1.首先需要先安装好apache服务器,此处不做叙述。
2.首先,判断CentOS7上是否已经安装了SSL证书服务模块:mod_ssl与openssl;
rpm -qa mod_ssl
rpm -qa openssl
键入上式,没有反应就是没有安装SSL证书服务模块 openssl。一般新装的CentOS7默认有安装。
安装mod_ssl 与openssl:
yum install mod_ssl openssl
安装后,CentOS7中会自动生成 /etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf 文件,ssl.conf文件就是SSL模块的配置文件。如果系统中没有找到ss.conf文件;
执行:yum remove mod_ssl; yum install mod_ssl即可重新生成一个;
3.创建mkdir /var/www/ssl 文件夹
将从云服务商中下载的证书上传到/var/www/ssl/下,从云服务商中下载的证书为: www.域名.com.zip 的zip文件。解压,有:
Apache/
IIS/
Nginx/
Tomcat/
共四个文件夹,分别用于存放适合对应的类型的服务系统的格式的SSL证书文件。
另外还有一个:www.域名.com.csr 的csr文件。
应为是配置Apache的httpd服务器系统,所以我们将只需要将Apache文件夹下面的三个ssl证书文件复制到在CentOS上创建的 /var/www/ssl 文件夹即可。
这三个ssl证书文件分别是:
1_root_bundle.crt
2_www.ydook.com.crt
3_www.ydook.com.key
4.通过OpenSSL生成自签名证书
openssl genrsa -des3 -out weapp.key 2048
openssl req -new -key weapp.key -out weapp.csr
openssl req -new -x509 -days 3650 -key weapp.key -out weapp.crt
如何执行过程中出现如下错误:
openssl: error while loading shared libraries: libssl.so.1.1: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
这是由于openssl库的位置不正确造成的。
解决办法,在root中
ln -s /usr/local/lib64/libssl.so.1.1 /usr/lib64/libssl.so.1.1
ln -s /usr/local/lib64/libcrypto.so.1.1 /usr/lib64/libcrypto.so.1.1
生成的证书为:weapp.crt ;weapp.key ;weapp.csr
对证书进行重命名:
mv weapp.crt _www.ydook.com.crt;
mv weapp.key _www.ydook.com.key;
5.修改/etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf文件
修改1:
SSLCertificateFile /etc/pki/tls/certs/localhost.crt 修改为:
SSLCertificateFile /var/www/ssl/2_www.ydook.com.crt
修改2:
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/pki/tls/private/localhost.key 修改为:
SSLCertificateKeyFile /var/www/ssl/3_www.ydook.com.key
修改3:
#SSLCACertificateFile /etc/pki/tls/certs/ca-bundle.crt 去掉#号,修改为:
SSLCACertificateFile /var/www/ssl/1_root_bundle.crt
修改4:查看设置是否为:SSLEngine on ,如果不是就改为 SSLEngine on 。
修改5:
修改为:
<VirtualHost *:443>
修改6:
#DocumentRoot “/var/www/html” 去掉#号注释,修改为:
DocumentRoot “/var/www/ydook”
修改7:
#ServerName www.example.com:443 去掉#号注释,修改为:
ServerName www.ydook.com:443
修改8:
ErrorLog logs/ssl_error_log 修改为:
ErrorLog /var/www/ydook/logs/error.log
修改9:
CustomLog logs/ssl_request_log 修改为:
CustomLog /var/www/ydook/logs/access.log combined
并将下面一行的:"%t %h %{SSL_PROTOCOL}x %{SSL_CIPHER}x “%r” %b" 注释掉。
或者 去掉 combined 直接改为:
CustomLog /var/www/ydook/logs/access.log (推荐这种方法,保留通配符)
6.创建mkdir /var/www/ydook/logs/文件夹
最后,重新httpd 服务,使得修改生效:
systemctl restart httpd
完成!!!
修改示例:
<VirtualHost *:443>
SSLEngine On
SSLCertificateFile /etc/pki/tls/certs/example.com.crt
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/pki/tls/private/example.com.key
SSLCACertificateFile /etc/pki/tls/certs/root-certificate.crt # 如果使用自签名的证书或者由 ca-certificates 提供的根证书, 请删除此行代码
7.开发https端口
firewall-cmd --add-service=https

出现该种请情况,说明没用开发443端口
注意:sysstemctl restart httpd需要输入密码
故在openssl中,需要实现确定号密码:如密码:一律填写:LongXing;其它一律填写:FL
访问服务器:http://10.50.36.172/

https://10.50.36.172/
当使用curl http://ip:prot/访问时,出现
Connection Refused 或者 No route to host时
如:

说明服务器端没用该端口号所绑定的进程,此时可以更改服务器端口号,占用该端口,即可访问,如果还不行,需要开发对应端口;
附件:
httpd.conf配置:

# # This is the main Apache HTTP server configuration file. It contains the # configuration directives that give the server its instructions. # See <URL:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/> for detailed information. # In particular, see # <URL:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/mod/directives.html> # for a discussion of each configuration directive. # # Do NOT simply read the instructions in here without understanding # what they do. They're here only as hints or reminders. If you are unsure # consult the online docs. You have been warned. # # Configuration and logfile names: If the filenames you specify for many # of the server's control files begin with "/" (or "drive:/" for Win32), the # server will use that explicit path. If the filenames do *not* begin # with "/", the value of ServerRoot is prepended -- so 'log/access_log' # with ServerRoot set to '/www' will be interpreted by the # server as '/www/log/access_log', where as '/log/access_log' will be # interpreted as '/log/access_log'. # # ServerRoot: The top of the directory tree under which the server's # configuration, error, and log files are kept. # # Do not add a slash at the end of the directory path. If you point # ServerRoot at a non-local disk, be sure to specify a local disk on the # Mutex directive, if file-based mutexes are used. If you wish to share the # same ServerRoot for multiple httpd daemons, you will need to change at # least PidFile. # ServerRoot "/etc/httpd" # # Listen: Allows you to bind Apache to specific IP addresses and/or # ports, instead of the default. See also the <VirtualHost> # directive. # # Change this to Listen on specific IP addresses as shown below to # prevent Apache from glomming onto all bound IP addresses. # #Listen 12.34.56.78:80 Listen 80 # # Dynamic Shared Object (DSO) Support # # To be able to use the functionality of a module which was built as a DSO you # have to place corresponding `LoadModule' lines at this location so the # directives contained in it are actually available _before_ they are used. # Statically compiled modules (those listed by `httpd -l') do not need # to be loaded here. # # Example: # LoadModule foo_module modules/mod_foo.so # Include conf.modules.d/*.conf # # If you wish httpd to run as a different user or group, you must run # httpd as root initially and it will switch. # # User/Group: The name (or #number) of the user/group to run httpd as. # It is usually good practice to create a dedicated user and group for # running httpd, as with most system services. # User apache Group apache # 'Main' server configuration # # The directives in this section set up the values used by the 'main' # server, which responds to any requests that aren't handled by a # <VirtualHost> definition. These values also provide defaults for # any <VirtualHost> containers you may define later in the file. # # All of these directives may appear inside <VirtualHost> containers, # in which case these default settings will be overridden for the # virtual host being defined. # # # ServerAdmin: Your address, where problems with the server should be # e-mailed. This address appears on some server-generated pages, such # as error documents. e.g. admin@your-domain.com # ServerAdmin root@localhost # # ServerName gives the name and port that the server uses to identify itself. # This can often be determined automatically, but we recommend you specify # it explicitly to prevent problems during startup. # # If your host doesn't have a registered DNS name, enter its IP address here. # #ServerName www.example.com:80 ServerName localhost:80 # # Deny access to the entirety of your server's filesystem. You must # explicitly permit access to web content directories in other # <Directory> blocks below. # <Directory /> AllowOverride none Require all denied </Directory> # # Note that from this point forward you must specifically allow # particular features to be enabled - so if something's not working as # you might expect, make sure that you have specifically enabled it # below. # # # DocumentRoot: The directory out of which you will serve your # documents. By default, all requests are taken from this directory, but # symbolic links and aliases may be used to point to other locations. # DocumentRoot "/var/www/html" # # Relax access to content within /var/www. # <Directory "/var/www"> AllowOverride All # Allow open access: Require all granted </Directory> # Further relax access to the default document root: <Directory "/var/www/html"> # # Possible values for the Options directive are "All", "All", # or any combination of: # Indexes Includes FollowSymLinks SymLinksifOwnerMatch ExecCGI MultiViews # # Note that "MultiViews" must be named *explicitly* --- "Options All" # doesn't give it to you. # # The Options directive is both complicated and important. Please see # http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/mod/core.html#options # for more information. # Options Indexes FollowSymLinks # # AllowOverride controls what directives may be placed in .htaccess files. # It can be "All", "All", or any combination of the keywords: # Options FileInfo AuthConfig Limit # AllowOverride All # # Controls who can get stuff from this server. # Require all granted </Directory> # # DirectoryIndex: sets the file that Apache will serve if a directory # is requested. # <IfModule dir_module> DirectoryIndex index.html </IfModule> # # The following lines prevent .htaccess and .htpasswd files from being # viewed by Web clients. # <Files ".ht*"> Require all denied </Files> # # ErrorLog: The location of the error log file. # If you do not specify an ErrorLog directive within a <VirtualHost> # container, error messages relating to that virtual host will be # logged here. If you *do* define an error logfile for a <VirtualHost> # container, that host's errors will be logged there and not here. # ErrorLog "logs/error_log" # # LogLevel: Control the number of messages logged to the error_log. # Possible values include: debug, info, notice, warn, error, crit, # alert, emerg. # LogLevel warn <IfModule log_config_module> # # The following directives define some format nicknames for use with # a CustomLog directive (see below). # LogFormat "%h %l %u %t "%r" %>s %b "%{Referer}i" "%{User-Agent}i"" combined LogFormat "%h %l %u %t "%r" %>s %b" common <IfModule logio_module> # You need to enable mod_logio.c to use %I and %O LogFormat "%h %l %u %t "%r" %>s %b "%{Referer}i" "%{User-Agent}i" %I %O" combinedio </IfModule> # # The location and format of the access logfile (Common Logfile Format). # If you do not define any access logfiles within a <VirtualHost> # container, they will be logged here. Contrariwise, if you *do* # define per-<VirtualHost> access logfiles, transactions will be # logged therein and *not* in this file. # #CustomLog "logs/access_log" common # # If you prefer a logfile with access, agent, and referer information # (Combined Logfile Format) you can use the following directive. # CustomLog "logs/access_log" combined </IfModule> <IfModule alias_module> # # Redirect: Allows you to tell clients about documents that used to # exist in your server's namespace, but do not anymore. The client # will make a new request for the document at its new location. # Example: # Redirect permanent /foo http://www.example.com/bar # # Alias: Maps web paths into filesystem paths and is used to # access content that does not live under the DocumentRoot. # Example: # Alias /webpath /full/filesystem/path # # If you include a trailing / on /webpath then the server will # require it to be present in the URL. You will also likely # need to provide a <Directory> section to allow access to # the filesystem path. # # ScriptAlias: This controls which directories contain server scripts. # ScriptAliases are essentially the same as Aliases, except that # documents in the target directory are treated as applications and # run by the server when requested rather than as documents sent to the # client. The same rules about trailing "/" apply to ScriptAlias # directives as to Alias. # ScriptAlias /cgi-bin/ "/var/www/cgi-bin/" </IfModule> # # "/var/www/cgi-bin" should be changed to whatever your ScriptAliased # CGI directory exists, if you have that configured. # <Directory "/var/www/cgi-bin"> AllowOverride All Options All Require all granted </Directory> <IfModule mime_module> # # TypesConfig points to the file containing the list of mappings from # filename extension to MIME-type. # TypesConfig /etc/mime.types # # AddType allows you to add to or override the MIME configuration # file specified in TypesConfig for specific file types. # #AddType application/x-gzip .tgz # # AddEncoding allows you to have certain browsers uncompress # information on the fly. Note: Not all browsers support this. # #AddEncoding x-compress .Z #AddEncoding x-gzip .gz .tgz # # If the AddEncoding directives above are commented-out, then you # probably should define those extensions to indicate media types: # AddType application/x-compress .Z AddType application/x-gzip .gz .tgz # # AddHandler allows you to map certain file extensions to "handlers": # actions unrelated to filetype. These can be either built into the server # or added with the Action directive (see below) # # To use CGI scripts outside of ScriptAliased directories: # (You will also need to add "ExecCGI" to the "Options" directive.) # #AddHandler cgi-script .cgi # For type maps (negotiated resources): #AddHandler type-map var # # Filters allow you to process content before it is sent to the client. # # To parse .shtml files for server-side includes (SSI): # (You will also need to add "Includes" to the "Options" directive.) # AddType text/html .shtml AddOutputFilter INCLUDES .shtml </IfModule> # # Specify a default charset for all content served; this enables # interpretation of all content as UTF-8 by default. To use the # default browser choice (ISO-8859-1), or to allow the META tags # in HTML content to override this choice, comment out this # directive: # AddDefaultCharset UTF-8 <IfModule mime_magic_module> # # The mod_mime_magic module allows the server to use various hints from the # contents of the file itself to determine its type. The MIMEMagicFile # directive tells the module where the hint definitions are located. # MIMEMagicFile conf/magic </IfModule> # # Customizable error responses come in three flavors: # 1) plain text 2) local redirects 3) external redirects # # Some examples: #ErrorDocument 500 "The server made a boo boo." #ErrorDocument 404 /missing.html #ErrorDocument 404 "/cgi-bin/missing_handler.pl" #ErrorDocument 402 http://www.example.com/subscription_info.html # # # EnableMMAP and EnableSendfile: On systems that support it, # memory-mapping or the sendfile syscall may be used to deliver # files. This usually improves server performance, but must # be turned off when serving from networked-mounted # filesystems or if support for these functions is otherwise # broken on your system. # Defaults if commented: EnableMMAP On, EnableSendfile Off # #EnableMMAP off EnableSendfile on # Supplemental configuration # # Load config files in the "/etc/httpd/conf.d" directory, if any. IncludeOptional conf.d/*.conf
ssl.conf配置:

# # When we also provide SSL we have to listen to the # the HTTPS port in addition. # Listen 443 https ## ## SSL Global Context ## ## All SSL configuration in this context applies both to ## the main server and all SSL-enabled virtual hosts. ## # Pass Phrase Dialog: # Configure the pass phrase gathering process. # The filtering dialog program (`builtin' is a internal # terminal dialog) has to provide the pass phrase on stdout. SSLPassPhraseDialog exec:/usr/libexec/httpd-ssl-pass-dialog # Inter-Process Session Cache: # Configure the SSL Session Cache: First the mechanism # to use and second the expiring timeout (in seconds). SSLSessionCache shmcb:/run/httpd/sslcache(512000) SSLSessionCacheTimeout 300 # Pseudo Random Number Generator (PRNG): # Configure one or more sources to seed the PRNG of the # SSL library. The seed data should be of good random quality. # WARNING! On some platforms /dev/random blocks if not enough entropy # is available. This means you then cannot use the /dev/random device # because it would lead to very long connection times (as long as # it requires to make more entropy available). But usually those # platforms additionally provide a /dev/urandom device which doesn't # block. So, if available, use this one instead. Read the mod_ssl User # Manual for more details. SSLRandomSeed startup file:/dev/urandom 256 SSLRandomSeed connect builtin #SSLRandomSeed startup file:/dev/random 512 #SSLRandomSeed connect file:/dev/random 512 #SSLRandomSeed connect file:/dev/urandom 512 # # Use "SSLCryptoDevice" to enable any supported hardware # accelerators. Use "openssl engine -v" to list supported # engine names. NOTE: If you enable an accelerator and the # server does not start, consult the error logs and ensure # your accelerator is functioning properly. # SSLCryptoDevice builtin #SSLCryptoDevice ubsec ## ## SSL Virtual Host Context ## #<VirtualHost _default_:443> <VirtualHost *:443> # General setup for the virtual host, inherited from global configuration #DocumentRoot "/var/www/html" DocumentRoot "/var/www/ydook" #ServerName www.example.com:443 ServerName www.ydook.com:443 # Use separate log files for the SSL virtual host; note that LogLevel # is not inherited from httpd.conf. #ErrorLog logs/ssl_error_log ErrorLog /var/www/ydook/logs/error.log TransferLog logs/ssl_access_log LogLevel warn # SSL Engine Switch: # Enable/Disable SSL for this virtual host. SSLEngine on # SSL Protocol support: # List the enable protocol levels with which clients will be able to # connect. Disable SSLv2 access by default: SSLProtocol all -SSLv2 -SSLv3 # SSL Cipher Suite: # List the ciphers that the client is permitted to negotiate. # See the mod_ssl documentation for a complete list. SSLCipherSuite HIGH:3DES:!aNULL:!MD5:!SEED:!IDEA # Speed-optimized SSL Cipher configuration: # If speed is your main concern (on busy HTTPS servers e.g.), # you might want to force clients to specific, performance # optimized ciphers. In this case, prepend those ciphers # to the SSLCipherSuite list, and enable SSLHonorCipherOrder. # Caveat: by giving precedence to RC4-SHA and AES128-SHA # (as in the example below), most connections will no longer # have perfect forward secrecy - if the server's key is # compromised, captures of past or future traffic must be # considered compromised, too. #SSLCipherSuite RC4-SHA:AES128-SHA:HIGH:MEDIUM:!aNULL:!MD5 #SSLHonorCipherOrder on # Server Certificate: # Point SSLCertificateFile at a PEM encoded certificate. If # the certificate is encrypted, then you will be prompted for a # pass phrase. Note that a kill -HUP will prompt again. A new # certificate can be generated using the genkey(1) command. #SSLCertificateFile /etc/pki/tls/certs/localhost.crt SSLCertificateFile /var/www/ssl/_www.ydook.com.crt # Server Private Key: # If the key is not combined with the certificate, use this # directive to point at the key file. Keep in mind that if # you've both a RSA and a DSA private key you can configure # both in parallel (to also allow the use of DSA ciphers, etc.) #SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/pki/tls/private/localhost.key SSLCertificateKeyFile /var/www/ssl/_www.ydook.com.key # Server Certificate Chain: # Point SSLCertificateChainFile at a file containing the # concatenation of PEM encoded CA certificates which form the # certificate chain for the server certificate. Alternatively # the referenced file can be the same as SSLCertificateFile # when the CA certificates are directly appended to the server # certificate for convinience. #SSLCertificateChainFile /etc/pki/tls/certs/server-chain.crt # Certificate Authority (CA): # Set the CA certificate verification path where to find CA # certificates for client authentication or alternatively one # huge file containing all of them (file must be PEM encoded) #SSLCACertificateFile /etc/pki/tls/certs/ca-bundle.crt # Client Authentication (Type): # Client certificate verification type and depth. Types are # none, optional, require and optional_no_ca. Depth is a # number which specifies how deeply to verify the certificate # issuer chain before deciding the certificate is not valid. #SSLVerifyClient require #SSLVerifyDepth 10 # Access Control: # With SSLRequire you can do per-directory access control based # on arbitrary complex boolean expressions containing server # variable checks and other lookup directives. The syntax is a # mixture between C and Perl. See the mod_ssl documentation # for more details. #<Location /> #SSLRequire ( %{SSL_CIPHER} !~ m/^(EXP|NULL)/ # and %{SSL_CLIENT_S_DN_O} eq "Snake Oil, Ltd." # and %{SSL_CLIENT_S_DN_OU} in {"Staff", "CA", "Dev"} # and %{TIME_WDAY} >= 1 and %{TIME_WDAY} <= 5 # and %{TIME_HOUR} >= 8 and %{TIME_HOUR} <= 20 ) # or %{REMOTE_ADDR} =~ m/^192.76.162.[0-9]+$/ #</Location> # SSL Engine Options: # Set various options for the SSL engine. # o FakeBasicAuth: # Translate the client X.509 into a Basic Authorisation. This means that # the standard Auth/DBMAuth methods can be used for access control. The # user name is the `one line' version of the client's X.509 certificate. # Note that no password is obtained from the user. Every entry in the user # file needs this password: `xxj31ZMTZzkVA'. # o ExportCertData: # This exports two additional environment variables: SSL_CLIENT_CERT and # SSL_SERVER_CERT. These contain the PEM-encoded certificates of the # server (always existing) and the client (only existing when client # authentication is used). This can be used to import the certificates # into CGI scripts. # o StdEnvVars: # This exports the standard SSL/TLS related `SSL_*' environment variables. # Per default this exportation is switched off for performance reasons, # because the extraction step is an expensive operation and is usually # useless for serving static content. So one usually enables the # exportation for CGI and SSI requests only. # o StrictRequire: # This denies access when "SSLRequireSSL" or "SSLRequire" applied even # under a "Satisfy any" situation, i.e. when it applies access is denied # and no other module can change it. # o OptRenegotiate: # This enables optimized SSL connection renegotiation handling when SSL # directives are used in per-directory context. #SSLOptions +FakeBasicAuth +ExportCertData +StrictRequire <Files ~ ".(cgi|shtml|phtml|php3?)$"> SSLOptions +StdEnvVars </Files> <Directory "/var/www/cgi-bin"> SSLOptions +StdEnvVars </Directory> # SSL Protocol Adjustments: # The safe and default but still SSL/TLS standard compliant shutdown # approach is that mod_ssl sends the close notify alert but doesn't wait for # the close notify alert from client. When you need a different shutdown # approach you can use one of the following variables: # o ssl-unclean-shutdown: # This forces an unclean shutdown when the connection is closed, i.e. no # SSL close notify alert is send or allowed to received. This violates # the SSL/TLS standard but is needed for some brain-dead browsers. Use # this when you receive I/O errors because of the standard approach where # mod_ssl sends the close notify alert. # o ssl-accurate-shutdown: # This forces an accurate shutdown when the connection is closed, i.e. a # SSL close notify alert is send and mod_ssl waits for the close notify # alert of the client. This is 100% SSL/TLS standard compliant, but in # practice often causes hanging connections with brain-dead browsers. Use # this only for browsers where you know that their SSL implementation # works correctly. # Notice: Most problems of broken clients are also related to the HTTP # keep-alive facility, so you usually additionally want to disable # keep-alive for those clients, too. Use variable "nokeepalive" for this. # Similarly, one has to force some clients to use HTTP/1.0 to workaround # their broken HTTP/1.1 implementation. Use variables "downgrade-1.0" and # "force-response-1.0" for this. BrowserMatch "MSIE [2-5]" nokeepalive ssl-unclean-shutdown downgrade-1.0 force-response-1.0 # Per-Server Logging: # The home of a custom SSL log file. Use this when you want a # compact non-error SSL logfile on a virtual host basis. #CustomLog logs/ssl_request_log CustomLog /var/www/ydook/logs/access.log combined # "%t %h %{SSL_PROTOCOL}x %{SSL_CIPHER}x "%r" %b" </VirtualHost>
脚本执行:
apache.sh:
rpm -qa mod_ssl rpm -qa openssl yum install mod_ssl openssl mkdir /var/www/ssl #apache服务器开启ssl功能 openssl genrsa -des3 -out weapp.key 2048 openssl req -new -key weapp.key -out weapp.csr openssl req -new -x509 -days 3650 -key weapp.key -out weapp.crt #!/bin/bash sed -i 's#SSLCertificateFile /etc/pki/tls/certs/localhost.crt#SSLCertificateFile /var/www/ssl/weapp.crt#g' /etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf sed -i 's#SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/pki/tls/private/localhost.key#SSLCertificateKeyFile /var/www/ssl/weapp.key#g' /etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf sed -i 's#<VirtualHost _default_:443>#<VirtualHost *:443>#' /etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf sed -i 's@#DocumentRoot "/var/www/html"@DocumentRoot "/var/www/ydook"' /etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf sed -i 's@#ServerName www.example.com:443@ServerName www.example.com:443@g' /etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf sed -i 's#ErrorLog logs/ssl_error_log#ErrorLog /var/www/ydook/logs/error.log#g' /etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf sed -i 's#CustomLog logs/ssl_request_log \#CustomLog /var/www/ydook/logs/access.log combined#g' /etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf sed -i 's@"%t %h %{SSL_PROTOCOL}x %{SSL_CIPHER}x \"%r\" %b"@#"%t %h %{SSL_PROTOCOL}x %{SSL_CIPHER}x \"%r\" %b"@g' /etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf mkdir /var/www/ydook cd /var/www/ydook mkdir logs firewall-cmd --add-service=https systemctl restart httpd
二、nginx启用https功能:
Centos7下nginx安装:

#CentOS7 nginx开启https yum install gcc -y yum install gcc-c++ yum install -y pcre pcre-devel yum install -y openssl openssl-devel yum install wget mkdir nginx cd nginx wget https://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.16.1.tar.gz tar -zxvf nginx-1.16.1.tar.gz cd nginx-1.16.1 ./configure make && make install whereis nginx 启动、停止nginx cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin/ ./nginx ./nginx -s stop ./nginx -s quit ./nginx -s reload ps aux|grep nginx firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=8082/tcp --permanent systemctl restart firewalld.service yum search 包名 nginx配置成功后无法访问页面: 执行:/sbin/iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
启用https功能:
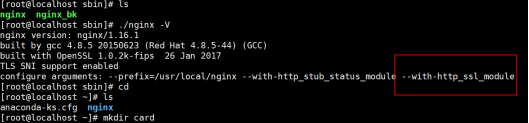
#注意这里是大写的V,小写的只显示版本号
./nginx -V
#可以看到这里出现了configure arguments: --with-http_ssl_module 证明已经安装成功
如果没用需要从安装ssl_modeul有
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_ssl_module
make
#切记不要执行make install,否则会重新安装nginx
上述操作执行完成以后,你的目录下会出现objs文件夹,文件夹内存在nginx文件
接下来使用新的nginx文件替换掉之前安装目录sbin下的nginx,注意这里的替换的时候可以先将之前的文件备份下,停掉nginx服务
cp /root/nginx/nginx-1.16.1/objs/nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
再次执行:
./nginx -V:
上传证书:
#在root目录下创建card文件夹,将公钥与私钥放入该文件夹下:
cd /root
mkdir card
在:vi /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf中修改:

重新启动nginx
发现报以下错误:
nginx: [error] open() "/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid" failed (2: No such file or directory)
解决办法,执行以下语法即可修复:
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
原理:
使用nginx -c的参数指定nginx.conf文件的位置
在此启用nginx
./nginx -s reload
开发443端口:
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=443/tcp --permanent
/sbin/iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 443 -j ACCEPT
nginx搭建IPV6服务器:
