重载
函数重载的关键是函数的参数列表——也称为函数特征标。如果两个函数的参数数目和类型相同,同时参数的排列顺序也相同,则它们的特征标相同,而变量名是无关紧要的。
char * left (const char * str, unsigned n); char * left (const char * str);
何时使用函数重载?
仅当函数基本上执行相同的任务,但使用不同形式的数据时,才应采用函数重载。另外,是否采用默认参数来实现与函数重载相同的功能也是在采用函数重载的过程中应该考虑的。如果是使用不同类型的参数,则默认参数便不管用了,在这种情况下,应该使用函数重载。
引用
- 创建引用变量
-
int rats; int & rodents = rats; //必须在声明引用的时候初始化
rodents = rats;//错误的做法
int * const pr = &rats; //注意引用运算符和取地址运算符的区别
-
- 将引用变量用作函数参数
-
void swap(int& a, int& b) { int t; t = a; a = b; b = t; }
swap(num1, num2);//在传递参数的时候对引用进行初始化
-
注意:不要返回指向局部变量或临时对象的引用。函数执行完毕后,局部变量和临时变量对象消失,引用将指向不存在的数据。
- 引用的属性和特别之处
-
// 临时变量 double refcube(double &ra) { ra *= ra * ra; return ra; }
double z = refcube(x + 3); // 产生警告,如果需要对引用修改的话将不会产生任何效果
-
由于x+3.0不是double类型的变量,因此程序将创建一个临时变量,并将其初始化为 表达式x + 3.0的值。然后ra将成为该临时变量的引用。
-
-
// const关键字 double refcube(const double &ra) { ra *= ra * ra; return ra; } double z = refcube(x + 3); // 编译通过
-
为什么对于常量引用,这种行为是可行的,其他情况下却不行呢?
该函数并没有对引用变量的值进行更改,因此临时变量的产生并不会产生不利的影响,反而会使函数在处理参数种类方面更加通用。但是,如果是想要通过引用来改变原来变量的值,这时候函数将不会产生任何效果,因为,此时改变的只是临时变量的值。
- 将引用用于结构体
-
struct free_throws { std::string name; int made; int attempts; float percent; }; void set_pc(free_throws &ft); // 如果不希望改变引用的值的话,可以使用const void display(const free_throws &ft);
-
- 将引用用于类对象
-
string version1(const string & s1, const string & s2) { string temp; temp = s2 + s1 + s2; return temp; } // 使用引用的好处是会使函数更加高效
-
- 何时使用引用参数
- 通过传递引用而不是整个数据对象,可以提高程序的运行速度。
- 如果数据对象很小,如内置数据类型或小型结构,则按值传递
- 如果数据对象是数组,则使用指针,因为这是唯一的选择,并将指针声明为const指针。
- 如果数据对象是较大的数据结构或者是类对象,则使用const引用,以提高程序的效率。
- 注意
- 引用临时变量必须加const关键字(最小特权原则)
友元
共有类方法提供唯一的访问途径,但是有时候这种限制太严格,以至于不适合特定的编程问题。
为类重载二元运算符时(带两个参数的运算符)常常需要友元,重载二元运算符时,左侧的操作数是调用对象。当执行
Cmytime A, B;
A = B * 2.75;
将转换为下面的成员函数调用
A = B.operator*(2.75);
那么,当我们想要执行下面的语句时又该怎么办呢?
A = 2.75 * B;
因为2.75不是对象,所以编译器不能使用成员函数来调用该表达式。使用非成员函数
Cmytime operator*(double m, const Time & t);
可以使上面的表达式执行,因为非成员函数的所有值都是显示参数,上面的语句就转化成下面非成员函数的调用匹配。
A = operator*(2.75, B);
但是,现在又有了一个新的的问题就是,非成员函数不可以访问类的私有变量,所以我们引入了友元函数,使非成员函数可以访问类的私有变量。
- 创建友元
-
friend Cmytime operator*(double m, const & t);
-
- 重载<<运算符
-
// 声明 friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, Fraction f); // 函数实现 ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, Fraction f) { os << f.nume << "/" << f.deno; return os; }
-
- 重载>>运算符
-
// 声明 friend istream& operator>>(istream& is, Fraction& f); // 函数实现 istream& operator>>(istream& is, Fraction& f) { is >> f.nume >> f.deno; return is; }
-
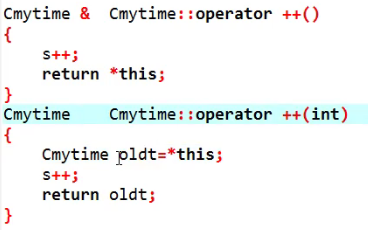
单目运算符的重载
单目运算符包括两种不同的类型:前置++和后置++。c++约定在自增运算符的参数列表中添加一个int形参就表示后置++,后置++返回的是自增前的数据,所以需要一个临时变量。
模板
如果我们需要一个类具有求绝对值的功能,那么可以这样来写:
double myabs(double x) { if (x < 0) return -x; else return x; } int myabs(int x) { if (x < 0) return -x; else return x; }
这种书写方式不进浪费时间,而且也很容易书写错误。函数模板的功能可以自动完成这一功能,可以节省时间,而且更加可靠。
template <typename mytype> mytype myabs(mytype x) { if (x < 0) return -x; else return x; }
练习:
reate a class called Fraction with 2 private fields Numerator, Denominator. And a public constructor that sets Numerator and Denominator to 1 by default.
class Fraction {
int numerator, denominator;
public:
....
};
1、overload + - * /
2、overload ==、!=、<、<=、>、>=
3、overload output/input operator << and >>
Sample input:
1 2
3 4
Sample output
a= 1/2, b = 3/4
1/2 + 3/4 = 5/4
1/2 - 3/4 = -1/4
1/2 * 3/4 = 3/8
1/2 / 3/4 = 2/3
a == b is 0
a != b is 1
a <= b is 1
a >= b is 0
a < b is 1
a > b is 0
Sample input:
2 4
3 4
Sample output:
a= 1/2, b = 3/4
1/2 + 3/4 = 5/4
1/2 - 3/4 = -1/4
1/2 * 3/4 = 3/8
1/2 / 3/4 = 2/3
a == b is 0
a != b is 1
a <= b is 1
a >= b is 0
a < b is 1
a > b is 0
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int _gcd(int x, int y) { if (y == 0) return x; else return _gcd(y, x % y); } int _abs(int x) { if (x < 0) return -x; else return x; } class Fraction { private: int nume; int deno; public: Fraction(int n = 1, int d = 1) { nume = n; deno = d; } Fraction operator+(Fraction f); Fraction operator-(Fraction f); Fraction operator*(Fraction f); Fraction operator/(Fraction f); int operator==(Fraction f); int operator!=(Fraction f); int operator<(Fraction f); int operator<=(Fraction f); int operator>(Fraction f); int operator>=(Fraction f); friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, Fraction f); friend istream& operator>>(istream& is, Fraction& f); }; Fraction Fraction::operator+(Fraction f) { Fraction temp; temp.deno = f.deno * deno; temp.nume = f.nume * deno + f.deno * nume; int gcd = _gcd(temp.deno, temp.nume); temp.deno /= gcd; temp.nume /= gcd; return temp; } Fraction Fraction::operator-(Fraction f) { Fraction temp; temp.deno = f.deno * deno; temp.nume = f.deno * nume - f.nume * deno; int gcd = _gcd(temp.deno, temp.nume); temp.deno /= gcd; temp.nume /= gcd; if (temp.deno < 0 && temp.nume < 0) { temp.deno = _abs(temp.deno); temp.nume = _abs(temp.nume); } else if (temp.deno < 0 && temp.nume > 0) { temp.deno = _abs(temp.deno); temp.nume = -temp.nume; } return temp; } Fraction Fraction::operator*(Fraction f) { Fraction temp; temp.deno = f.deno * deno; temp.nume = nume * f.nume; int gcd = _gcd(temp.deno, temp.nume); temp.deno /= gcd; temp.nume /= gcd; return temp; } Fraction Fraction::operator/(Fraction f) { Fraction temp; temp.deno = f.nume * deno; temp.nume = f.deno * nume; int gcd = _gcd(temp.deno, temp.nume); temp.deno /= gcd; temp.nume /= gcd; return temp; } int Fraction::operator==(Fraction f) { int gcd = _gcd(deno, nume); deno /= gcd; nume /= gcd; gcd = _gcd(f.deno, f.nume); f.deno /= gcd; f.nume /= gcd; if (deno == f.deno && nume == f.nume) return 1; else return 0; } int Fraction::operator!=(Fraction f) { int gcd = _gcd(deno, nume); deno /= gcd; nume /= gcd; gcd = _gcd(f.deno, f.nume); f.deno /= gcd; f.nume /= gcd; if (deno == f.deno && nume == f.nume) return 0; else return 1; } int Fraction::operator<(Fraction f) { if (nume * f.deno < deno * f.nume) return 1; else return 0; } int Fraction::operator<=(Fraction f) { if (nume * f.deno <= deno * f.nume) return 1; else return 0; } int Fraction::operator>(Fraction f) { if (nume * f.deno > deno * f.nume) return 1; else return 0; } int Fraction::operator>=(Fraction f) { if (nume * f.deno >= deno * f.nume) return 1; else return 0; } ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, Fraction f) { os << f.nume << "/" << f.deno; return os; } istream& operator>>(istream& is, Fraction& f) { is >> f.nume >> f.deno; return is; } int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { Fraction a(1), b(1, 3); cin >> a >> b; cout << "a= " << a << ", b = " << b << endl; cout << a << " + " << b << " = " << a + b << endl; cout << a << " - " << b << " = " << a - b << endl; cout << a << " * " << b << " = " << a * b << endl; cout << a << " / " << b << " = " << a / b << endl; cout << "a == b is " << (a == b) << endl; cout << "a != b is " << (a != b) << endl; cout << "a <= b is " << (a <= b) << endl; cout << "a >= b is " << (a >= b) << endl; cout << "a < b is " << (a < b) << endl; cout << "a > b is " << (a > b) << endl; return 1; }