There is a kind of balanced binary search tree named red-black tree in the data structure. It has the following 5 properties:
- (1) Every node is either red or black.
- (2) The root is black.
- (3) Every leaf (NULL) is black.
- (4) If a node is red, then both its children are black.
- (5) For each node, all simple paths from the node to descendant leaves contain the same number of black nodes.
For example, the tree in Figure 1 is a red-black tree, while the ones in Figure 2 and 3 are not.
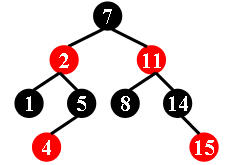 | 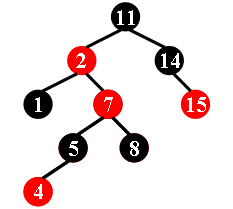 | 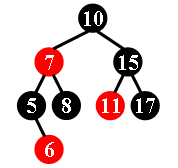 |
|---|---|---|
| Figure 1 | Figure 2 | Figure 3 |
For each given binary search tree, you are supposed to tell if it is a legal red-black tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains several test cases. The first line gives a positive integer K (≤30) which is the total number of cases. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤30), the total number of nodes in the binary tree. The second line gives the preorder traversal sequence of the tree. While all the keys in a tree are positive integers, we use negative signs to represent red nodes. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space. The sample input cases correspond to the trees shown in Figure 1, 2 and 3.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in a line "Yes" if the given tree is a red-black tree, or "No" if not.
Sample Input:
3
9
7 -2 1 5 -4 -11 8 14 -15
9
11 -2 1 -7 5 -4 8 14 -15
8
10 -7 5 -6 8 15 -11 17
Sample Output:
Yes
No
No题意:
给出一棵二叉查找树,判断这棵树是不是红黑树。
思路:
建树, 根据红黑树的定义来判断是不是二叉树。
Code:
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 3 using namespace std; 4 5 typedef struct Node* node; 6 7 struct Node { 8 int val; 9 int color; 10 node left; 11 node right; 12 Node(int v, int c) { 13 val = v; 14 color = c; 15 left = NULL; 16 right = NULL; 17 } 18 }; 19 20 node buildTree(vector<node>& v) { 21 node root = v[0]; 22 for (int i = 1; i < v.size(); ++i) { 23 node temp = root; 24 while (temp != NULL) { 25 if (v[i]->val < temp->val) { 26 if (temp->left != NULL) 27 temp = temp->left; 28 else { 29 temp->left = v[i]; 30 break; 31 } 32 } else { 33 if (temp->right != NULL) 34 temp = temp->right; 35 else { 36 temp->right = v[i]; 37 break; 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 } 42 return root; 43 } 44 45 bool travelTree(node root) { 46 if (root == NULL) return true; 47 if (root->color == -1) { 48 if (root->left && root->left->color == -1) return false; 49 if (root->right && root->right->color == -1) return false; 50 } 51 bool left = travelTree(root->left); 52 bool right = travelTree(root->right); 53 return left && right; 54 } 55 56 vector<int> nums; 57 58 void judgeFunction(node root, int level) { 59 if (root == NULL) { 60 nums.push_back(level); 61 return; 62 } 63 if (root->color == 1) level = level + 1; 64 judgeFunction(root->left, level); 65 judgeFunction(root->right, level); 66 } 67 68 bool isRedBlackTree(node root) { 69 if (root->color == -1) return false; 70 if (!travelTree(root)) return false; 71 nums.clear(); 72 judgeFunction(root, 0); 73 for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); ++i) { 74 // cout << nums[i] << " "; 75 if (nums[i - 1] != nums[i]) return false; 76 } 77 78 return true; 79 } 80 81 int main() { 82 int n, k, t; 83 cin >> n; 84 for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { 85 cin >> k; 86 node temp; 87 vector<node> v; 88 for (int j = 0; j < k; ++j) { 89 cin >> t; 90 if (t > 0) 91 temp = new Node(t, 1); 92 else 93 temp = new Node(-t, -1); 94 v.push_back(temp); 95 } 96 node root = buildTree(v); 97 if (isRedBlackTree(root)) 98 cout << "Yes" << endl; 99 else 100 cout << "No" << endl; 101 } 102 103 return 0; 104 }
判断左右子树中黑色的叶子结点的个数的时候可以采用递归的方法来判断,代码看起来更加的简单。
1 bool judge2(node *root) { 2 if (root == NULL) return true; 3 int l = getNum(root->left); 4 int r = getNum(root->right); 5 if(l != r) return false; 6 return judge2(root->left) && judge2(root->right); 7 }