在贴源码之前先介绍一个将要用到的很重要的函数--pcap_open(),下面是pcap_open()在remote-ex.h中的声明:
pcap_t *pcap_open(const char *source, int snaplen, int flags, int read_timeout, struct pcap_rmtauth *auth, char *errbuf);
第一个参数不用多说,它表示的是设备的名称。在获取适配器链表后,通过返回数据域name即可知道设备的名称。
第二个参数制定要捕获数据包中的哪些部分。技术文档中介绍说,在一些操作系统中,驱动可以被配置成只捕获数据包的初始化部分,它的好处就是可以减少应用程序间复制数量的量,从而提高捕获效率。下面将要给出的实例程序中设为65535。我们知道对于使用以太网的局域网来说,最大传输单元为1500字节,那么设为65535则能保证收到完整的数据包。
第三个参数是最重要的一个值,它用来指示适配器是否需要设置成混杂模式,这里引用一下技术文档中对设置混杂模式的说明:
一般情况下,适配器只接收发给它自己的数据包, 而那些在其他机器之间通讯的数据包,将会被丢弃。 相反,如果适配器是混杂模式,那么不管这个数据包是不是发给我的,我都会去捕获。也就是说,我会去捕获所有的数据包。 这意味着在一个共享媒介(比如总线型以太网),WinPcap能捕获其他主机的所有的数据包。 大多数用于数据捕获的应用程序都会将适配器设置成混杂模式,所以,我们也会在下面的范例中,使用混杂模式。
它的意思就是说设置混杂模式可以捕获到所有经过适配器的数据包,不论是不是发给机器本身的。PCAP_OPENFLAG_PROMISCUOUS这个值就是设置成混杂模式的意思。
第四个参数表示的是读取数据的超时时间,单位是毫秒。意思就是说会在read_timeout时间内对适配器的读取操作进行响应,不管有没有读到数据。这里有两个特殊的值需要说明一下,如果将时间设置为0意味着没有超时,那么如果没有数据到达的话,读操作就永远不会返回;如果设置为-1则恰恰相反,不论有没有读到数据都会立即返回。
第五个参数之前提到过,它表示的是连接远程用户的验证信息,由于我们不需要连接到远程用户,这里置为NULL。
第六个参数是错误信息缓冲,如果该函数在调用过程中出错则会将出错信息保存在缓冲中。
函数的返回值是一个pcap_t的指针类型,查看声明处我们可以发现pcap_t实际上是pcap结构体,而文档上说明它是一个已打开的捕捉实例的描述符。这个结构体对用户来说是不透明的(我们查看pcap的声明处是找不到的),它通过wpcap.dll提供的函数,维护了它的内容。
下面我们来看一下这个程序的代码!
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <string.h> 4 #define HAVE_REMOTE 5 #include <pcap.h> 6 7 /* packet handler 函数原型 */ 8 void packet_handler(u_char *param, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *pkt_data); 9 10 int main() 11 { 12 pcap_if_t *alldevs; 13 pcap_if_t *d; 14 int inum; 15 int i=0; 16 pcap_t *adhandle; 17 char errbuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE]; 18 19 /* 获取本机设备列表 */ 20 if (pcap_findalldevs_ex(PCAP_SRC_IF_STRING, NULL, &alldevs, errbuf) == -1) 21 { 22 fprintf(stderr,"Error in pcap_findalldevs: %s ", errbuf); 23 exit(1); 24 } 25 26 /* 打印列表 */ 27 for(d=alldevs; d; d=d->next) 28 { 29 printf("%d. %s", ++i, d->name); 30 if (d->description) 31 printf(" (%s) ", d->description); 32 else 33 printf(" (No description available) "); 34 } 35 36 if(i==0) 37 { 38 printf(" No interfaces found! Make sure WinPcap is installed. "); 39 return -1; 40 } 41 42 printf("Enter the interface number (1-%d):",i); 43 scanf("%d", &inum); 44 45 if(inum < 1 || inum > i) 46 { 47 printf(" Interface number out of range. "); 48 /* 释放设备列表 */ 49 pcap_freealldevs(alldevs); 50 return -1; 51 } 52 53 /* 跳转到选中的适配器 */ 54 for(d=alldevs, i=0; i< inum-1 ; d=d->next, i++); 55 56 /* 打开设备 */ 57 if ( (adhandle= pcap_open(d->name, // 设备名 58 65535, // 65535保证能捕获到不同数据链路层上的每个数据包的全部内容 59 PCAP_OPENFLAG_PROMISCUOUS, // 混杂模式 60 1000, // 读取超时时间 61 NULL, // 远程机器验证 62 errbuf // 错误缓冲池 63 ) ) == NULL) 64 { 65 fprintf(stderr," Unable to open the adapter. %s is not supported by WinPcap ", d->name); 66 /* 释放设备列表 */ 67 pcap_freealldevs(alldevs); 68 return -1; 69 } 70 71 printf(" listening on %s... ", d->description); 72 73 /* 释放设备列表 */ 74 pcap_freealldevs(alldevs); 75 76 /* 开始捕获 */ 77 pcap_loop(adhandle, 0, packet_handler, NULL); 78 79 return 0; 80 } 81 82 83 /* 每次捕获到数据包时,libpcap都会自动调用这个回调函数 */ 84 void packet_handler(u_char *param, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *pkt_data) 85 { 86 struct tm *ltime; 87 char timestr[16]; 88 time_t local_tv_sec; 89 90 /* 将时间戳转换成可识别的格式 */ 91 local_tv_sec = header->ts.tv_sec; 92 ltime=localtime(&local_tv_sec); 93 strftime( timestr, sizeof timestr, "%H:%M:%S", ltime); 94 95 printf("%s,%.6ld len:%d ", timestr, header->ts.tv_usec, header->len); 96 97 }
引用一下文档里面对于pcap_loop()函数的介绍:
Collect a group of packets.
pcap_loop() is similar to pcap_dispatch() except it keeps reading packets until cnt packets are processed or an error occurs. It does not return when live read timeouts occur. Rather, specifying a non-zero read timeout to pcap_open_live() and then callingpcap_dispatch() allows the reception and processing of any packets that arrive when the timeout occurs. A negative cnt causespcap_loop() to loop forever (or at least until an error occurs). -1 is returned on an error; 0 is returned if cnt is exhausted; -2 is returned if the loop terminated due to a call to pcap_breakloop() before any packets were processed. If your application uses pcap_breakloop(), make sure that you explicitly check for -1 and -2, rather than just checking for a return value < 0.
大致就是说pcap_loop()函数是用来捕获一组数据分组的。pcap_loop()函数跟pcap_dispath()函数很类似,唯一不同之处就是pcap_loop()会一直读数据直到cnt数据被处理或者出现错误。不论读取时间是否超时它都不返回。当然有一种特殊情况,就是在调用pcap_open_live()函数时指定非0的读取超时时间,调用pcap_dispath()函数可以在超时发生时对读到的数据进行接收和处理。将cnt设为正数可以使pcap_loop()一直循环(或至少到错误发生之前)。返回-1则出错;返回0则说明cnt被耗尽;返回-2则是由于在数据被处理之前调用pcap_breakloop()来中断循环。如果你的应用程序使用了pcap_breakloop()函数,你需要对返回值-1和-2进行详细的检查,而不是只检查<0的情况。(如果翻译有误还请指正!!!)
文档里说得很详细,看得也是一头雾水,也不知道究竟在说些什么。简单来讲就是说,pcap_loop()只有当cnt数据包被捕获时才会返回,即它会在一小段时间内阻塞网络的利用。pcap_loop()函数的第三个参数很重要,它是一个回调函数的函数指针,即pcap_loop()函数返回时会自动调用这个回调函数。这个回调函数的参数类型是规定好的:
typedef void (*pcap_handler)(u_char *, const struct pcap_pkthdr *,
const u_char *);
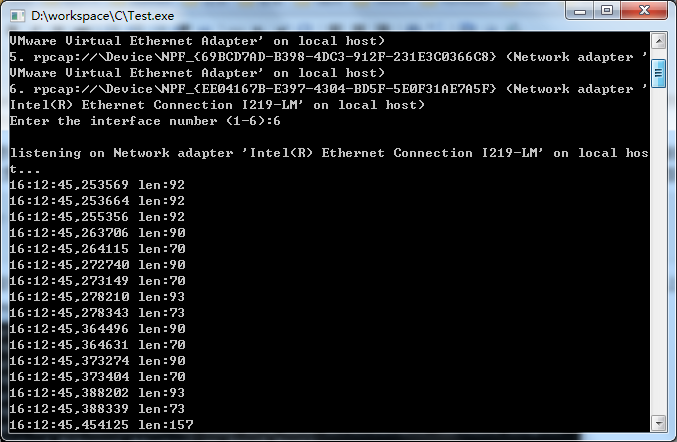
这个程序当中我们只用到了第二个参数,将每一个数据包的时间戳和长度从它的首部当中解析出来,并打印在屏幕上。细节的东西就不赘述了,看一下运行的结果:
输入6并按回车,开始捕获数据并打印: