(一)timer库的简介
timer是一个很小的库,提供简单的时间度量和进度显示功能,也可用于性能测试等计时任务。timer库包含三个组件:计时器类timer、progress_timer和进度指示类progress_display。
(二)timer类
timer类可以测量时间的流逝,是一个小型的计时器,提供毫秒级别的计时精度和操作函数。它位于boost命名空间下。使用时需要包含头文件:
include <boost/timer.hpp>
(1)timer的使用
#include <boost/timer.hpp> #include <iostream> int main(int argc,char * argv[]){ boost::timer t; //获取timer能够表示的最大时间精度 std::cout<<"max timespan : "<<t.elapsed_max()/3600<<"h"<<std::endl; //获取timer能够表示的最小时间精度 std::cout<<"min timespan : "<<t.elapsed_min()<<"s"<<std::endl; std::cout<<"now time elapsed : "<<t.elapsed()<<"s"<<std::endl; return 0; }

timer对象一旦被声明,它的构造函数就启动了计时工作,之后可以调用elapsed()函数获得从对象创建到elapsed()函数调用这段时间间隔。
(2)timer的源码
// boost timer.hpp header file ---------------------------------------------// // Copyright Beman Dawes 1994-99. Distributed under the Boost // Software License, Version 1.0. (See accompanying file // LICENSE_1_0.txt or copy at http://www.boost.org/LICENSE_1_0.txt) // See http://www.boost.org/libs/timer for documentation. // Revision History // 01 Apr 01 Modified to use new <boost/limits.hpp> header. (JMaddock) // 12 Jan 01 Change to inline implementation to allow use without library // builds. See docs for more rationale. (Beman Dawes) // 25 Sep 99 elapsed_max() and elapsed_min() added (John Maddock) // 16 Jul 99 Second beta // 6 Jul 99 Initial boost version #ifndef BOOST_TIMER_HPP #define BOOST_TIMER_HPP #include <boost/config.hpp> #include <ctime> #include <boost/limits.hpp> # ifdef BOOST_NO_STDC_NAMESPACE namespace std { using ::clock_t; using ::clock; } # endif namespace boost { // timer -------------------------------------------------------------------// // A timer object measures elapsed time. // It is recommended that implementations measure wall clock rather than CPU // time since the intended use is performance measurement on systems where // total elapsed time is more important than just process or CPU time. // Warnings: The maximum measurable elapsed time may well be only 596.5+ hours // due to implementation limitations. The accuracy of timings depends on the // accuracy of timing information provided by the underlying platform, and // this varies a great deal from platform to platform. class timer { public: timer() { _start_time = std::clock(); } // postcondition: elapsed()==0 // timer( const timer& src ); // post: elapsed()==src.elapsed() // ~timer(){} // timer& operator=( const timer& src ); // post: elapsed()==src.elapsed() void restart() { _start_time = std::clock(); } // post: elapsed()==0 double elapsed() const // return elapsed time in seconds { return double(std::clock() - _start_time) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; } double elapsed_max() const // return estimated maximum value for elapsed() // Portability warning: elapsed_max() may return too high a value on systems // where std::clock_t overflows or resets at surprising values. { return (double((std::numeric_limits<std::clock_t>::max)()) - double(_start_time)) / double(CLOCKS_PER_SEC); } double elapsed_min() const // return minimum value for elapsed() { return double(1)/double(CLOCKS_PER_SEC); } private: std::clock_t _start_time; }; // timer } // namespace boost #endif // BOOST_TIMER_HPP
注意:timer中使用了CLOCKS_PER_SEC宏,这个宏在win32下值是1000,而在linux下值是1000000,也就是说它具体平台或编译器相关,所以不适合跨平台使用,也不适合做大跨度时间的测量。
(二)progress_timer类
progress_timer继承自timer,它在析构时自动输出时间。位于boost命名空间下,使用时包含头文件:#include <boost/progress.hpp>。其它用法和timer类似。
如果要在程序中测量一段代码运行时间,可以将这段代码用{}包含起来,同时在{}中一行代码为定义一个progress_timer的对象。
{ boost::progress_timer t; //析构时自动输出时间间隔(从对象创建到析构) //do something... }
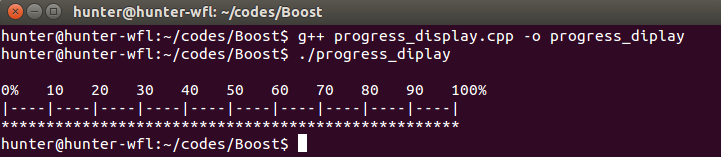
(三)progress_display类
progress_display可以在控制台上显示程序的执行进度。位于boost命名空间下,使用时加入头文件:#include <boost/progress.hpp>即可。
它是一个独立的类,与timer和progress_timer没有联系。
#include <iostream> #include <boost/progress.hpp> int main(int argc,char * argv[]){ //声明基数大小为100 boost::progress_display pd(100); for(int i=0;i<100;i++){ ++pd; } return 0; }