一、JavaScript简介:
概念:JavaScript是一种解释性的、跨平台的、基于对象的脚本语言,一般用于客户端来给HTML页面增加动态的功能。
组成:
1.ECMAScript,描述了该语言的语法和基本对象
2.DOM 文档对象模型,描述处理网页内容的方法和接口
3.BOM 浏览器对象模型,描述与浏览器进行交互的方法和接口。
二、JavaScript
1.js的引入方式
1.1 放在HTML的<head>部分
1.2 放在HTML的<body>部分
1.3 从外部文件引入:
<script src="myScript.js"></script>
2.变量
2.1变量的声明:
使用“var”关键字来声明变量
声明时赋值var x=1
或先声明后赋值:var x; x=1
对于没有赋值的变量,其值为:undefined
2.2变量的命名规则:
英文字母、数字、下划线
2.3变量名格式:
匈牙利命名法:变量名=类型+对象描述 例:var sname="hello"; var nage=18
驼峰命名法:
全部小写,单词用下划线分割
每个单词首字母大写
首字母小写,其他单词首字母大写
2.4作用域:
局部作用域:函数内部定义
全局作用域: 函数外定义
优先级:局部变量>全局变量
3.运算符
3.1算数运算符 + - * 、 % ++ --
/* var a=1 b = a++ //先赋值后加减 alert(b) //b=1 alert(a) //a=2 */ /* var a=1 b=++a //先加减后赋值 alert(b) //b=2 alert(a) //a=2 */ /* var x=1 alert(x++) x=x+1 先赋值,x=1 alert结果为1 ,执行完成后x=2 alert(++x) 此时x=2,先加减后赋值,alert结果为3 x=3 alert(--x) 先加减,后赋值,此时alert结果为2 alert(x--) */
3.2赋值运算符 += -= *= /= %=
3.3关系运算符 == != ===
alert(2=="2") --> true alert(2==="2") -->flase ===不进行数据转换,直接进行比较
var s="hello" alert(typeof(s)) // typeof:只能判断基础数据类型,对于对象无法准确判断具体是什么对象 var s2=new String("hello") alert(typeof(s2)) alert(s2 instanceof String);
3.4逻辑运算符 ! && ||
3.5位运算符 ~ & | ^ << >>
3.5一元加减法:
<!--一元加减法-->
var a=3
b=+a
alert(b)
alert(typeof(b))
<!--可以对数据类型进行转换-->
var a="3"
b=+a
alert(b)
alert(typeof(b))
<!--有非数字类型,转换失败-->
var a="3a"
b=+a
alert(b)
alert(typeof(b))
4.基本数据类型
number
string
Boolean
null
undefined
5.流程语句
5.1 while
<script type="text/javascript"> i=0 while (i<5) { // statement console.log(i) i++ } </script>
5.2 do while
<script type="text/javascript"> i=0 do{ //至少执行一次循环 console.log(i) i++ } while (i<5); </script>
5.3 for
<script type="text/javascript">
for (var i=0; i<5; i++) {
console.log(i)
}
</script>
5.4 for in
<script type="text/javascript">
for (i in [1,2,3,4]) {
console.log(i)
}
</script>
5.5 if else
1 <head> 2 <meta charset="utf-8"> 3 <title>JavaScript</title> 4 </head> 5 <body> 6 7 <script type="text/javascript"> 8 var d = new Date(); 9 var time = d.getHours(); 10 if (time<10) 11 { 12 document.write("<b>早上好</b>"); 13 } 14 else if (time>=10 && time<14) 15 { 16 document.write("<b>中午好</b>"); 17 } 18 else 19 { 20 document.write("<b>下午好!</b>"); 21 } 22 </script> 23 </body> 24 </html>
5.6 switch
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>JavaScript</title> </head> <body> <button onclick="myFunction()">今天是周几?</button> <p id="demo"></p> <script> function myFunction(){ var x; var d=new Date().getDay(); switch (d){ case 0:x="今天是星期日"; break; case 1:x="今天是星期一"; break; case 2:x="今天是星期二"; break; case 3:x="今天是星期三"; break; case 4:x="今天是星期四"; break; case 5:x="今天是星期五"; break; case 6:x="今天是星期六"; break; } document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML=x; } </script> </body> </html>
5.7 异常处理
function func (argument) { try { console.log('hello') if(true){ throw "主动抛出错误" } } catch(e) { alert(e); } finally { console.log("执行完毕") } } func()
5.8 continue break default
6.对象
6.1 Number
var num=new Number(15) console.log(num) console.log(num.toString()) //数字转字符串 console.log(num.toString(2)) //数字转2进制 console.log(num.toString(8)) //数字转8进制 console.log(num.toString(16)) //数字转16进制
6.2 String
var str1=new String("hello"); var str2=" world"; //属性 console.log(str1.length); //字符串的长度 // 方法 //获取指定字符串 console.log(str1.charAt('1')); //返回在指定位置的字符。 //查找 console.log(str1.indexOf('l')); //返回某个指定的字符串值在字符串中首次出现的位置。 console.log(str1.lastIndexOf('l')); //从后向前搜索字符串,并从起始位置(0)开始计算返回字符串最后出现的位置。 console.log(str1.replace('e','a')); //替换 console.log(str1.slice(1,3)); //切片[start,end) console.log(str1.substring(1,3)) //和slice相同 console.log(str.split(" ")); //把字符串分割为字符串数组。 console.log(str1.substr(1,3)) //从起始索引号提取字符串中指定数目的字符 (index,num) //大小写转换 console.log("HELLO".toLowerCase(str1)) //转小写 console.log("hello".toUpperCase(str1)) //转大写 //编排方法 document.write(s.italics()); document.write(s.bold()); document.write(s.anchor()); console.log(" hello ".trim()) //去除字符串两边的空白 var str=str1.concat(str2);//字符串拼接 console.log(str);
6.3 Array
//声明 var cars = ["Volvo","Saab","BMW"]; //方法一 var arr1=[1,2,3,4]; //方法二 var arr3=new Array(); //方法三 var arr4=new Array(3,); //初始化一个长度为3的数组,该数组可变长 //属性 console.log(cars.length) //方法: //插入和删除 console.log([1,2,3].concat([4,5,6])) //数字合并 console.log(cars.join("#")) console.log(cars.pop()) //删除最后一个元素 console.log(cars.push('jeep')) //数组的末尾添加一个或更多元素,并返回新的长度 console.log(cars.shift()) //删除并返回数组的第一个元素 console.log(cars.unshift('abc')) //向数组的开头添加一个或更多元素,并返回新的长度。 console.log(cars) //排序 console.log(cars.reverse()) //反转数组顺序 console.log(cars.sort()) //数组排序 console.log(cars.toString()) //数组转字符串
6.4 Boolean
//方法 var bool = new Boolean(1); console.log(bool.toString()) console.log(bool.valueOf())
6.5 Date
//时间创建 var today = new Date() var d1 = new Date("October 13, 1975 11:13:00") var d2 = new Date(79,5,24) var d3 = new Date(79,5,24,11,33,0) console.log(today) console.log(d1) console.log(d2) console.log(d3) //方法 y=today.getFullYear() m=today.getMonth() d=today.getDate() H=today.getHours() M=today.getMinutes() S=today.getSeconds() console.log(y+'年'+m+'月' +d+'日'+" "+H+":"+M+":"+S) console.log(today.getTime())
6.6 Mtch
console.log(Math.abs(-2)) console.log(Math.max(1,3,5)) console.log(Math.min(1,3,5)) console.log(Math.random()) //[0.0,1.0)随机数 console.log(Math.round(2.5)); //四舍五入
6.7 RedExp
//语法 // var patt=new RegExp(pattern,modifiers); // 或者更简单的方式: // var patt=/pattern/modifiers; /* 修饰符 i 执行对大小写不敏感的匹配。 g 执行全局匹配(查找所有匹配而非在找到第一个匹配后停止)。 m 执行多行匹配。 */ var str="hello world" console.log(str.search("o")) //返回第一个匹配的索引值 console.log(str.search("a")) //没找到返回-1 console.log(str.match(/o/g)); console.log(/hello/g.test(str))
7.函数
7.1函数创建的三种方法
// 方法一 function func (argument) { return "hello" } console.log(func()) // 方法二:构造函数 var func = new Function("参数1", "参数2", "函数体") var func = new Function("a","b","return a+b") console.log(func(1,2)) // 方法三 匿名函数(函数表达式) console.log(function(x,y){return x+y}(3,5))
7.2函数调用
this 关键字:一般而言,在Javascript中,this指向函数执行时的当前对象。 void() // void的作用:阻拦方法的返回值 function f() { return 8 } alert(void(f()))
7.3参数
arguments对象 //遍历传入的参数 function func() { for (var i = 0; i<arguments.length; i++) { console.log(arguments[i]) } } func(1,2,3,4,5)
三、DOM
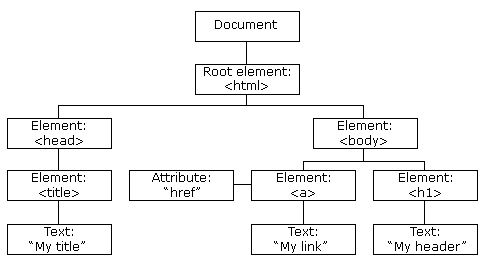
1.介绍
DOM (Document Object Model,文档对象模型):W3C定义的访问HTML和XML文档的标准
DOM组成:
核心DOM :针对任何结构化文档的标准模型
XML DOM :针对 XML 文档的标准模型
HTML DOM :针对 HTML 文档的标准模型
2.节点
文档节点
元素节点
文本节点
属性节点
注释节点
3.属性
3.1自身属性
nodeName
nodeValue
nodeType
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="h">
<p>hello</p>
<p>world</p>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
console.log(document.getElementById("h").nodeName)
console.log(document.getElementById("h").nodeValue)
console.log(document.getElementById("h").nodeType)
console.log(document.getElementById("h").innerHTML)
</script>
</body>
</html>
3.2导航属性
第一类:不建议使用,如果两个元素之间有文本(空格或换行)会把文本作为下一个元素
parentNode ☆
firstChild
lastChild
nextSibling
previousSibling
第二类:建议使用
getElementById("div1")
firstElementChild
lastElementChild;
nextElementSibling;
4.全局查找与局部查找
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>JavaScript</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<div class="div2">hello</div>
<div class="div3" name="name">world
<p>你好 世界!</p>
<p class="ppp">hello html</p>
</div>
<p>hello world</p>
</div>
<script>
//全局查找
//通过id查找
var e=document.getElementById("div1")
//通过class查找
var ele=document.getElementsByClassName("div2")[0] //结果是一个数组
var ele2=ele.nextElementSibling;
alert(ele2.innerHTML)
//通过标签查找
var ele3=document.getElementsByTagName("p");
alert(ele3[0].innerHTML)
//通过name查找
ele4=document.getElementsByName("name")
console.log(ele4[0].innerHTML)
//局部查找
//通过tag
var ele5=document.getElementsByClassName("div3");
var ele6=ele5[0].getElementsByTagName("p")
console.log(ele6[0].innerHTML)
//通过class
var ele7=ele5[0].getElementsByClassName("ppp")
console.log(ele7[0].innerHTML)
//不可以通过id和name进行局部查找
</script>
</body>
</html
5. DOM 修改、添加、删除
5.1创建HTML内容并改变样式
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<p id="p1"></p>
<script type="text/javascript">
document.getElementById("p1").innerHTML="hello world" //创建内容
document.getElementById("p1").style.color = 'blue'; //更改样式
</script>
</body>
</html>
5.2添加新的元素:appendChild()
<script>
//创建 <p> 元素:
var para = document.createElement("p");
// <p> 元素添加文本节点
var node = document.createTextNode("这是一个新的段落。");
//将文本节点添加到 <p> 元素中:
para.appendChild(node);
//查找已存在的元素
var element = document.getElementById("div1");
//添加到已存在的元素中:
element.appendChild(para);
</script>
5.3 插入到已有元素之前:insertBefore()
5.4 移除元素:removeChild()
5.5 替换元素:replaceChild()
6.事件
6.1鼠标事件
<p onclick="alert('单击')">单击鼠标</p>
<p ondblclick="alert('双击')">双击鼠标</p>
<p onmousedown="alert('鼠标按下')">鼠标按下</p>
<p onmouseup="alert('鼠标松开')">鼠标松开</p>
<p onmouseover="alert('放上鼠标')">鼠标移到元素之上。</p>
<p onmouseout="alert('移开鼠标')">鼠标移开</p>
6.2框架/对象事件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload=function () {
//把js代码写在头部,等页面加载完之后执行
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
6.3表单事件

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<input class="keyword" type="text" value="请输入查找内容" onfocus="func1()" blur="func2()">
<script>
//事件
// onfocus 获取焦点时触发
// onblur 失去焦点时触发
function func1 () {
// body...
var ky=document.getElementsByClassName("keyword")[0];
ky.value="";
}
function func2 () {
var ky=document.getElementsByClassName("keyword")[0];
if (ky.value.trim().length==0){
ky.value="请输入查找内容";
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<!-- //方法一 -->
<form id="form" onsubmit="return check()">
<!-- 方法二 -->
<!-- <form id="form"> -->
<input type="text" name="username">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
<script>
//阻止事件方法一
function check() {
/* body... */
alert("验证失败");
return false
}
//阻止事件方法二
// var f=document.getElementById("form")
// f.onsubmit=function () {
// /* body... */
// alert(123);
// return false
// }
</script>
</body>
</html>

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<select id="province" onchange="func(this)"></select>
<select id="city"></select>
<script>
data={"北京市":["海淀区","朝阳区"],"河北省":["石家庄","廊坊"]}
var pro=document.getElementById("province");
var city=document.getElementById("city");
for (var i in data){
var option_pro=document.createElement("option");
option_pro.innerHTML=i;
pro.appendChild(option_pro)
}
function func (self) {
// body...
var choice=self.options[self.selectedIndex].innerHTML;
//添加之前删除元素
// city.options.length=0;
options=city.children
for (var k=0; k<options.length; k++){
city.removeChild(options[k--]);
}
for (var i in data[choice]){
var option_city=document.createElement("option");
option_city.innerHTML=data[choice][i];
city.appendChild(option_city)
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
四、BOM(Browser Object Model,浏览器对象模型)
1.Window对象
表示浏览器窗口
属性: <script> var w=window.innerWidth || document.documentElement.clientWidth || document.body.clientWidth; var h=window.innerHeight || document.documentElement.clientHeight || document.body.clientHeight; x=document.getElementById("demo"); x.innerHTML="浏览器window宽度: " + w + ", 高度: " + h + "。" </script> 方法: window.alert("sometext"); window.confirm("sometext"); 例:r=window.confirm("是否取消?")
计时事件

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <button onclick="start()">开始</button> <button onclick="stop()">停止</button> <p>页面上显示时钟:</p> <p id="demo"></p> <hr> <p>点击第一个按钮等待3秒后出现"Hello"弹框。</p> <p>点击第二个按钮来阻止第一个函数运行。(你必须在3秒之前点击它)。</p> <button onclick="myFunction()">点我</button> <button onclick="myStopFunction()">停止弹框</button> <script> function start () { myVar=setInterval(function(){myTimer()},1000); } function myTimer(){ var d=new Date(); var t=d.toLocaleTimeString(); document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML=t; } function stop(){ clearInterval(myVar); } var myVar; function myFunction(){ myVar=setTimeout(function(){alert("Hello")},3000); } function myStopFunction(){ clearTimeout(myVar); } </script> </body> </html>
2.Screen对象
<script> document.write("总宽度/高度: "); document.write(screen.width + "*" + screen.height); document.write("<br>"); document.write("可用宽度/高度: "); document.write(screen.availWidth + "*" + screen.availHeight); document.write("<br>"); document.write("色彩深度: "); document.write(screen.colorDepth); document.write("<br>"); document.write("色彩分辨率: "); document.write(screen.pixelDepth); </script>
3.Location对象
location.hostname 返回 web 主机的域名 location.pathname 返回当前页面的路径和文件名 location.port 返回 web 主机的端口 (80 或 443) location.protocol 返回所使用的 web 协议(http:// 或 https://) location.href 属性返回当前页面的 URL。 location.pathname 属性返回 URL 的路径名。 location.assign() 方法加载新的文档。 location.reload() 刷新
4.History对象
history.length 返回历史列表中的网址数
history.back() 加载 history 列表中的前一个 URL
history.forward() 加载 history 列表中的下一个 URL
history.go(Number|URL) 加载 history 列表中的某个具体页面
