由于通过ResultSet的光标实现数据分页存在占用大量资源等性能方便的缺陷,所以,在实际开发中,通过采用数据库的分页机制来实现分页查询功能更为上上之策。
下面我就通过MySQL数据库提供的分页机制来作为案例。
创建Product类,用于封装商品信息。该类是商品信息的JavaBean。
package bean;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class Product {
public static final int PAGE_SIZE = 2;//每页记录数
private int p_id;//编号
private String p_name;//名称
private BigDecimal p_price;//价格
public int getP_id() {
return p_id;
}
public void setP_id(int p_id) {
this.p_id = p_id;
}
public String getP_name() {
return p_name;
}
public void setP_name(String p_name) {
this.p_name = p_name;
}
public BigDecimal getP_price() {
return p_price;
}
public void setP_price(BigDecimal p_price) {
this.p_price = p_price;
}
}
在Product类中,主要封装了商品对象的基本信息。除此之外,我还定义了分页的每页记录数。
创建ProductDao类,主要用于封装商品对象的数据库相关操作。该类是商品信息的Dao层。
package dao;
import bean.Product;
import util.DBUtil;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ProductDao {
/**
* 分页查询所有商品信息
*
* @param page 页数
* @return List<Product>
*/
public List<Product> findAllProduct(int page) {
List<Product> productList = new ArrayList<>();//实例化List对象
Connection conn = null;//数据库连接
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;//PreparedStatement
ResultSet rs = null;//结果集
//limit arg0,arg1 指定查询起始位置,指定查询数据所返回的记录数
String sql = "select p_id,p_name,p_price from product order by p_id limit ?,?";//分页查询的SQL语句
try {
conn = DBUtil.getCon();//获取数据库连接
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);//获取PreparedStatement
pstmt.setInt(1, (page - 1) * Product.PAGE_SIZE);//对SQL语句第一个参数赋值
pstmt.setInt(2, Product.PAGE_SIZE);//对SQL语句第二个参数赋值
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();//执行查询操作
while (rs.next()) {
Product product = new Product();
product.setP_id(rs.getInt("p_id"));//对p_id属性赋值
product.setP_name(rs.getString("p_name"));//对p_name属性赋值
product.setP_price(rs.getBigDecimal("p_price"));//对p_price属性赋值
productList.add(product);//将Product对象添加到List集合中
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(rs, pstmt, conn);//关闭进行回收资源
}
return productList;
}
/**
* 查询总记录数
*
* @return count总记录数
*/
public int findAllProductCount() {
int count = 0;//总记录数
Connection conn = null;//数据库连接
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;//PreparedStatement
ResultSet rs = null;//结果集
String sql = "select count(*) from product";//查询总记录数的SQL语句
try {
conn = DBUtil.getCon();//获取数据库连接
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);//获取PreparedStatement
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();//执行查询操作
if (rs.next()) {//光标向后移动,并判断是否有效
count = rs.getInt(1);//对总记录数赋值
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(rs, pstmt, conn);//关闭回收资源
}
return count;//返回总记录数
}
}
findAllProduct(int page) ;方法,用来查询指定页数的商品。page参数,用来指定页数。
findAllProductCount();方法,用来查询总记录数。这样一次查询,即可知道总记录数。
缺点在于,一旦有新的记录产生,在下一次查询后,有一些记录不会被查询到,因此待优化。
创建FindAllProduct类,该类是分页查询商品信息的Servlet对象。在doGet()方法中,对分页请求进行处理。
package servlet;
import bean.Product;
import dao.ProductDao;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
@WebServlet("/FindAllProduct")
public class FindAllProduct extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
int currPage = 1;//当前页码
if (request.getParameter("page") != null) {//判断传递页面是否有效
currPage = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("page"));//对当前页码赋值
}
ProductDao dao = new ProductDao();//实例化ProductDao
List<Product> productList = dao.findAllProduct(currPage);//查询所有商品的信息
request.setAttribute("productList", productList);//将list放置到request中
int pages;//总页数
int count = dao.findAllProductCount();//查询总记录数
if (count % Product.PAGE_SIZE == 0) {
pages = count / Product.PAGE_SIZE;//对总页数赋值
} else {
pages = count / Product.PAGE_SIZE + 1;//对总页数赋值
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();//实例化StringBuffer
for (int i = 1; i <= pages; i++) {
if (i == currPage) {
sb.append("[").append(i).append("]");//构建分页条
} else {
sb.append("<a href='FindAllProduct?page=").append(i).append("'>").append(i).append("</a>");//构建分页条
}
}
sb.append(" ");//构建分页条
request.setAttribute("bar", sb.toString());//将分页条的字符串放置到request中
request.getRequestDispatcher("product.jsp").forward(request, response);//将请求转发到product.jsp页面中
}
}
FindAllProduct类主要做两件事,获取分页查询结果集和构造分页条对象。
分页查询结果集的实现,通过调用ProductDao类的findAllProduct(page)方法。
构造分页条对象是通过拼接html字符串进行构造,然后使用Servlet中的HttpServletRequest对象,将请求转发至product.jsp页面做出展示。
创建product.jsp页面,该页面通过EL表达式和JavaAPI获取查询的结果集与分页条来分页显示商品信息数据。
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: wen
Date: 2019/1/20
Time: 15:43
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>商品展示</title>
</head>
<body>
<table align="center" width="450" border="1">
<tr>
<td align="center" colspan="3">
<h2>商品信息展示</h2>
</td>
</tr>
<tr align="center">
<td>ID</td>
<td>商品名称</td>
<td>价格</td>
</tr>
<c:forEach items="${requestScope.productList}" var="item">
<tr>
<td>${item.p_id}</td>
<td>${item.p_name}</td>
<td>${item.p_price}</td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
<tr>
<td align="center" colspan="5">
<%=request.getAttribute("bar")%>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
最后附上我封装的JDBC连接数据库的工具类DBUtil
package util;
/**
* 连接数据库
*/
import java.sql.CallableStatement;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class DBUtil {
/**
* 获取连接
*
* @return Connection
* @throws Exception 异常
*/
public static Connection getCon() throws Exception {
//数据库驱动名字
String jdbcName = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
Class.forName(jdbcName);
//数据库协议地址
String dbUrl = "jdbc:mysql://129.204.104.108:3306/guowenrui?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8";
//数据库用户名
String dbUser = "guowenrui";
//数据库密码
String dbPassword = "gwr123";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(dbUrl, dbUser, dbPassword);
return conn;
}
/**
* 关闭连接
*
* @param stmt Statement
* @param conn Connection
* @throws Exception 异常
*/
public static void close(Statement stmt, Connection conn) throws Exception {
if (stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
}
}
/**
* 关闭连接
*
* @param cstmt CallableStatement
* @param conn Connection
* @throws Exception 异常
*/
public static void close(CallableStatement cstmt, Connection conn) throws Exception {
if (cstmt != null) {
cstmt.close();
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
}
}
/**
* 关闭连接
*
* @param pstmt PreparedStatement
* @param conn Connection
* @throws SQLException SQL异常
*/
public static void close(PreparedStatement pstmt, Connection conn) {
if (pstmt != null) {
try {
pstmt.close();
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 重载关闭方法
*
* @param pstmt PreparedStatement
* @param conn Connection
* @throws Exception 异常
*/
public static void close(ResultSet rs, PreparedStatement pstmt, Connection conn) {
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
if (pstmt != null) {
pstmt.close();
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
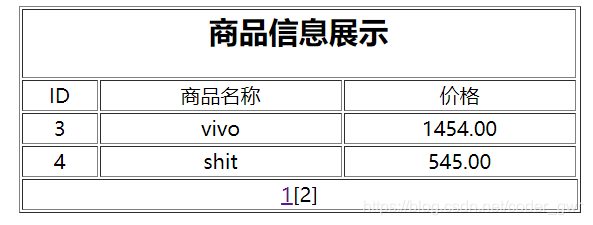
展示效果图如下: