructor:
SoapSerializationEnvelope (int version)
Fields:Type
Field
Description
boolean
dotNetSet this variable to true for compatibility with what seems to be the default encoding for .Net-Services.
Methods:
Return Type
Method Name
Description
void
setOutputSoapObject(java.lang.Object soapObject)Assigns the object to the envelope as the outbound message for the soap call.
-
HttpTransportSE (org.ksoap2.transport.HttpTransportSE)
A J2SE based HttpTransport layer.
Constructor:
HttpTransportSE(java.lang.String url)
Method:Return TypeMethodDescriptionvoidcall(java.lang.String SoapAction, SoapEnvelope envelope)set the desired soapAction header field
Step 7:
Open your "WebServiceDemo -> src -> WebServiceDemoActivity.java" file and enterr following code:
WebServiceDemoActivity.java
import org.ksoap2.SoapEnvelope;
import org.ksoap2.serialization.SoapObject;
import org.ksoap2.serialization.SoapSerializationEnvelope;
import org.ksoap2.transport.HttpTransportSE;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class WebServiceDemoActivity extends Activity
{
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
private static String SOAP_ACTION1 = "http://tempuri.org/FahrenheitToCelsius";
private static String SOAP_ACTION2 = "http://tempuri.org/CelsiusToFahrenheit";
private static String NAMESPACE = "http://tempuri.org/";
private static String METHOD_NAME1 = "FahrenheitToCelsius";
private static String METHOD_NAME2 = "CelsiusToFahrenheit";
private static String URL = "http://www.w3schools.com/webservices/tempconvert.asmx?WSDL";
Button btnFar,btnCel,btnClear;
EditText txtFar,txtCel;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
btnFar = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btnFar);
btnCel = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btnCel);
btnClear = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btnClear);
txtFar = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.txtFar);
txtCel = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.txtCel);
btnFar.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener()
{
@Override
public void onClick(View v)
{
//Initialize soap request + add parameters
SoapObject request = new SoapObject(NAMESPACE, METHOD_NAME1);
//Use this to add parameters
request.addProperty("Fahrenheit",txtFar.getText().toString());
//Declare the version of the SOAP request
SoapSerializationEnvelope envelope = new SoapSerializationEnvelope(SoapEnvelope.VER11);
envelope.setOutputSoapObject(request);
envelope.dotNet = true;
try {
HttpTransportSE androidHttpTransport = new HttpTransportSE(URL);
//this is the actual part that will call the webservice
androidHttpTransport.call(SOAP_ACTION1, envelope);
// Get the SoapResult from the envelope body.
SoapObject result = (SoapObject)envelope.bodyIn;
if(result != null)
{
//Get the first property and change the label text
txtCel.setText(result.getProperty(0).toString());
}
else
{
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "No Response",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
btnCel.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener()
{
@Override
public void onClick(View v)
{
//Initialize soap request + add parameters
SoapObject request = new SoapObject(NAMESPACE, METHOD_NAME2);
//Use this to add parameters
request.addProperty("Celsius",txtCel.getText().toString());
//Declare the version of the SOAP request
SoapSerializationEnvelope envelope = new SoapSerializationEnvelope(SoapEnvelope.VER11);
envelope.setOutputSoapObject(request);
envelope.dotNet = true;
try {
HttpTransportSE androidHttpTransport = new HttpTransportSE(URL);
//this is the actual part that will call the webservice
androidHttpTransport.call(SOAP_ACTION2, envelope);
// Get the SoapResult from the envelope body.
SoapObject result = (SoapObject)envelope.bodyIn;
if(result != null)
{
//Get the first property and change the label text
txtFar.setText(result.getProperty(0).toString());
}
else
{
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "No Response",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
btnClear.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener()
{
@Override
public void onClick(View v)
{
txtCel.setText("");
txtFar.setText("");
}
});
}
}
Step 8:
Now, open your "WebServiceDemo -> android.manifest" file. Add the following line before the <application> tag:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
This will allow the application to use the internet.
Step 9:
Run your application in the Android Cell. You will get the following outcome:
Note: In the emulator, we need to fix a proxy, so try the application in an Android Cell.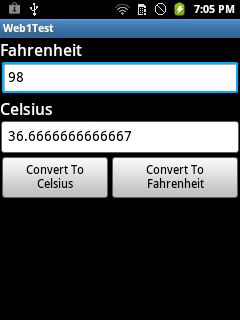
Summary
In this brief tutorial, we learned about Web Services, SOAP envelopes, WSDL files, HTTP transport, and how to use the in an Android application.