留言案例
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>模板</title> <style> span { margin-left: 100px; cursor:pointer; color:green; } span :hover{ color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <p> <input type="text" v-model="val"> <button @click="add">评论</button> </p> <ul> <li v-for="(info,i) in infos"> {{info}} {{i}} <span @click="del(i)">删除</span> </li> </ul> </div> </body> <script src="test/vue.js"></script> <script> l=[1,2,3]; l.splice(1,1); console.log(l); </script> <script> new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { infos:[], val:"" }, methods:{ del:function (i) { this.infos.splice(i,1) }, add:function () { let val =this.val; if(val){ this.infos.splice(0,0,val); this.val ='' } } } }) </script> </html>
留言案例主要就是用到了splice,
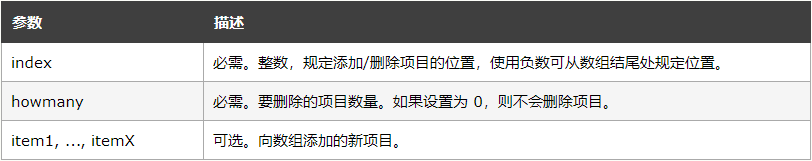
所以我们是后写的评论是在列表的索引0,也就是说是在楼顶处,高出不胜寒啊。
实例成员
computed

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>模板</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <p> 姓: <input type="text" v-model="first_name"> 名: <input type="text" v-model="last_name"> </p> <p>姓名:<b>{{full_name}}</b></p> </div> </body> <script src="test/vue.js"></script> <script> new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { first_name:'', last_name:'', //full_name:'None' }, computed:{ //1在computed中定义的变量的值等于绑定的函数的返回值 //2绑定的函数中出现的所有的vue变量都会被监听 full_name: function () { console.log('被调用了'); return this.first_name+this.last_name; } } }) </script> </html>
watch

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>模板</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <p>姓名: <input type="text" v-model="full_name"></p> <p> 姓:<b>{{first_name}}</b> 名:<b>{{last_name}}</b> </p> </div> </body> <script src="test/vue.js"></script> <script> new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { full_name:'', first_name:'', last_name:'' }, watch:{ full_name: function () { let res=this.full_name.split(''); this.first_name =res[0]; this.last_name = res[1]; } } }) </script> </html>
这两个实例成员,computed是将变量的值进行监听然后进行计算,但是不是实时的监听,绑定的变量也不需要在data中声明,
watch则是实时的监听,绑定的变量一定需要在data中声明。
分隔符
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>模板</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> {{msg}} {{{msg} ${msg} </div> </body> <script src="test/vue.js"></script> <script> new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { msg:'12345' }, delimiters:['{{{','}'] }) </script> </html>
其实就是规定了前端渲染语言的方法,文中用的是{{{},但是实际中用到的是第三种${},
组件
有html模板,有css样式,有js逻辑的集合体
根组件的模板就使用挂载点,子组件必须自己定义template(局部子组件、全局子组件)
组件案例

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>模板</title> <style> h2 { color: yellowgreen; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <h1>组件的概念</h1> </div> </body> <script src="test/vue.js"></script> <script> new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { }, template:` <div> <h1 style="color:red">组件的渲染</h1> <h2 @click="action">副标题</h2> </div>`, methods:{ action:function () { alert('123') } } }) </script> </html>
局部组件

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>模板</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <abc></abc> <abc></abc> </div> </body> <script src="test/vue.js"></script> <script> let localTag ={ //1data要达到组件的作用,必须为每个组件提供一个名称空间(作用域) //2data的值就是一个存放数据的字典 //需要满足1和2 的值就是为有一个可以产生名称空间的函数的返回值,返回值是字典 data: function () { return { count :0, } } , template: ` <div class="box" style="border: solid; 100px"> <h1>标题</h1> <p class="p1">文本内容</p> <p @click="action" class="p2" style="background: yellowgreen">被点击了{{count}}下</p> </div>`, methods:{ action: function () { this.count++ }, } }; new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { }, components: { 'abc':localTag } }) </script> </html>
全局组件
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>模板</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <old-boy></old-boy> </div> </body> <script src="test/vue.js"></script> <script> Vue.component('oldBoy',{ data: function(){ return{ count:0 } }, template:` <div class="box" style="border: solid;100px"> <h1>全局</h1> <p clas="p1">文本内容</p> <p @click="action" class="p2" style="background: yellowgreen">被点击了{{count}}次</p> </div>`, methods:{ action:function () { this.count++ }, } }); new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { } }) </script> </html>
组件之间信息传递
父组件信息传给子组件
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>模板</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <!-- local-tag就可以理解为自定义标签,使用msg变量值由父组件提供 --> <!-- local-tag标签代表的是子组件,owen为标签的自定义属性 --> <!-- 在子组件内部能拿到owen,就可以拿到父组件的信息 --> <local-tag :owen="msg"></local-tag> </div> </body> <script src="js/vue.js"></script> <script> let localTag = { // 子组件拿自定义属性 props: ['owen'], template: ` <div> <h1>信息</h1> <p>{{ owen }}</p> </div> ` }; new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { msg: '父级的信息' }, components: { // 'localTag': localTag, // localTag: localTag, localTag // 在页面中 <local-tag> } }) </script> </html>
子组件信息传给父组件
method
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>模板</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <h1>{{ title }}</h1> <global-tag @recv="get_title"></global-tag> </div> </body> <script src="js/vue.js"></script> <script> Vue.component('global-tag', { template: ` <div> <input type="text" v-model="msg"> <button @click="action">修改标题</button> </div> `, data: function () { return { msg: '' } }, methods: { action: function () { let msg = this.msg; // recv是自定义的事件 this.$emit('recv', msg) } }, }); new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { title: '父组件定义的标题' }, methods: { get_title: function (msg) { this.title = msg } } }) </script> </html>
watch
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>模板</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <h1>{{ title }}</h1> <global-tag @recv="get_title"></global-tag> </div> </body> <script src="js/vue.js"></script> <script> Vue.component('global-tag', { template: ` <div> <input type="text" v-model="msg"> <!--<button @click="action">修改标题</button>--> </div> `, data: function () { return { msg: '' } }, methods: { // action: function () { // let msg = this.msg; // // recv是自定义的事件 // this.$emit('recv', msg) // } }, watch: { msg: function () { this.$emit('recv', this.msg) } } }); new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { title: '父组件定义的标题' }, methods: { get_title: function (msg) { this.title = msg } } }) </script> </html>
