React中的事件处理
React 中文官网中有提到:"你必须谨慎对待 JSX 回调函数中的 this,类的方法默认是不会绑定 this 的" 。 "这并不是 React 的特殊行为;它是函数如何在 JavaScript 中运行的一部分" 。因此,如果忘记绑定,对应函数的 this 的值会是 undefined。当然,在没有用到函数的 this 的时候,绑定就不是必要的了。下面主要是从两个部分对 React 中的事件处理进行理解:第一部分是事件函数仅在在当前组件中进行事件处理,第二部分是将事件函数传递给其他组件进行事件处理。每部分分为用到 this 的事件函数,和没有用到 this 的事件函数。第一部分中例子使用没有传递参数,第二部分中使用参数。最后例中也同样展示了函数的几种绑定方式。
对 react 中的事件处理关注的重点可以总结为两点: ① this 是否为当前上下文 ② 传递给事件处理程序的参数是从哪里来的
一、事件处理:事件函数仅在在当前组件中(例中没有传递参数,传递参数的情况与之类似)
1、没有用到事件处理程序中的 this 时
代码如下:
1 var React = require('react'); 2 var ReactDOM = require('react-dom'); 3 class Index extends React.Component { 4 constructor() { 5 super(); //调用基类的所有的初始化方法 6 7 }; 8 9 showName(){ 10 alert('username: "Guang"'); 11 } 12 13 render() { 14 return ( 15 <div> 16 {/* 传递数据: 不传递参数或者有传递参数但是不涉及事件处理程序中的 this ,对事件处理程序的绑定:不是必须的 */} 17 <input type="button" value="显示名称 没有绑定" onClick={this.showName}></input><br></br> 18 <input type="button" value="显示名称 箭头函数绑定" onClick={()=>this.showName()}></input><br></br> 19 <input type="button" value="显示名称 bind绑定" onClick={this.showName.bind(this)}></input> 20 {/* 也可以在构造函数中通过: this.showName=this.showName.bind(this); 语句来绑定 */} 21 </div> 22 ); 23 } 24 } 25 ReactDOM.render( 26 <Index/>, document.getElementById('example'));
运行结果:
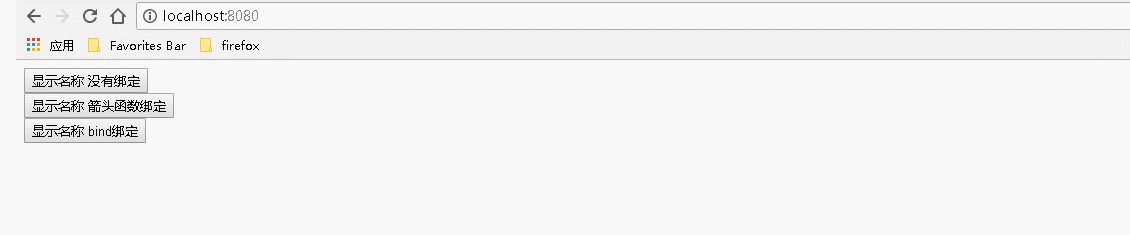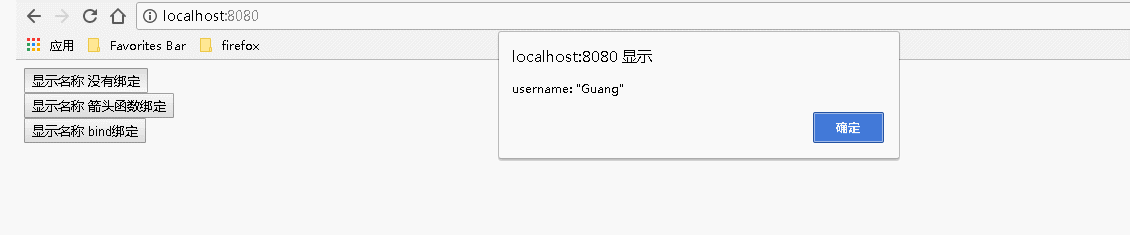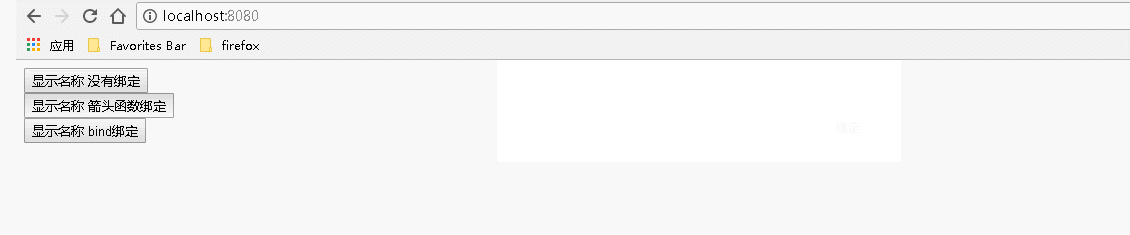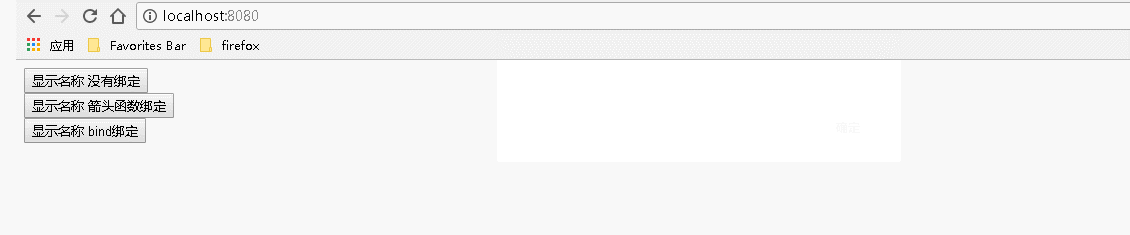
2、用到事件处理程序中的 this 时
代码如下:
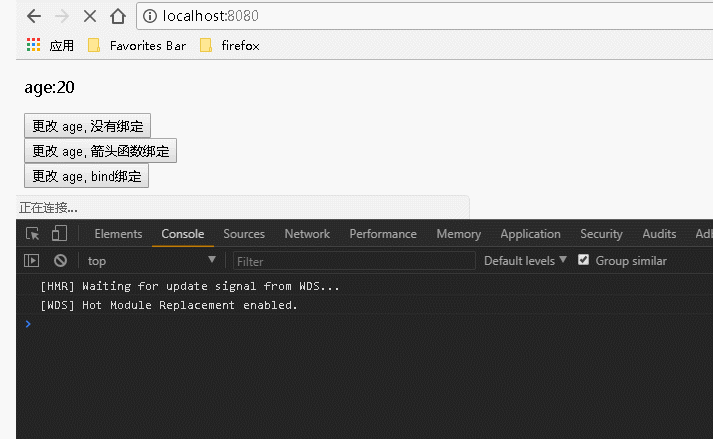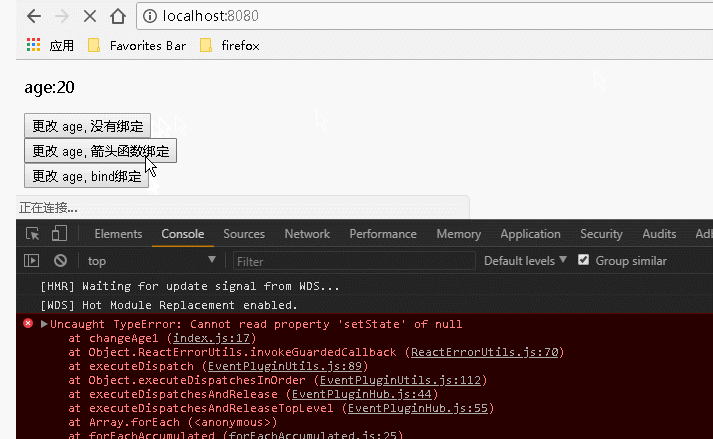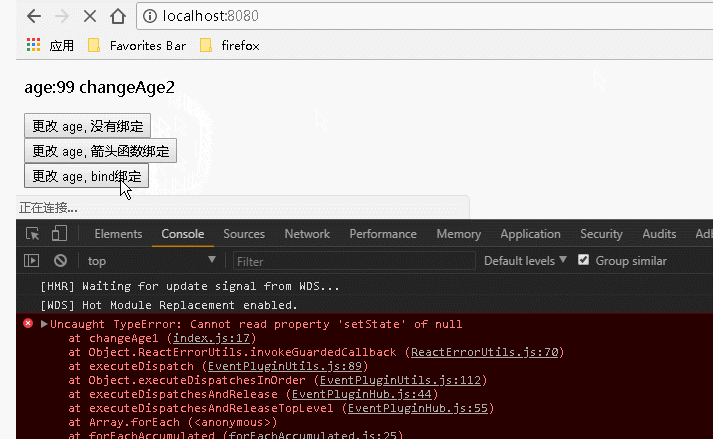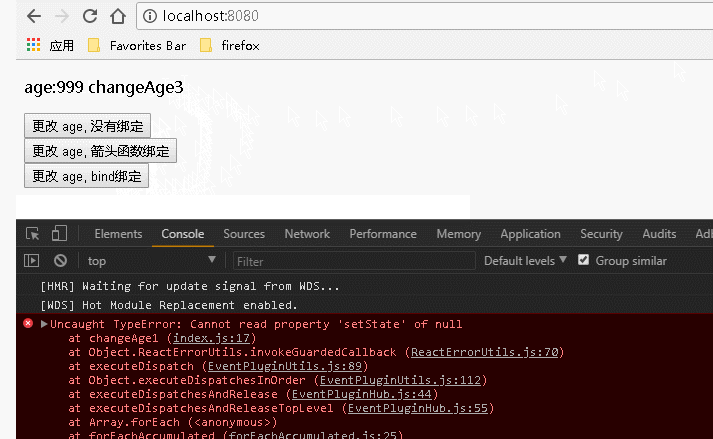
1 var React = require('react'); 2 var ReactDOM = require('react-dom'); 3 class Index extends React.Component { 4 constructor() { 5 super(); //调用基类的所有的初始化方法 6 this.state = { 7 username: "Guang", 8 age: 20, 9 newage1:"9 changeAge1", 10 newage2:"99 changeAge2", 11 newage3:"999 changeAge3" 12 }; 13 }; 14 15 changeAge1(){ 16 this.setState({age:this.state.newage1}); 17 }; 18 changeAge2(){ 19 this.setState({age:this.state.newage2}); 20 }; 21 changeAge3(){ 22 this.setState({age:this.state.newage3}); 23 }; 24 25 render() { 26 return ( 27 <div> 28 <p>age:{this.state.age}</p> 29 {/* 传递数据: 不传递参数但是涉及到事件处理程序中的 this ,对事件处理程序的绑定:是必须的 */} 30 <input type="button" value="更改 age, 没有绑定" onClick={this.changeAge1}></input><br></br> 31 <input type="button" value="更改 age, 箭头函数绑定" onClick={()=>this.changeAge2()}></input><br></br> 32 <input type="button" value="更改 age, bind绑定" onClick={this.changeAge3.bind(this)}></input> 33 {/* 也可以在构造函数中通过: this.changeAge3=this.changeAge3.bind(this); 语句来绑定 */} 34 </div> 35 ); 36 } 37 } 38 ReactDOM.render( 39 <Index/>, document.getElementById('example'));
运行结果: 可以看到,在需要用到事件处理程序中的 this 时,如果没有对事件处理程序进行绑定,会报错。而对事件处理程序进行绑定后正确运行
二、事件处理:事件函数传递到其他组件中(例中有传递参数,没有传递参数的情况与之类似)
1、没有用到事件处理程序中的 this 时(当传递的参数只有事件对象无其他数据时)
父组件代码如下:
1 var React = require('react'); 2 var ReactDOM = require('react-dom'); 3 import BodyChild from './components/bodychild'; 4 class Index extends React.Component { 5 6 // 该函数将获取的事件保持在 this.state.eventobject 中 7 parentEventHandler(e){ 8 alert(e.target.value); 9 } 10 11 render() { 12 return ( 13 <div> 14 {/* 事件处理:事件函数传递给其他组件 */} 15 {/* 传递的数据: 传递参数 只有事件对象 无其他数据 但是没有用到事件处理程序的 this */} 16 <BodyChild 17 // 匿名函数赋值给子组件的 this.props.childAnonymous ,匿名函数后面的 bind(this) 是传入当前上下文,使得匿名函数内的 this 为当前上下文 18 childAnonymous={function(e){this.parentEventHandler(e)}.bind(this)} 19 // 箭头函数将函数 this 设置为当前上下文 20 childArrow={(e)=>this.parentEventHandler(e)} 21 // 使用 bind 将函数 this 设置为当前上下文 22 childBind={this.parentEventHandler.bind(this)} 23 // 也可以在构造函数中通过: this.childBind=this.parentEventHandler.bind(this) 语句来绑定 24 /> 25 </div> 26 ); 27 } 28 } 29 ReactDOM.render( 30 <Index/>, document.getElementById('example'));
子组件代码如下:
1 import React from 'react'; 2 export default class BodyChild extends React.Component{ 3 4 render(){ 5 return( 6 <div> 7 {/* 匿名函数后面的 bind(this) 是传入当前上下文,使得匿名函数内的 this 为当前上下文 */} 8 <input type="button" value="childAnonymous 匿名函数传参 无绑定" onClick={function(e){this.props.childAnonymous(e)}}></input><br></br> 9 <input type="button" value="childAnonymous 匿名函数传参 匿名函数使用 bind 绑定" onClick={function(e){this.props.childAnonymous(e)}.bind(this)}></input><br></br> 10 11 {/* 12 对于箭头函数绑定过程的个人理解 13 使用箭头函数 this 被设置为当前箭头函数所在的上下文,其原理有点类似于下面的过程(并不是说过程就是这样的,只是原理与之类似,个人理解) 14 源代码: 15 <input type="button" onClick={(parameters)=>FunctionName(parameters)}/></input> 16 过程原理: 17 function anonymous(parameters){ 18 // 通过某种方式,将函数绑定当前上下文,将 this 设置为当前上下文(比如: FunctionName.bind(当前上下文)) 19 // 通过某种方式,将参数 parameters 传递给 FunctionName(比如:FunctionName(parameters)) 20 } 21 <input type="button" onClick=anonymous /></input> 22 */} 23 <input type="button" value="childArrow 箭头函数传参 箭头函数绑定" onClick={(e)=>this.props.childArrow(e)}></input><br></br> 24 25 {/* 通过箭头函数的方式,事件对象必须显式的进行传递,但是通过 bind 的方式,事件对象以及更多的参数将会被隐式的进行传递。 */} 26 <input type="button" value="childBind 直接传参 bind 绑定" onClick={this.props.childBind.bind(this)}></input> 27 </div> 28 ) 29 } 30 }
运行结果:可以看到,在没有用到事件处理程序的 this 时,无论是父组件还是子组件中,若没有绑定事件处理程序会报错,这是由于函数从父组件传递到子组件后,子组件需要调用传递过来的函数(子组件要调用传递过来的函数就要用到 this ,因此匿名函数需要绑定当前上下文。又由于需要传递一个事件参数,无论是通过使用箭头函数还是使用 bind ,都会完成对事件处理程序的绑定),因此几种情况都要绑定,前者是绑定匿名函数,后两者是对事件处理程序进行绑定。

2、用到事件处理程序的 this 时
由于不需要用到事件处理程序的 this 时都需要绑定事件处理程序,因此要用到事件处理程序的 this 的情况下必然要绑定事件处理程序,用法与上面相同。
3、给事件处理程序传递多个参数,参数没有事件对象,只有其他参数时
父组件代码如下:
1 var React = require('react'); 2 var ReactDOM = require('react-dom'); 3 import BodyChild from './components/bodychild'; 4 class Index extends React.Component { 5 6 constructor(){ 7 super(); 8 this.state={ 9 p1:"等待第一个数据", 10 p2:"等待第二个数据" 11 } 12 } 13 14 parentAnonymous(param1,param2){ 15 this.setState({ 16 p1:param1, 17 p2:param2 18 }) 19 } 20 21 parentArrow(param1,param2){ 22 this.setState({ 23 p1:param1, 24 p2:param2 25 }) 26 } 27 28 parentBind(param1,param2){ 29 this.setState({ 30 p1:param1, 31 p2:param2 32 }) 33 } 34 35 render() { 36 return ( 37 <div> 38 <p>从子组件中获取到的数据:<b>参数一:</b>{this.state.p1} ,<b>参数二:</b> {this.state.p2}</p> 39 <BodyChild 40 // 使用匿名函数的方式 匿名函数后面的 bind(this) 是传入当前上下文,使得匿名函数内的 this 为当前上下文 41 childAnonymous={function(param1,param2){this.parentBind(param1,param2)}.bind(this)} 42 // 箭头函数将函数 this 设置为当前上下文 43 childArrow={(param1,param2)=>this.parentArrow(param1,param2)} 44 // 使用 bind 将函数 this 设置为当前上下文 45 childBind={this.parentBind.bind(this)} 46 /> 47 </div> 48 ); 49 } 50 } 51 ReactDOM.render( 52 <Index/>, document.getElementById('example'));
子组件代码如下:
1 import React from 'react'; 2 export default class BodyChild extends React.Component{ 3 4 constructor(props){ 5 super(props); 6 this.state={ 7 name:"anonymous", 8 age:20, 9 nameforarrow:"arrow", 10 ageforarrow:"99+", 11 nameforbind:"bind", 12 ageforbind:"81192/81194", 13 } 14 } 15 16 render(){ 17 return( 18 <div> 19 {/* 使用匿名函数的方式 匿名函数后面的 bind(this) 是传入当前上下文,使得匿名函数内的 this 为当前上下文*/} 20 <input type="button" value="匿名函数 bind 绑定" onClick={function(){this.props.childAnonymous(this.state.name,this.state.age)}.bind(this)}></input> 21 {/* 通过箭头函数的方式 */} 22 <input type="button" value="箭头函数传参 箭头函数绑定" onClick={()=>this.props.childArrow(this.state.nameforarrow,this.state.ageforarrow)}></input> 23 {/* 通过 bind 的方式,虽然本例中不需要传递事件对象,但是事件对象以及更多的参数将会被隐式的进行传递 */} 24 <input type="button" value="直接传参 bind 绑定" onClick={this.props.childBind.bind(this,this.state.nameforbind,this.state.ageforbind)}></input> 25 </div> 26 ) 27 } 28 } 29 30
运行结果:
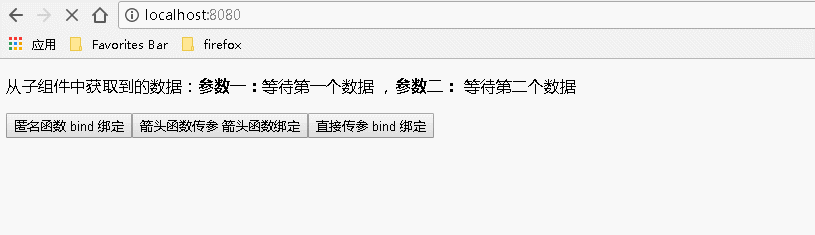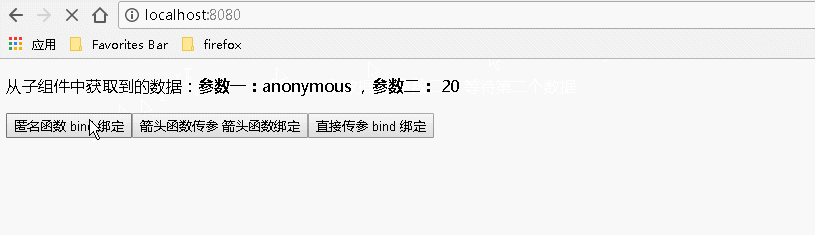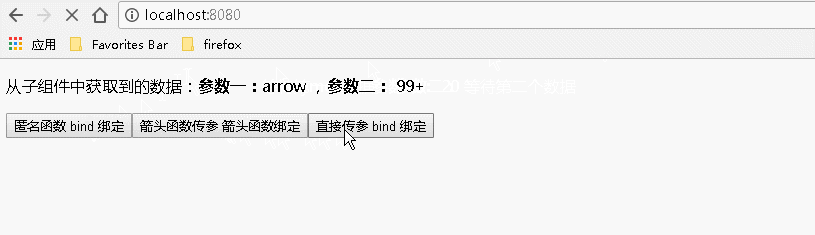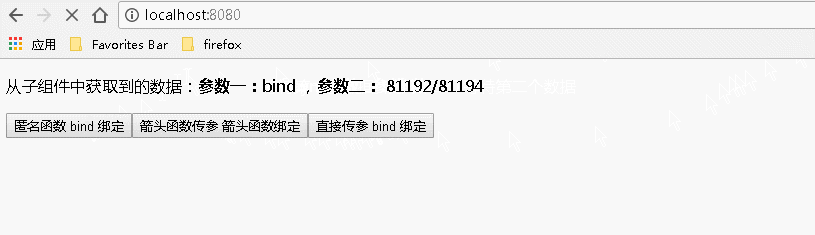
4、给事件处理程序传递的多个参数既有事件对象又有其他参数时
父组件代码如下:
1 var React = require('react'); 2 var ReactDOM = require('react-dom'); 3 import BodyChild from './components/bodychild'; 4 class Index extends React.Component { 5 6 constructor(){ 7 super(); 8 this.state={ 9 value:"等待与事件有关的数据", 10 p1:"等待第一个数据", 11 p2:"等待第二个数据" 12 } 13 } 14 15 // 由于通过箭头函数的方式,事件对象必须显式的进行传递,在子组件中 e 为第一个参数,传参格式如下 16 parentEventHandler(e,param1,param2){ 17 this.setState({ 18 value:e.target.value, 19 p1:param1, 20 p2:param2 21 }) 22 } 23 24 // 通过 bind 方式向监听函数传参,在类组件中定义的监听函数,事件对象 e 要排在所传递参数的后面,传参格式如下 25 parentEventHandlerForBind(param1,param2,e){ 26 this.setState({ 27 value:e.target.value, 28 p1:param1, 29 p2:param2 30 }) 31 } 32 33 render() { 34 return ( 35 <div> 36 <p>从子组件中获取到的数据:<b>值:</b>{this.state.value} ,<b>参数一:</b>{this.state.p1} ,<b>参数二:</b> {this.state.p2}</p> 37 <BodyChild 38 // 箭头函数将函数 this 设置为当前上下文 39 childArrow={(e,param1,param2)=>this.parentEventHandler(e,param1,param2)} 40 // 使用 bind 将函数 this 设置为当前上下文 41 childBind={this.parentEventHandlerForBind.bind(this)} 42 // 也可以通过匿名函数绑定后传参 childBind={function(param1,param2,e){this.parentEventHandlerForBind(param1,param2,e)}.bind(this)} 43 /> 44 </div> 45 ); 46 } 47 } 48 ReactDOM.render( 49 <Index/>, document.getElementById('example'));
子组件代码如下:
1 import React from 'react'; 2 export default class BodyChild extends React.Component{ 3 4 constructor(props){ 5 super(props); 6 this.state={ 7 name:"Guang", 8 age:20, 9 nameforbind:"Guang Zai", 10 ageforbind:"99+" 11 } 12 } 13 14 render(){ 15 return( 16 <div> 17 {/* 通过箭头函数的方式,事件对象必须显式的进行传递 */} 18 <input type="button" value="箭头函数传参 箭头函数绑定" onClick={(e)=>this.props.childArrow(e,this.state.name,this.state.age)}></input><br></br> 19 20 {/* 通过 bind 的方式,事件对象以及更多的参数将会被隐式的进行传递 */} 21 <input type="button" value="直接传参 bind 绑定" onClick={this.props.childBind.bind(this,this.state.nameforbind,this.state.ageforbind)}></input> 22 23 </div> 24 ) 25 } 26 }
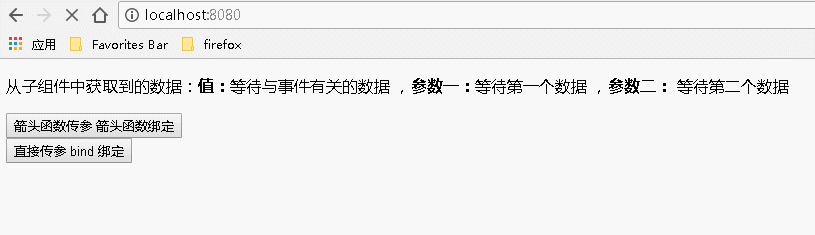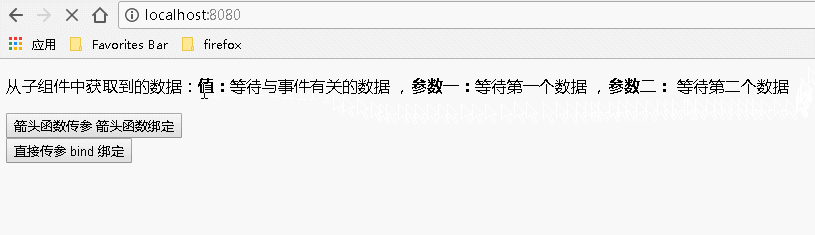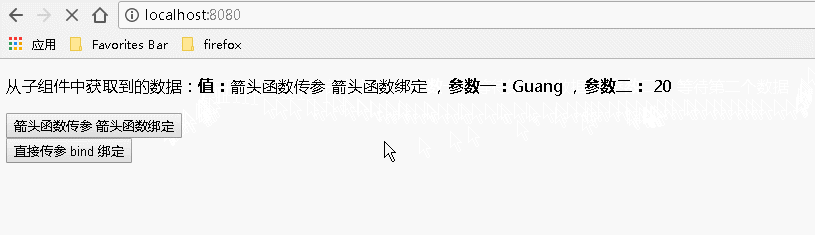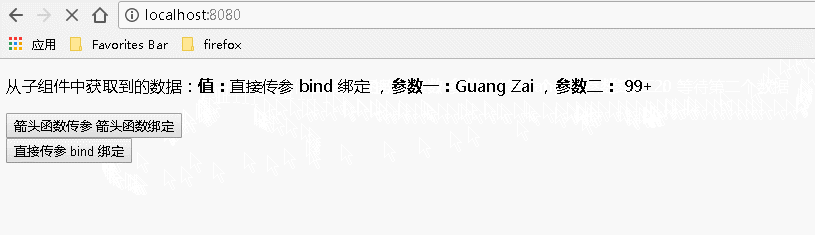
运行结果如下: