在JDBC API中提供了调用存储过程的方法,通过CallableStatement对象进行操作。CallableStatement对象位于java.sql包中,它继承于Statement对象,主要用于执行数据库中定义的存储过程,其调用方法如下:
{call <procedure-name>[(<arg1>,<arg2>,...)]}
其中,arg1、arg2为存储过程中的参数,如果存储过程中需要传递参数,可以对其进行赋值操作。
技巧:存储过程是一个SQL语句和可选控制流语句的预编译集合。编译完成后存放在数据库中,这样就省去了执行SQL语句时对SQL语句进行编译所花费的时间。在执行存储过程时只需要将参数传递到数据库中,而不需要将整条SQL语句都提交给数据库,从而减少了网络传输的流量,从另一方面提高了程序的运行速度。
例1.1 创建查询所有图书信息的存储过程,通过JDBC API对其调用获取所有图书信息,并将其输出到JSP页面中。
(1)在数据库test中创建名称为findAllBook的存储过程,用于查询所有图书信息。关键代码如下:
BEGIN SELECT* FROM books ORDER BY id DESC; END
各种数据库创建存储过程的方法并非一致,本实例使用的是MySQL数据库,如果使用其他数据库创建存储过程请参阅数据库提供的帮助文档。
(2) 创建名称为Book的类,该类用于封装图书信息的JavaBean对象。关键代码如下:
package com.cn.gao; public class Book { private int id; private String name; private double price; private int bookCount; private String author; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(double price) { this.price = price; } public int getBookCount() { return bookCount; } public void setBookCount(int bookCount) { this.bookCount = bookCount; } public String getAuthor() { return author; } public void setAuthor(String author) { this.author = author; } }
(3)创建名称为FindBook的类,用于执行查询图书信息的存储过程。首先在该类中编写getConnection()方法,获取数据库连接对象Connection,其关键代码如下:
/** * 获取数据库连接 * @return Connection 对象 */ public Connection getConnection(){ Connection conn=null; try { Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test"; String user = "root"; String password = "1234"; conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } return conn; }
然后编写findAll()方法,调用数据库中定义的存储过程findAllBook,查询所有图书信息,并将查询到的图书的信息放置到List集合中。关键代码如下:
/** * 通过存储过程查询数据 * @return List<Book> */ public List<Book> findAll(){ List<Book> list = new ArrayList<Book>(); Connection conn = getConnection(); try { //调用存储过程 CallableStatement cs = conn.prepareCall("{call findAllBook()}"); ResultSet rs = cs.executeQuery(); //执行查询操作,并获取结果集 while(rs.next()){ Book book = new Book(); book.setId(rs.getInt("id")); book.setName(rs.getString("name")); book.setPrice(rs.getDouble("price")); book.setBookCount(rs.getInt("bookCount")); book.setAuthor(rs.getString("author")); list.add(book); } } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } return list; }
由于存储过程findAllBook中没有定义参数,所以实例中通过调用“{call findAllBook()}"来调用存储过程。
(4)创建程序中的主页index1.jsp,在该页面中实例化FindBook对象,并调用它的findAll()方法获取所有图书信息,将图书信息数据显示在页面中。关键代码如下:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=GB18030" pageEncoding="GB18030"%> <%@ page import="java.util.*" %> <%@ page import="com.cn.gao.*" %> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=GB18030"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <jsp:useBean id="findBook" class="com.cn.gao.FindBook"></jsp:useBean> <table align="center" width="450" border="1"> <tr> <td align="center" colspan="5"> <h2>所有图书信息</h2> </td> </tr> <tr align="center"> <td><b>ID</b></td> <td><b>图书名称</b></td> <td><b>价格</b></td> <td><b>数量</b></td> <td><b>作者</b></td> </tr> <% List<Book> list = findBook.findAll(); if(list==null||list.size()<1){ out.print("没有数据!"); }else{ for(Book book:list){ %> <tr align="center"> <td><%=book.getId() %></td> <td><%=book.getName() %></td> <td><%=book.getPrice() %></td> <td><%=book.getBookCount() %></td> <td><%=book.getAuthor() %></td> </tr> <% } } %> </table> </body> </html>
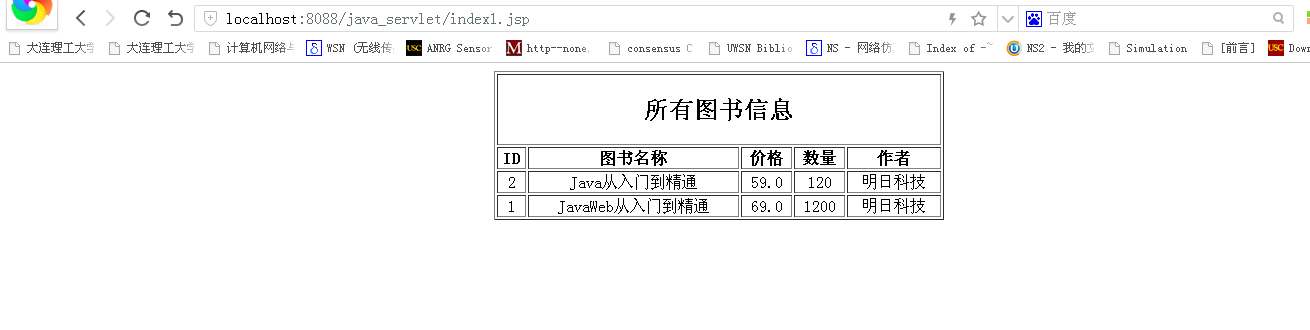
实例运行后,进入到index1.jsp页面,程序将执行数据库中定义的存储过程findAllBook查询图书信息,其运行结果如下图所示: