组合模式,也称作部分整体模式。组合模式画成图就是数据结构中的树结构,有一个根节点,然后有很多分支。将最顶部的根节点叫做根结构件,将有分支的节点叫做枝干构件,将没有分支的末端节点叫做叶子构件.
1.定义
将对象组合成树形结构以表示“部分-整体”的层次结构,使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性。
2.使用场景
- 想表示对象的部分-整体层次结构时。
- 希望用户忽略单个对象和组合对象的不同,对对象使用具有统一性时。
- 从一个整体中能够独立出部分模块或功能时。
3.安全的组合模式
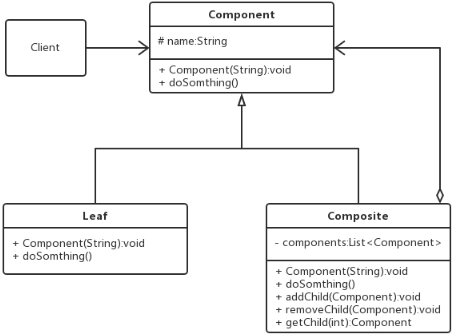
①抽象的节点:
public abstract class Component { protected String name; public Component(String name) { this.name = name; } public abstract void doSonthing(); }
②枝干节点:
1 public class Composite extends Component { 2 private List<Component> components = new ArrayList<>(); 3 public Composite(String name) { 4 super(name); 5 } 6 7 @Override 8 public void doSonthing() { 9 System.out.println(name); 10 if (null!=components){ 11 for (Component c:components) { 12 c.doSonthing(); 13 } 14 } 15 } 16 17 public void addChild(Component child){ 18 components.add(child); 19 } 20 public void removeChild(Component child){ 21 components.remove(child); 22 } 23 public Component getChild(int index){ 24 return components.get(index); 25 } 26 27 }
③叶子节点:
1 public class Leaf extends Component { 2 public Leaf(String name) { 3 super(name); 4 } 5 6 @Override 7 public void doSonthing() { 8 System.out.println(name); 9 } 10 }
④客户端调用:
1 public class CLient { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Composite root = new Composite("root"); 4 Composite branch1 = new Composite("branch1"); 5 Composite branch2 = new Composite("branch2"); 6 Composite branch3 = new Composite("branch3"); 7 8 Leaf leaf1 = new Leaf("leaf1"); 9 Leaf leaf2 = new Leaf("leaf2"); 10 Leaf leaf3 = new Leaf("leaf3"); 11 12 branch1.addChild(leaf1); 13 branch3.addChild(leaf2); 14 branch3.addChild(leaf3); 15 16 root.addChild(branch1); 17 root.addChild(branch2); 18 root.addChild(branch3); 19 20 root.doSonthing(); 21 } 22 }
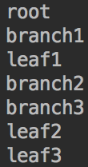
我们可以发现在Client使用的时候,根本没用到接口Component。违反了依赖倒置原则。
因为接口中没有定义公共方法,必须使用对应搞得实现节点才能完成相应的操作,叫安全的组合模式。
4.透明的组合模式
所以就有一种透明的组合模式,所有的节点都包含有同样的结构
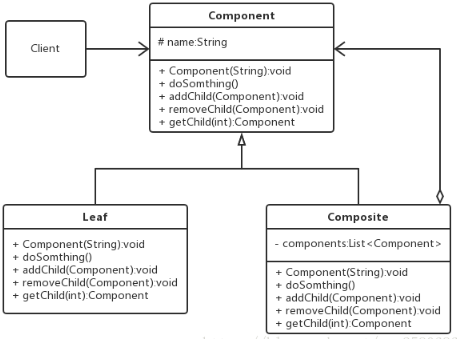
①抽象的节点:
1 public abstract class Component { 2 protected String name; 3 4 public Component(String name) { 5 this.name = name; 6 } 7 public abstract void doSonthing(); 8 9 public abstract void addChild(Component child); 10 public abstract void removeChild(Component child); 11 public abstract Component getChild(int index); 12 }
②枝干节点:
1 public class Composite extends Component { 2 private List<Component> components = new ArrayList<>(); 3 public Composite(String name) { 4 super(name); 5 } 6 7 @Override 8 public void doSonthing() { 9 System.out.println(name); 10 if (null!=components){ 11 for (Component c:components) { 12 c.doSonthing(); 13 } 14 } 15 } 16 17 public void addChild(Component child){ 18 components.add(child); 19 } 20 public void removeChild(Component child){ 21 components.remove(child); 22 } 23 public Component getChild(int index){ 24 return components.get(index); 25 } 26 27 }
③叶子节点:
1 public class Leaf extends Component { 2 public Leaf(String name) { 3 super(name); 4 } 5 6 @Override 7 public void doSonthing() { 8 System.out.println(name); 9 } 10 11 @Override 12 public void addChild(Component child) { 13 throw new UnsupportedOperationException("叶子节点没有子节点"); 14 } 15 16 @Override 17 public void removeChild(Component child) { 18 throw new UnsupportedOperationException("叶子节点没有子节点"); 19 } 20 21 @Override 22 public Component getChild(int index) { 23 throw new UnsupportedOperationException("叶子节点没有子节点"); 24 } 25 }
