1、synchronized
Synchronized修饰一个方法很简单,就是在方法的前面加synchronized,synchronized修饰方法和修饰一个代码块类似,只是作用范围不一样,修饰代码块是大括号括起来的范围,而修饰方法范围是整个函数。
synchronized关键字不能继承。
虽然可以使用synchronized来定义方法,但synchronized并不属于方法定义的一部分,因此,synchronized关键字不能被继承。如果在父类中的某个方法使用了synchronized关键字,而在子类中覆盖了这个方法,在子类中的这个方法默认情况下并不是同步的,而必须显式地在子类的这个方法中加上synchronized关键字才可以。当然,还可以在子类方法中调用父类中相应的方法,这样虽然子类中的方法不是同步的,但子类调用了父类的同步方法,因此,子类的方法也就相当于同步了。这两种方式的例子代码如下:
在子类方法中加上synchronized关键字
public synchronized void method() { // todo }
public void method() { synchronized(this) { // todo } }
class Parent { public synchronized void method() { } } class Child extends Parent { public synchronized void method() { } }
总结:
A. 无论synchronized关键字加在方法上还是对象上,如果它作用的对象是非静态的,则它取得的锁是对象;如果synchronized作用的对象是一个静态方法或一个类,则它取得的锁是对类,该类所有的对象同一把锁。
B. 每个对象只有一个锁(lock)与之相关联,谁拿到这个锁谁就可以运行它所控制的那段代码。
C. 实现同步是要很大的系统开销作为代价的,甚至可能造成死锁,所以尽量避免无谓的同步控制。
2、interrupt()方法:
interrupt()只是改变中断状态而已. interrupt()不会中断一个正在运行的线程。这一方法实际上完成的是,给受阻塞的线程抛出一个中断信号,这样受阻线程就得以退出阻塞的状态。
如果线程被Object.wait, Thread.join和Thread.sleep三种方法之一阻塞,它将接收到一个中断异常(InterruptedException),从而提早地终结被阻塞状态。
public class InterruptWait extends Thread { public static Object lock = new Object(); @Override public void run() { System.out.println("start"); synchronized (lock) { try { lock.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()); Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); // set interrupt flag again System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()); e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { Thread thread = new InterruptWait(); thread.start(); try { sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } thread.interrupt(); } }
在这种方式下,如果使用 wait 方法处于等待中的线程,被另一个线程使用中断唤醒,于是抛出 InterruptedException,同时,
中断标志清除,这时候我们通常会在捕获该异常的地方重新设置中断,以便后续的逻辑通过检查中断状态来了解该线程是如何结束的 。
3、wait 和 notify的方法使用
在 Java 中可以用 wait、notify 和 notifyAll 来实现线程间的通信。线程在运行的时候,如果发现某些条件没有被满足,可以调用wait方法暂停自己的执行,并且放弃已经获得的锁,然后进入等待状态。当该线程被其他线程唤醒并获得锁后,可以沿着之前暂停的地方继续向后执行,而不是再次从同步代码块开始的地方开始执行。但是需要注意的一点是,对线程等待的条件的判断要使用while而不是if来进行判断。这样在线程被唤醒后,会再次判断条件是否正真满足。
想象一下一个生产者,多个消费者的场景。一个消费者Consumer1了最后一个元素,并且唤醒了其他线程,如果被唤醒的正好是Consumer2,那么此时是没有元素可以消费的。如果用的是if判断,那么被唤醒后就不会再次进行条件的判断,而是直接向下执行导致运行错误。这问题在后边进行代码讨论!
notify方法会唤醒等待一个对象锁的线程,但是具体唤醒哪个是不确定的。
3、1先看一个因为多线程导致 数据数据读取有错误的例子:
写着:
public class WritePerson implements Runnable{ private Person person = null; WritePerson(Person p) { this.person = p; } private boolean flag = true; @Override public void run() { while(true) { if( flag == true) { person.setName("Jack"); person.setSex('男'); flag = false; }else { person.setName("Lily"); person.setSex('女'); flag = true; } } } }
读者:
public class ReadPerson implements Runnable{ private Person person = null; ReadPerson(Person p) { this.person = p; } @Override public void run() { while(true) { System.out.println("name---->: " + person.getName() + " sex----->: " + person.getSex()); } } }
测试:
public static void main(String[] args) { Person person = new Person(); WritePerson wp = new WritePerson(person); ReadPerson rp = new ReadPerson(person); Thread t1 = new Thread(wp); Thread t2 = new Thread(rp); t1.start(); t2.start(); }
测试结果:
name---->: Lily sex----->: 女 name---->: Jack sex----->: 男 name---->: Lily sex----->: 男 name---->: Lily sex----->: 女 name---->: Jack sex----->: 女 name---->: Lily sex----->: 女 name---->: Lily sex----->: 男 name---->: Jack sex----->: 男 name---->: Jack sex----->: 男 name---->: Jack sex----->: 女 name---->: Lily sex----->: 女 name---->: Jack sex----->: 女 name---->: Lily sex----->: 女 name---->: Lily sex----->: 男 name---->: Lily sex----->: 女 name---->: Jack sex----->: 男 name---->: Lily sex----->: 男 name---->: Lily sex----->: 男 name---->: Lily sex----->: 男 name---->: Lily sex----->: 男 name---->: Jack sex----->: 女
可以看到数据中存在读取错误问题;导致问题的根因是读者和写着没有实现同步;
3、2 下面进行使用wait 和 notify 实现同步:
读者:
public class ReadPerson implements Runnable{ private Person person = null; ReadPerson(Person p) { this.person = p; } @Override public void run() { synchronized (person) { while(person.getFlag() == true) { try { person.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println("name---->: " + person.getName() + " sex----->: " + person.getSex()); person.setFlag(true); person.notifyAll(); } } }
写者;
public class WritePerson implements Runnable{ private Person person = null; WritePerson(Person p) { this.person = p; } private boolean flag = true; private boolean flag2 = true; @Override public void run() { synchronized (person) { while(person.getFlag() == false) { try { person.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if( flag == true) { person.setName("Jack"); person.setSex('男'); flag = false; }else { person.setName("Lily"); person.setSex('女'); flag = true; } person.notifyAll(); person.setFlag(false); } } }
执行;
public static void main(String[] args) { Person person = new Person(); person.setFlag(true); WritePerson wp = new WritePerson(person); ReadPerson rp = new ReadPerson(person); Thread t1 = new Thread(wp); Thread t2 = new Thread(rp); Thread t3 = new Thread(wp); Thread t4 = new Thread(rp); Thread t5 = new Thread(wp); Thread t6 = new Thread(rp); Thread t7 = new Thread(wp); Thread t8 = new Thread(rp); Thread t9 = new Thread(wp); Thread t10 = new Thread(rp); t1.start(); t3.start(); t5.start(); t2.start(); t4.start(); t6.start(); t7.start(); t8.start(); t9.start(); t10.start(); }
结果:
name---->: Jack sex----->: 男 name---->: Lily sex----->: 女 name---->: Jack sex----->: 男 name---->: Lily sex----->: 女 name---->: Jack sex----->: 男
3、3 将同步Synchronized替换为显示的Lock操作;将Object中的wait,notify,notifyAll替换为Condition对象,该对象可以通过Lock锁进行获取。
读者:
public class ReadPerson implements Runnable{ private Lock lock = null; Person person = null; private boolean flag = true; private Condition condition_pro = null; //condition绑定Lock private Condition condition_con = null; //1个lock可以绑定多个condition ReadPerson(Lock lock, Person person, Condition condition_pro, Condition condition_con) { this.lock = lock; this.person = person; this.condition_pro = condition_pro; this.condition_con = condition_con; } @Override public void run() { lock.lock(); while(person.getFlag() == true) { try { condition_con.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println("name---->: " + person.getName() + " sex----->: " + person.getSex()); person.setFlag(true); condition_pro.signalAll(); lock.unlock(); } }
写者:
public class WritePerson implements Runnable{ private Lock lock = null; Person person = null; private boolean flag = true; private Condition condition_pro = null; //condition绑定Lock private Condition condition_con = null; //1个lock可以绑定多个condition WritePerson(Lock lock, Person person, Condition condition_pro, Condition condition_con) { this.lock = lock; this.person = person; this.condition_pro = condition_pro; this.condition_con = condition_con; } @Override public void run() { lock.lock(); while(person.getFlag() == false) { try { condition_pro.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if( flag == true) { person.setName("Jack"); person.setSex('男'); flag = false; }else { person.setName("Lily"); person.setSex('女'); flag = true; } condition_con.signalAll(); person.setFlag(false); lock.unlock(); }
测试:
public static void main(String[] args) { Person person = new Person(true); Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); Condition condition_pro = lock.newCondition(); //condition绑定Lock Condition condition_con = lock.newCondition(); //1个lock可以绑定多个condition System.out.println(condition_pro); System.out.println(condition_con); WritePerson wp = new WritePerson(lock, person, condition_pro, condition_con); ReadPerson rp = new ReadPerson(lock, person, condition_pro, condition_con); Thread t1 = new Thread(wp); Thread t2 = new Thread(rp); Thread t3 = new Thread(wp); Thread t4 = new Thread(rp); Thread t5 = new Thread(wp); Thread t6 = new Thread(rp); Thread t7 = new Thread(wp); Thread t8 = new Thread(rp); Thread t9 = new Thread(wp); Thread t10 = new Thread(rp); t1.start(); t3.start(); t5.start(); t2.start(); t4.start(); t6.start(); t7.start(); t8.start(); t9.start(); t10.start(); }
输出:
name---->: Jack sex----->: 男 name---->: Lily sex----->: 女 name---->: Jack sex----->: 男 name---->: Lily sex----->: 女 name---->: Jack sex----->: 男
3、4 实现多存多出取得多线程效果
从上面的测试结果可以看出读者和写者的关系是通过 共享变量flag进行控制,这使得读者和写者只能实现写一次 读一次的状态,现在我们对其进行改装;
实现可以多次写入多次读出的效果;同时对前边说的 必须使用While 而不能 使用if 进行说明:
为什么多线程中 消费者和生产者中的条件判断要使用 while 而不能使用 if ;
个人的理解如下:
当消费者在wait的状态时,会释放掉锁,但是此时生产者没有获得锁,而是由第二个消费者获得了锁,然后继续进入到了wait的地方,然后继续进行释放锁,
此时生产者拿到锁,然后进行生产操作,此时生产了后,使用notifyAll 唤醒其他消费者,如果此时第一个消费者拿到了执行权限,在wait处继续往下执行,然后将
生产者生产的产品全部消费了,然后第二个消费者如果再获得了执行权,会使用while进行再次判断,此时不满足向下执行的条件,通过while判断,他会继续悲惨
的进入到wait状态,等待合适条件; 可以评选为年度最悲惨的线程,刚复活又被打入冷宫!!!
消费者:
public class Consumer implements Runnable{ Queue<Integer> queue = null; int maxsize; String name = null; public Consumer(Queue queue, int maxsize, String name) { this.queue = queue; this.maxsize = maxsize; this.name = name; } @Override public void run() { synchronized (queue) { try{ Thread.sleep(500); } catch (Exception e) {} System.out.println(this.getName() + "获得队列的锁"); while(queue.isEmpty()) { try { System.out.println("队列为空,消费者" + this.getName() + "等待"); queue.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } int num = queue.poll(); System.out.println(this.getName() + "开始消费一个元素:"+num); queue.notifyAll(); System.out.println(this.getName() + "完成一次消费过程!"); } } public Queue<Integer> getQueue() { return queue; } public void setQueue(Queue<Integer> queue) { this.queue = queue; } public int getMaxsize() { return maxsize; } public void setMaxsize(int maxsize) { this.maxsize = maxsize; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
生产者:
public class Producer implements Runnable{ Queue<Integer> queue = null; int maxsize; String name = null; Producer(Queue<Integer> queue, int maxsize, String name) { this.queue = queue; this.maxsize = maxsize; this.name = name; } @Override public void run() { synchronized(queue) { try{ Thread.sleep(500); } catch (Exception e) {} System.out.println(this.getName() + "获得队列的锁"); while(maxsize == queue.size()) { try { System.out.println("队列已满,生产者" + this.getName() + "等待"); queue.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } int num = (int)(Math.random()*10); queue.offer(num); System.out.println(this.getName() + "生产一个元素:" + num); queue.notifyAll(); System.out.println(this.getName() + "完成一次生产过程!"); } } public Queue<Integer> getQueue() { return queue; } public void setQueue(Queue<Integer> queue) { this.queue = queue; } public int getMaxsize() { return maxsize; } public void setMaxsize(int maxsize) { this.maxsize = maxsize; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
测试:
public static void main(String[] args) { Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>(); int maxsize = 20; Producer producer1 = new Producer(queue, maxsize, "Producer1"); Producer producer2 = new Producer(queue, maxsize, "Producer2"); Consumer consumer1 = new Consumer(queue, maxsize,"Consumer1"); Consumer consumer2 = new Consumer(queue, maxsize,"Consumer2"); Consumer consumer3 = new Consumer(queue, maxsize,"Consumer3"); Thread t1 = new Thread(producer1); Thread t11 = new Thread(producer2); Thread t2 = new Thread(consumer1); Thread t3 = new Thread(consumer2); Thread t4 = new Thread(consumer3); t1.start(); t11.start(); t2.start(); t3.start(); t4.start(); }
测试结果:
Producer1获得队列的锁 Producer1生产一个元素:8 Producer1完成一次生产过程! Consumer3获得队列的锁 Consumer3开始消费一个元素:8 Consumer3完成一次消费过程! Consumer2获得队列的锁 队列为空,消费者Consumer2等待 Consumer1获得队列的锁 队列为空,消费者Consumer1等待 Producer2获得队列的锁 Producer2生产一个元素:7 Producer2完成一次生产过程! Consumer1开始消费一个元素:7 Consumer1完成一次消费过程! 队列为空,消费者Consumer2等待
此时consumer2 成功成为年度最佳吃不饱线程!!!
4、yield()and join()方法;
yield()方法
理论上,yield意味着放手,放弃,投降。一个调用yield()方法的线程告诉虚拟机它乐意让其他线程占用自己的位置。这表明该线程没有在做一些紧急的事情。注意,这仅是一个暗示,并不能保证不会产生任何影响。
- Yield是一个静态的原生(native)方法
- Yield告诉当前正在执行的线程把运行机会交给线程池中拥有相同优先级的线程。
- Yield不能保证使得当前正在运行的线程迅速转换到可运行的状态
- 它仅能使一个线程从运行状态转到可运行状态,而不是等待或阻塞状态
调用yield()方法时,两个线程依次打印,然后将执行机会交给对方,一直这样进行下去。注意不能保证每次都依次进行;
package test.core.threads; public class YieldExample { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread producer = new Producer(); Thread consumer = new Consumer(); producer.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY); //Min Priority consumer.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); //Max Priority producer.start(); consumer.start(); } } class Producer extends Thread { public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { System.out.println("I am Producer : Produced Item " + i); Thread.yield(); } } } class Consumer extends Thread { public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { System.out.println("I am Consumer : Consumed Item " + i); Thread.yield(); } } }
上述程序在没有调用yield()方法情况下的输出: I am Consumer : Consumed Item 0 I am Consumer : Consumed Item 1 I am Consumer : Consumed Item 2 I am Consumer : Consumed Item 3 I am Consumer : Consumed Item 4 I am Producer : Produced Item 0 I am Producer : Produced Item 1 I am Producer : Produced Item 2 I am Producer : Produced Item 3 I am Producer : Produced Item 4
上述程序在调用yield()方法情况下的输出: I am Producer : Produced Item 0 I am Consumer : Consumed Item 0 I am Producer : Produced Item 1 I am Consumer : Consumed Item 1 I am Producer : Produced Item 2 I am Consumer : Consumed Item 2 I am Producer : Produced Item 3 I am Consumer : Consumed Item 3 I am Producer : Produced Item 4 I am Consumer : Consumed Item 4
join()方法
线程实例的方法join()方法可以使得一个线程在另一个线程结束后再执行。如果join()方法在一个线程实例上调用,当前运行着的线程将阻塞直到这个线程实例完成了执行。
在join()方法内设定超时,使得join()方法的影响在特定超时后无效。当超时时,主方法和任务线程申请运行的时候是平等的。然而,当涉及sleep时,join()方法依靠操作系统计时,所以你不应该假定join()方法将会等待你指定的时间。
像sleep,join通过抛出InterruptedException对中断做出回应。
public class JoinExample { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread t = new Thread(new Runnable() { public void run() { System.out.println("First task started"); System.out.println("Sleeping for 2 seconds"); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("First task completed"); } }); Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { public void run() { System.out.println("Second task completed"); } }); t.start(); // Line 15 t.join(); // Line 16 t1.start(); } }
执行结果:
First task started Sleeping for 2 seconds First task completed Second task completed
5、setDaemon(boolean on)守护线程
在Java中有两类线程:User Thread(用户线程)、Daemon Thread(守护线程)
用个比较通俗的比如,任何一个守护线程都是整个JVM中所有非守护线程的保姆:
只要当前JVM实例中尚存在任何一个非守护线程没有结束,守护线程就全部工作;只有当最后一个非守护线程结束时,守护线程随着JVM一同结束工作。
Daemon的作用是为其他线程的运行提供便利服务,守护线程最典型的应用就是 GC (垃圾回收器),它就是一个很称职的守护者。
User和Daemon两者几乎没有区别,唯一的不同之处就在于虚拟机的离开:如果 User Thread已经全部退出运行了,只剩下Daemon Thread存在了,虚拟机也就退出了。 因为没有了被守护者,Daemon也就没有工作可做了,也就没有继续运行程序的必要了。
值得一提的是,守护线程并非只有虚拟机内部提供,用户在编写程序时也可以自己设置守护线程。下面的方法就是用来设置守护线程的。
这里有几点需要注意:
(1) thread.setDaemon(true)必须在thread.start()之前设置,否则会跑出一个IllegalThreadStateException异常。你不能把正在运行的常规线程设置为守护线程。
(2) 在Daemon线程中产生的新线程也是Daemon的。
(3) 不要认为所有的应用都可以分配给Daemon来进行服务,比如读写操作或者计算逻辑。
因为你不可能知道在所有的User完成之前,Daemon是否已经完成了预期的服务任务。一旦User退出了,可能大量数据还没有来得及读入或写出,计算任务也可能多次运行结果不一样。这对程序是毁灭性的。造成这个结果理由已经说过了:一旦所有User Thread离开了,虚拟机也就退出运行了。
实际应用例子:
在使用长连接的comet服务端推送技术中,消息推送线程设置为守护线程,服务于ChatServlet的servlet用户线程,在servlet的init启动消息线程,servlet一旦初始化后,一直存在服务器,servlet摧毁后,消息线程自动退出
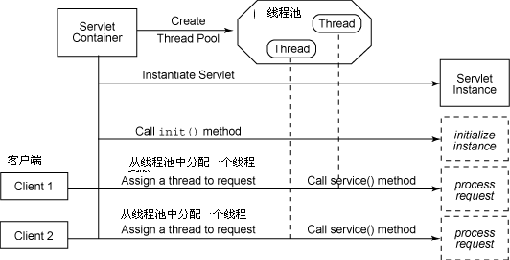
容器收到一个Servlet请求,调度线程从线程池中选出一个工作者线程,将请求传递给该工作者线程,然后由该线程来执行Servlet的 service方法。当这个线程正在执行的时候,容器收到另外一个请求,调度线程同样从线程池中选出另一个工作者线程来服务新的请求,容器并不关心这个请求是否访问的是同一个Servlet.当容器同时收到对同一个Servlet的多个请求的时候,那么这个Servlet的service()方法将在多线程中并发执行。
Servlet容器默认采用单实例多线程的方式来处理请求,这样减少产生Servlet实例的开销,提升了对请求的响应时间,对于Tomcat可以在server.xml中通过<Connector>元素设置线程池中线程的数目。
如图: