STL - 内存分配 - 内存池
前言
本文为:STL源码分析第二章《allocator》的阅读记录。
如果具有很多小额区块的内存分配,那么采用直接分配的方式,不仅会产生很多的碎片内存,对这些空间进行管理也会带来额外的负担。
文中记录的方法是,如果区块够大,超过128bytes,就向系统直接申请对应的内存空间;当区块小于128bytes的时候,采用内存池进行管理,一次性申请大块的内存空间,用freelist管理剩余空间。为了方便管理,当申请小区块的时候,为将申请的空间上调至8的倍数,16个freelists,管理了大小分别为8,16,24,32,40,48,56,64,72,80,88,96,104,112,120,128bytes的小区块。
完整代码及流程示意图
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <memory.h>
namespace {
enum {__ALIGN = 8};
enum {__MAX_BYTES = 128};
enum {__NFREELISTS = __MAX_BYTES/__ALIGN};
template <bool threads, int inst/*not used*/>
class __default_alloc_template {
private:
// 将bytes上调至8的倍数
static size_t ROUND_UP(size_t bytes) {
return (((bytes) + __ALIGN - 1) & ~(__ALIGN - 1));
}
union obj {
union obj * free_list_link;
char client_data[1];
};
static obj * volatile free_list[__NFREELISTS];
static size_t FREELIST_INDEX(size_t bytes) {
return (((bytes) + __ALIGN - 1) / __ALIGN - 1);
}
// 当发现list中没有足够的空间的时候,通过refill,
// 传回一个大小为n的物件,并可能加入大小为n的其他区块到free list
// 其中n已经上调至8的倍数
static void* refill(size_t n)
{
int nobjs = 20;
char * chunk = chunk_alloc(n, nobjs);
obj * volatile * my_free_list;
obj * result;
obj * current_obj, * next_obj;
if (1 == nobjs) return (chunk);
my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(n);
result = (obj*)chunk;
*my_free_list = next_obj = (obj*)(chunk + n);
for (int i = 1; ; i++) {
current_obj = next_obj;
next_obj = (obj*)((char*)next_obj + n);
if (nobjs - 1 == i) {
current_obj->free_list_link = 0;
break;
} else {
current_obj->free_list_link = next_obj;
}
}
return (result);
}
// 配置大块空间,可容纳nobjs个大小为“size”的区块
// 如果,无法配置nobjs个区块,nobjs的值会减小
static char* chunk_alloc(size_t size, int &nobjs)
{
char * result;
size_t total_bytes = size * nobjs;
size_t bytes_left = end_free - start_free;
if (bytes_left >= total_bytes) {
// 内存池中剩余空间完全满足需求量
result = start_free;
start_free += total_bytes;
return result;
} else if (bytes_left >= size) {
// 内存池剩余空间不能完全满足需求量,但足够供应一个以上区块
nobjs = bytes_left / size;
total_bytes = size * nobjs;
result = start_free;
start_free += total_bytes;
return result;
} else {
// 内存池剩余空间连一个区块大小都无法提供
size_t bytes_to_get = 2 * total_bytes + ROUND_UP(heap_size >> 4);
if (bytes_left > 0) {
// 内存池汇中还有剩余,先配给适当的freelist
obj * volatile * my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(bytes_left);
// 调整freelist,将内存池剩余空间编入
((obj*)start_free)->free_list_link = *my_free_list;
*my_free_list = ((obj*)start_free);
}
// 配置heap空间
start_free = (char*)malloc(bytes_to_get);
if (0 == start_free) {
// heap 空间不足,malloc失败
int i;
obj * volatile * my_free_list, *p;
// 尝试从freelist中查找是不是有足够大的没有用过的区块
for (i = size; i <= __MAX_BYTES; i += __ALIGN) {
my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(i);
p = *my_free_list;
if (0 != p) {
*my_free_list = p->free_list_link;
start_free = (char*)p;
end_free = start_free + i;
return (chunk_alloc(size, nobjs));
}
}
end_free = 0;
start_free = (char*)malloc(bytes_to_get); // 再次尝试,此处原本为malloc_alloc::allocate,内部实现,如果失败后会调用回调,然后再反复尝试
if (0 == start_free)
{
printf("out of memory
");
exit(1);
}
}
heap_size += bytes_to_get;
end_free = start_free + bytes_to_get;
// 调用自己,回了修正nobjs
return (chunk_alloc(size, nobjs));
}
}
// chunk allocation state
static char *start_free; // 内存池的起始位置,只在chunk_alloc中变化
static char *end_free; // 内存池的结束位置,只在chunk_alloc中变化
static size_t heap_size;
public:
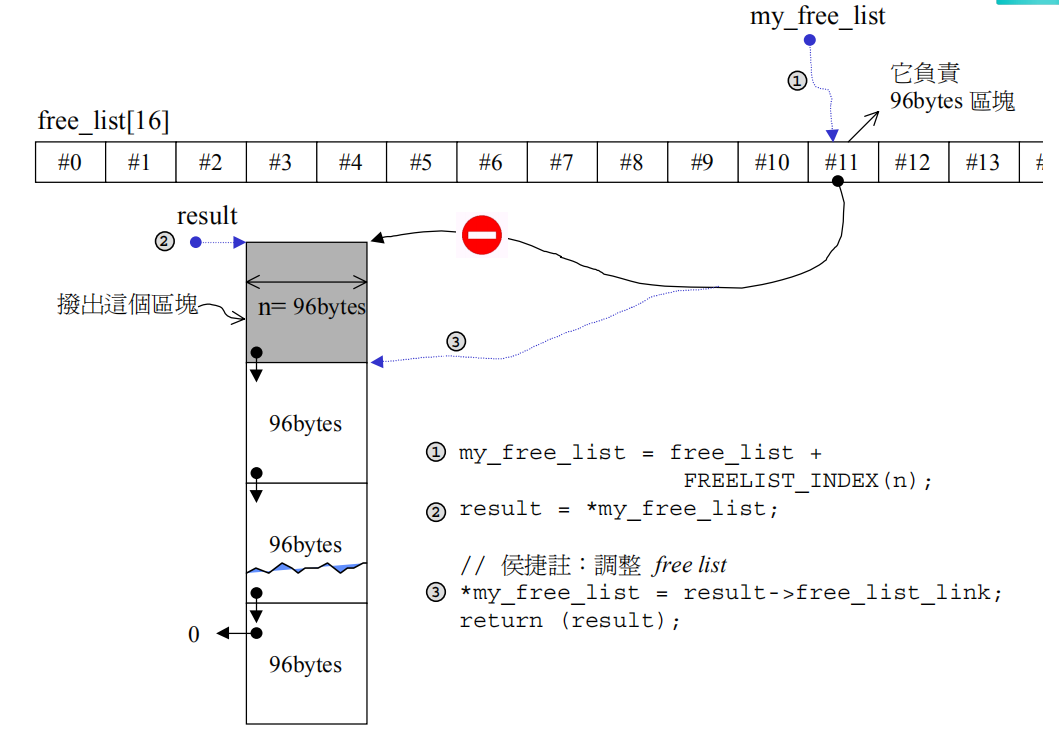
static void * allocate(size_t n) {
obj * volatile * my_free_list;
obj * result;
// 大于最大值的时候直接分配内存
if (n > (size_t) __MAX_BYTES)
return malloc(n); // 此处不用,内存不足时,反复尝试的机制
my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(n);
result = *my_free_list;
if (result == nullptr) {
// 没有找到可用的freelist,准备重新填充freelist
void *r = refill(ROUND_UP(n));
return r;
}
*my_free_list = result->free_list_link;
return (result);
}
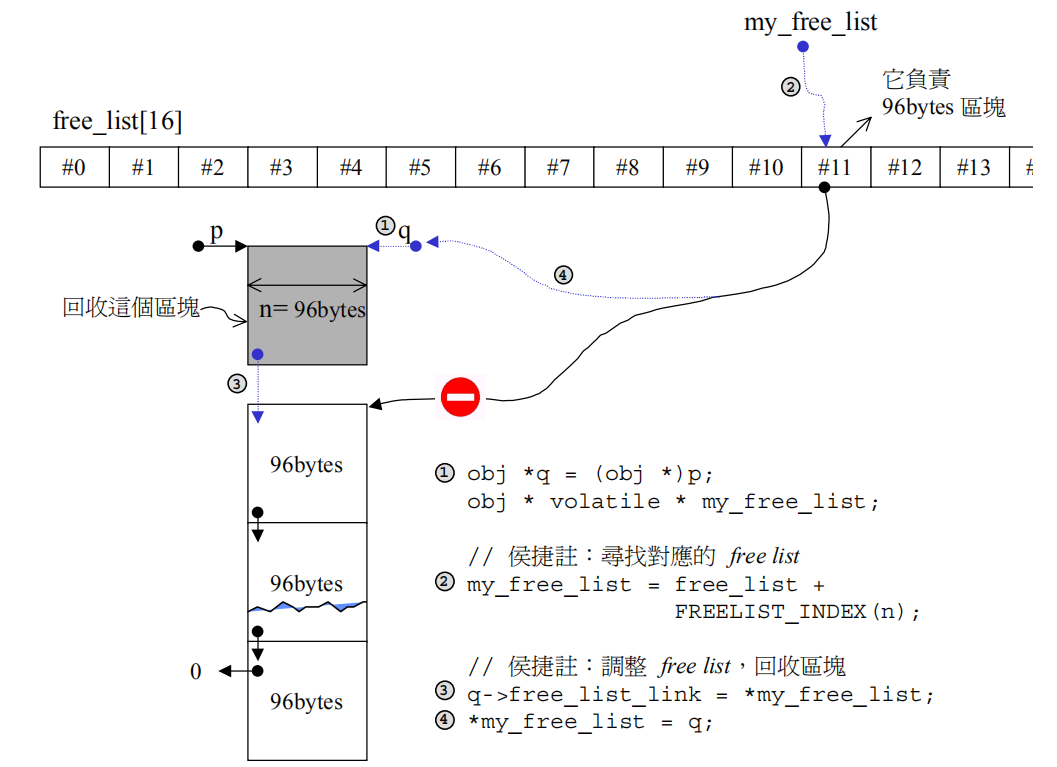
static void deallocate(void *p, size_t n)
{
obj *q = (obj *)p;
obj * volatile * my_free_list;
// 大于最大值,直接释放内存
if (n > (size_t) __MAX_BYTES) {
free(p);
return;
}
my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(n);
q->free_list_link = *my_free_list;
*my_free_list = q;
}
};
template <bool threads, int inst>
typename __default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::obj * volatile
__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::free_list[__NFREELISTS] = {0};
template<bool threads, int inst>
char *__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::start_free = 0;
template<bool threads, int inst>
char *__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::end_free = 0;
template<bool threads, int inst>
size_t __default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::heap_size = 0;
}
using My_Alloc = __default_alloc_template<false, 0>;
int main()
{
int nCount = 4;
int *a = (int *)My_Alloc::allocate(sizeof(int)*nCount);
for (int i=0; i<nCount; ++i)
{
a[i] = i;
}
std::cout << "a[](" << a << "): ";
for (int i=0; i<nCount; ++i)
{
std::cout << a[i] << " ";
}
My_Alloc::deallocate(a, sizeof(int)*nCount);
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "a[](" << a << "): ";
for (int i=0; i<nCount; ++i)
{
std::cout << a[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
输出为:
a[](00175A20): 0 1 2 3
a[](00175A20): 1530416 1 2 3
其中static void * allocate(size_t n) 对应的示意图如下:
其中static void deallocate(void *p, size_t n)对应的示意图如下:
小结
整个过程对应的示意图如下:
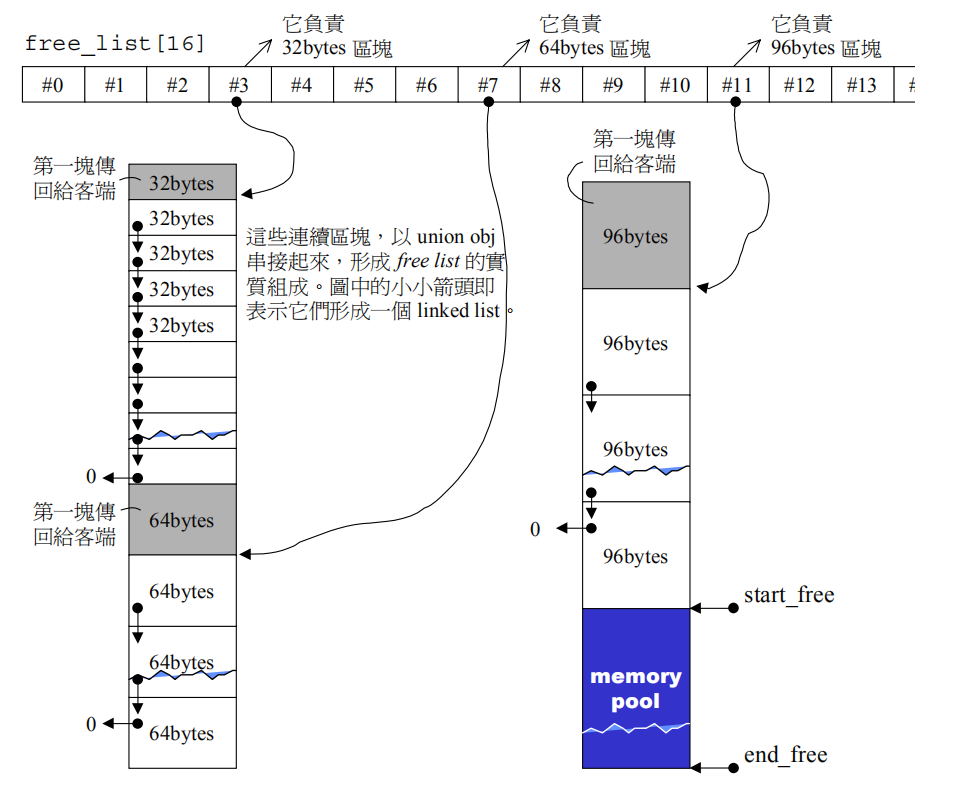
整体流程大致说明:
- 一开始有个freelist列表,系统的内存空间;
- 请求分配内存;
- 如果分配的内存块很大,直接从系统内存中申请对应大小的内存空间返回;
- 如果分配的内存块比较小,从freelist中查找,
- 如果没找到,那么从memory pool中查找特定大小的内存空间,
- 如果还没找到,那么从系统内存中申请特定大小的内存空间,一部分返回放到memory pool,一部分返回放到freelist,还有一部分返回给内存申请者。
接下来就可以进一步理解《learn nginx - 共享内存 - 小记》。