论文:GhostNet: More Features from Cheap Operations,CVPR 2020
代码:https://github.com/iamhankai/ghostnet.pytorch/
GhostNet是华为诺亚方舟实验室在CVPR2020提出,可以在同样精度下,速度和计算量均少于SOTA方法。当前神经网络偏向于移动设备应用,一些重于模型的压缩,比如剪枝、量化、知识蒸馏等。另一些着重于高效的网络设计,比如 MobileNet, ShuffleNet 等。
训练好的网络里的feature map存在大量的冗余信息,相追似的 feature map 类似于 ghost,如下图所示:
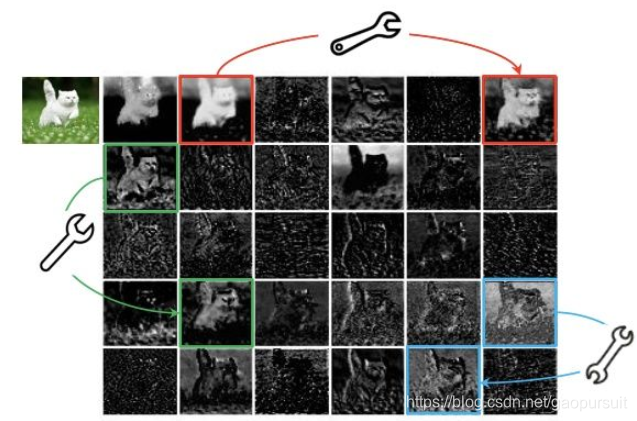
作者认为:并非所有 feature map 都需要用卷积操作来得到,“ghost” feature map可以用更加廉价的操作来生成,因此,作者就提出了 Ghost module。
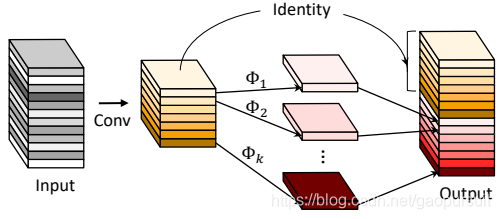
Ghost module 如上图所示,可以看到,包括两次卷积。假设output的通道数为 \(init\_channels * ratio\),那么第一次卷积生成 \(init\_channels\) 个 feature map。
第二次卷积:每个 feature map 通过映射生成 \(ratio-1\) 个新的 feature map,这样会生成 \(init_channels*(ratio-1)\) 个 feature map。最后,把第一次卷积和第二次卷积得到的 feature map 拼接在一起,得到output,通道数为\(init\_channels * ratio\)。
Ghost module 的代码如下所示,关键步骤我添加了备注说明:
class GhostModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inp, oup, kernel_size=1, ratio=2, dw_size=3, stride=1, relu=True):
super(GhostModule, self).__init__()
self.oup = oup
init_channels = math.ceil(oup / ratio)
new_channels = init_channels*(ratio-1)
# 第一次卷积:得到通道数为init_channels,是输出的 1/ratio
self.primary_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inp, init_channels, kernel_size, stride, kernel_size//2, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(init_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True) if relu else nn.Sequential())
# 第二次卷积:注意有个参数groups,为分组卷积
# 每个feature map被卷积成 raito-1 个新的 feature map
self.cheap_operation = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(init_channels, new_channels, dw_size, 1, dw_size//2, groups=init_channels, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(new_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True) if relu else nn.Sequential(),
)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.primary_conv(x)
x2 = self.cheap_operation(x1)
# 第一次卷积得到的 feature map,被作为 identity
# 和第二次卷积的结果拼接在一起
out = torch.cat([x1,x2], dim=1)
return out[:,:self.oup,:,:]
最有趣的是模块里,第二次卷积,作者也考虑了仿射变换、小波变换等,因为卷积运算有较好的硬件支持,作者更推荐卷积。
Ghost Bottleneck(G-bneck)与residual block类似,主要由两个Ghost模块堆叠二次,第一个模块用于增加特征维度,增大的比例称为expansion ratio,而第二个模块则用于减少特征维度,使其与输入一致。G-bneck包含stride=1和stride=2版本,对于stride=2,shortcut路径使用下采样层,并在Ghost模块中间插入stride=2的depthwise卷积。为了加速,Ghost模块的原始卷积均采用pointwise卷积
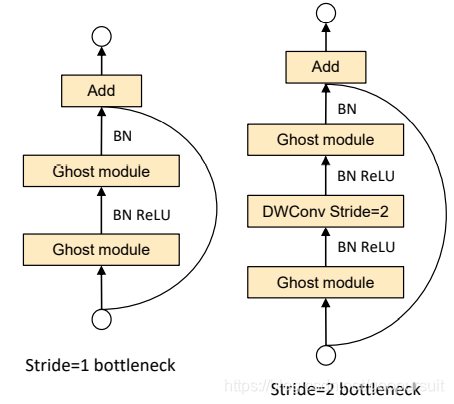
在网络架构上,GhostNet 将 MobileNetV3 的 bottleneck block 替换为 Ghost bottleneck,部分 Ghost模块 加入了SE模块。
论文思路比较容易懂,今天就总结到这里。