④客户端调用:
1 public class CLient { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Component root = new Composite("root"); 4 Component branch1 = new Composite("branch1"); 5 Component branch2 = new Composite("branch2"); 6 Component branch3 = new Composite("branch3"); 7 8 Component leaf1 = new Leaf("leaf1"); 9 Component leaf2 = new Leaf("leaf2"); 10 Component leaf3 = new Leaf("leaf3"); 11 12 branch1.addChild(leaf1); 13 branch3.addChild(leaf2); 14 branch3.addChild(leaf3); 15 16 root.addChild(branch1); 17 root.addChild(branch2); 18 root.addChild(branch3); 19 20 root.doSonthing(); 21 } 22 }
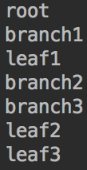
5.简单实现
以文件夹系统举个例子:
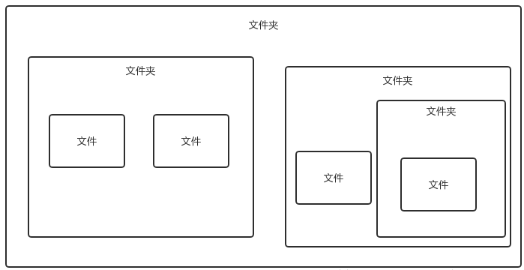
①.抽象的文件系统:
1 public abstract class Dir { 2 protected List<Dir> dirs = new ArrayList<>(); 3 private String name; 4 5 public Dir(String name) { 6 this.name = name; 7 } 8 9 public abstract void addDir(Dir dir); 10 public abstract void rmDir(Dir dir);//删除文件或文件夹 11 public abstract void clear();//清空所有元素 12 public abstract void print();//打印文件夹系统结构 13 public abstract List<Dir> getFiles(); 14 public String getName(){ 15 return name; 16 } 17 }
②.文件夹:
1 public class Folder extends Dir { 2 public Folder(String name) { 3 super(name); 4 } 5 6 @Override 7 public void addDir(Dir dir) { 8 dirs.add(dir); 9 } 10 11 @Override 12 public void rmDir(Dir dir) { 13 dirs.remove(dir); 14 } 15 16 @Override 17 public void clear() { 18 dirs.clear(); 19 } 20 21 @Override 22 public void print() { 23 //利用递归来输出文件夹结构 24 System.out.print(getName()+"("); 25 Iterator<Dir> i = dirs.iterator(); 26 while (i.hasNext()){ 27 Dir dir = i.next(); 28 dir.print(); 29 if (i.hasNext()){ 30 System.out.print(", "); 31 } 32 } 33 System.out.print(")"); 34 } 35 36 @Override 37 public List<Dir> getFiles() { 38 return dirs; 39 } 40 }
③.文件:
1 public class File extends Dir { 2 public File(String name) { 3 super(name); 4 } 5 6 @Override 7 public void addDir(Dir dir) { 8 throw new UnsupportedOperationException("文件不支持此操作"); 9 } 10 11 @Override 12 public void rmDir(Dir dir) { 13 throw new UnsupportedOperationException("文件不支持此操作"); 14 } 15 16 @Override 17 public void clear() { 18 throw new UnsupportedOperationException("文件不支持此操作"); 19 } 20 21 @Override 22 public void print() { 23 System.out.print(getName()); 24 } 25 26 @Override 27 public List<Dir> getFiles() { 28 throw new UnsupportedOperationException("文件不支持此操作"); 29 } 30 }
④.客户端调用:
1 public class Client { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 //创建根目录 root 4 Dir root = new Folder("root"); 5 //root下有个文件log.txt和三个文件夹 system,user,lib; 6 root.addDir(new File("log.txt")); 7 Dir system = new Folder("system"); 8 system.addDir(new File("systemlog.txt")); 9 root.addDir(system); 10 Dir user = new Folder("user"); 11 user.addDir(new File("usernamelist.txt")); 12 root.addDir(user); 13 Dir lib = new Folder("lib"); 14 lib.addDir(new File("libs.txt")); 15 root.addDir(lib); 16 root.print(); 17 } 18 }
输出:
6.Android源码中的组合模式
组合模式在Android中太常用了,View和ViewGroup就是一种很标准的组合模式:
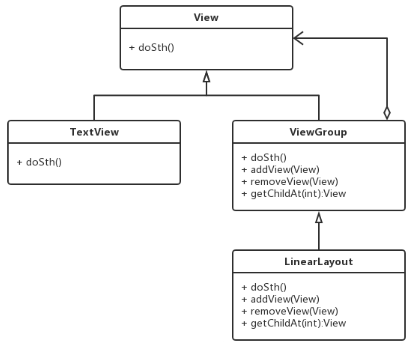
在Android的视图树中,容器一定是ViewGroup,只有ViewGroup才能包含其他View和ViewGroup。View是没有容器的。者是一种安全的组合模式。
7.总结
在Android开发中用到组合模式并不很多,组合模式更多的用于界面UI的架构设计上,而这部分让开发者去实现的并不多。
优点
- 可以清楚定义分层次的复杂对象,表示全部或部分层次,让高层忽略层次的差异,方便对整个层次结构进行控制。
- 高层模块可以一致的使用一个组合结构或其中的单个对象,不必挂心处理的是单个对象还是整个组合结构,简化了高层模块的代码。
- 增加新的枝干和叶子构件都很方便,无需对现有类进行任何修改,就像增加一个自定义View一样。
- 将对象之间的关系形成树形结构,便于控制。
缺点
- 设计变得更加抽象,因此很难限制组合中的组件,因为他们都来自相同的抽象层。所以必须在运行时进行类型检查才能实现。
