迪杰斯特拉算法
迪杰斯特拉算法是由荷兰计算机科学家狄克斯特拉于1959 年提出的,因此又叫狄克斯特拉算法。是从一个顶点到其余各顶点的最短路径算法,解决的是有向图中最短路径问题。迪杰斯特拉算法主要特点是以起始点为中心向外层层扩展,直到扩展到终点为止。具体的计算规则我们可以通过下图进行查看。
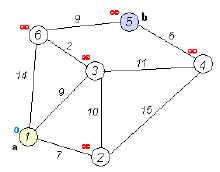
通过这幅图我们可以简单的理解迪杰斯特拉算法算法的基础思路,下面我们就通过JAVA来实现这个算法。
算法实现
在迪杰斯特拉算法中我们需要保存从起点开始到每一个节点最短步长,这也是图中需要比较得出的步长,同时我们还需要存储该步长下的前一个节点是哪个,这样我们就可以通过终点一个一个往前推到起点,这样就出来了完整的最优路径。
每一个节点的最优前一节点
public class PreNode {
private String preNodeName;//最优的前一个节点
private int nodeStep;// 起点到前一个节点的步长+前一个节点本身的步长
public PreNode(String preNodeName, int nodeStep) {
this.preNodeName = preNodeName;
this.nodeStep = nodeStep;
}
public String getPreNodeName() {
return preNodeName;
}
public void setPreNodeName(String preNodeName) {
this.preNodeName = preNodeName;
}
public int getNodeStep() {
return nodeStep;
}
public void setNodeStep(int nodeStep) {
this.nodeStep = nodeStep;
}
}
定义返回的数据结构
package dijkstra;
import java.util.List;
public class MinStep {
private boolean reachable;// 是否可达
private int minStep;// 最短步长
private List<String> step;// 最短路径
public MinStep() {
}
public MinStep(boolean reachable, int minStep) {
this.reachable = reachable;
this.minStep = minStep;
}
public boolean isReachable() {
return reachable;
}
public void setReachable(boolean reachable) {
this.reachable = reachable;
}
public int getMinStep() {
return minStep;
}
public void setMinStep(int minStep) {
this.minStep = minStep;
}
public List<String> getStep() {
return step;
}
public void setStep(List<String> step) {
this.step = step;
}
}
定义接口
package dijkstra;
import java.util.HashMap;
public interface Distance {
public static final MinStep UNREACHABLE = new MinStep(false, -1);
/**
* @param start
* @param end
* @param stepLength
* @return
* @Description: 起点到终点的最短路径
*/
public MinStep getMinStep(String start, String end, final HashMap<String, HashMap<String, Integer>> stepLength);
}
功能实现
package dijkstra;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
public class DistanceDijkstraImpl implements Distance {
// 图中相邻两个节点的距离
private HashMap<String, HashMap<String, Integer>> stepLength;
// 非独立节点个数
private int nodeNum;
// 移除节点
private HashSet<String> outNode;
// 起点到各点的步长,key为目的节点,value为到目的节点的步长
private HashMap<String, PreNode> nodeStep;
// 下一次计算的节点
private LinkedList<String> nextNode;
// 起点、终点
private String startNode;
private String endNode;
/**
* @param start
* @param end
* @param stepLength
* @return
* @Description: start 到 end 的最短距离
*/
public MinStep getMinStep(String start, String end, final HashMap<String, HashMap<String, Integer>> stepLength) {
this.stepLength = stepLength;
this.nodeNum = this.stepLength != null ? this.stepLength.size() : 0;
// 起点、终点不在目标节点内,返回不可达
if (this.stepLength == null || (!this.stepLength.containsKey(start)) || (!this.stepLength.containsKey(end))) {
return UNREACHABLE;
}
initProperty(start, end);
step();
if (nodeStep.containsKey(end)) {
return changeToMinStep();
}
return UNREACHABLE;
}
/**
* 返回最短距离以及路径
*/
private MinStep changeToMinStep() {
MinStep minStep = new MinStep();
minStep.setMinStep(nodeStep.get(endNode).getNodeStep());
minStep.setReachable(true);
LinkedList<String> step = new LinkedList<String>();
minStep.setStep(step);
// 先将终点添加到路径第一位中
String tempNode = endNode;
step.addFirst(tempNode);
// 再将所经过的节点添加到路径第一位中
while (nodeStep.containsKey(tempNode)) {
PreNode preNode = nodeStep.get(tempNode);
String preNodeName = preNode.getPreNodeName();
// System.out.println(preNodeName + " " + preNode.getNodeStep());
step.addFirst(preNodeName);
tempNode = preNodeName;
}
return minStep;
}
/**
* @param start
* @Description: 初始化属性
*/
private void initProperty(String start, String end) {
outNode = new HashSet<String>();
nodeStep = new HashMap<String, PreNode>();
nextNode = new LinkedList<String>();
nextNode.add(start);
startNode = start;
endNode = end;
}
/**
* @param end
* @Description:
*/
private void step() {
if (nextNode == null || nextNode.size() < 1) {
return;
}
if (outNode.size() == nodeNum) {
return;
}
// 获取下一个计算节点
String start = nextNode.removeFirst();
// 到达该节点的最小距离
int step = 0;
if (nodeStep.containsKey(start)) {
step = nodeStep.get(start).getNodeStep();
}
// 获取该节点可达节点
HashMap<String, Integer> nextStep = stepLength.get(start);
Iterator<Entry<String, Integer>> iter = nextStep.entrySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Entry<String, Integer> entry = iter.next();
String key = entry.getKey();
// 如果是起点到起点,不计算之间的步长
if (key.equals(startNode)) {
continue;
}
// 起点到可达节点的距离
Integer value = entry.getValue() + step;
if ((!nextNode.contains(key)) && (!outNode.contains(key))) {
nextNode.add(key);
}
if (nodeStep.containsKey(key)) {
// 比较步长
if (value < nodeStep.get(key).getNodeStep()) {
nodeStep.put(key, new PreNode(start, value));
}
} else {
nodeStep.put(key, new PreNode(start, value));
}
}
// 将该节点移除
outNode.add(start);
// 计算下一个节点
step();
}
}
step()逻辑解析
这一步也就是迪杰斯特拉算法的核心部分,在计算的过程中,我们需要进行如下步骤:
1)判断是否达到终止条件,如果达到终止条件,结束本次算法,如果没有达到,执行下一步;(终止条件:下一次需要计算的节点队列没有数据或已经计算过的节点数等于节点总数)
2)获取下一次计算的节点A;
3)从起点到各节点之间的最短距离map中获取到达A点的最小距离L;
4)获取A节点的可达节点B,计算从起点先到A再到B是否优于已有的其他方式到B,如果优于,则更新B节点,否则不更新;
5)判断B是否是已经移除的节点,如果不是移除的节点,把B添加到下一次需要计算的节点队列中,否则不做操作;
6)判断A节点是否还有除B以外的其他节点,如果有,执行第4)步,否则执行下一步;
7)将A节点从下一次需要计算的节点中移除添加到已经计算过的节点中;
8)执行第一步。
Demo运行
import java.util.HashMap;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
public class DistanceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
HashMap<String, HashMap<String, Integer>> stepLength = new HashMap<String, HashMap<String, Integer>>();
HashMap<String, Integer> step1 = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
stepLength.put("1", step1);
step1.put("2", 2);
HashMap<String, Integer> step2 = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
stepLength.put("2", step2);
step2.put("1", 2);
step2.put("3", 1);
HashMap<String, Integer> step3 = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
stepLength.put("3", step3);
step3.put("2", 1);
step3.put("4", 1);
step3.put("9", 1);
HashMap<String, Integer> step4 = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
stepLength.put("4", step4);
step4.put("5", 1);
step4.put("3", 1);
HashMap<String, Integer> step5 = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
stepLength.put("5", step5);
step5.put("4", 1);
HashMap<String, Integer> step6 = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
stepLength.put("6", step6);
step6.put("9", 1);
HashMap<String, Integer> step7 = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
stepLength.put("7", step7);
step7.put("10", 1);
HashMap<String, Integer> step8 = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
stepLength.put("8", step8);
step8.put("11", 3);
HashMap<String, Integer> step9 = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
stepLength.put("9", step9);
step9.put("3", 1);
step9.put("6", 1);
step9.put("10", 1);
HashMap<String, Integer> step10 = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
stepLength.put("10", step10);
step10.put("9", 1);
step10.put("7", 1);
step10.put("11", 1);
HashMap<String, Integer> step11 = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
stepLength.put("11", step11);
step11.put("8", 3);
step11.put("10", 1);
System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSON(stepLength));
Distance distance = new DistanceDijkstraImpl();
MinStep step = distance.getMinStep("1", "5", stepLength);
System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSON(step));
step = distance.getMinStep("1", "8", stepLength);
System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSON(step));
step = distance.getMinStep("8", "1", stepLength);
System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSON(step));
step = distance.getMinStep("11", "7", stepLength);
System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSON(step));
step = distance.getMinStep("10", "8", stepLength);
System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSON(step));
}
}
{“11”:{“8”:1,“10”:1},“1”:{“2”:2},“2”:{“1”:2,“3”:1},“3”:{“4”:1,“9”:1,“2”:1},“4”:{“5”:1,“3”:1},“5”:{“4”:1},“6”:{“9”:1},“7”:{“10”:1},“8”:{“11”:1},“9”:{“6”:1,“3”:1,“10”:1},“10”:{“11”:1,“9”:1,“7”:1}}
{“minStep”:5,“step”:[“1”,“2”,“3”,“4”,“5”],“reachable”:true}
{“minStep”:7,“step”:[“1”,“2”,“3”,“9”,“10”,“11”,“8”],“reachable”:true}
{“minStep”:7,“step”:[“8”,“11”,“10”,“9”,“3”,“2”,“1”],“reachable”:true}
{“minStep”:2,“step”:[“11”,“10”,“7”],“reachable”:true}
{“minStep”:2,“step”:[“10”,“11”,“8”],“reachable”:true}
