传送门:http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=3716
http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=4251
【题解】
非常妙的网络流转化
首先可以把警卫和宝藏看成最大权闭合子图,用最小割的那种建模方法,即一开始加进来所有宝藏的价值
然后S连宝藏,警卫连T,有覆盖关系的连inf
那么就是一个最小割,复杂度是$O(maxflow(n+m, nm)$,显然承受不了。
由于最小割和最大流等价,所以转化最大流考虑。
问题变为
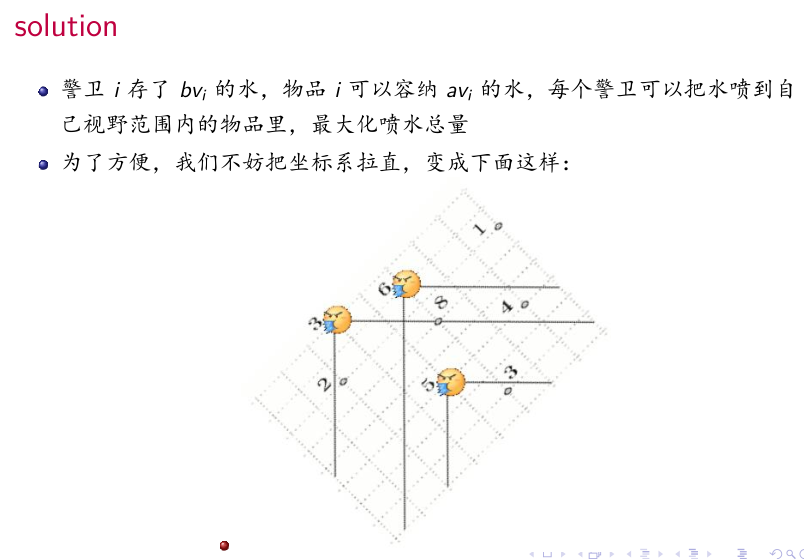
那么按x从大到小排序,每次2种操作:加入一个物品;有一个警卫可以喷水给所有y小于它物品。
显然按照y从大到小喷最优,因为小的限制条件小。
用个set维护即可,注意set的时候lower_bound只能s.lower_bound(...),不能lower_bound(s.begin(), s.end(), ..)!!!

# include <set> # include <stdio.h> # include <string.h> # include <iostream> # include <algorithm> // # include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef long double ld; typedef unsigned long long ull; const int N = 2e5 + 10; const int mod = 1e9+7; const ll inf = 5e18; inline int getint() { int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while(!isdigit(ch)) { if(ch == '-') f = 0; ch = getchar(); } while(isdigit(ch)) { x = (x<<3) + (x<<1) + ch - '0'; ch = getchar(); } return f ? x : -x; } int n, m, W, H; struct pa { ll x, y; int v; pa () {} pa (ll x, ll y, int v) : x(x), y(y), v(v) {} inline friend bool operator < (pa a, pa b) { return a.y < b.y || (a.y == b.y && a.x < b.x); } }a[N], b[N]; struct option { ll x, y; int v, op; option() {} option(int op, ll x, ll y, int v) : op(op), x(x), y(y), v(v) {} inline friend bool operator < (option a, option b) { return a.x < b.x || (a.x == b.x && a.op > b.op); } }p[N + N]; set<pa> s; set<pa>::iterator it; int main() { ll ans = 0; cin >> n >> m >> W >> H; for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i) { a[i].x = 1ll * H * getint(), a[i].y = 1ll * W * getint(), a[i].v = getint(); p[i] = option(1, a[i].x - a[i].y, a[i].x + a[i].y, a[i].v); ans += a[i].v; } for (int i=1; i<=m; ++i) { b[i].x = 1ll * H * getint(), b[i].y = 1ll * W * getint(), b[i].v = getint(); p[n + i] = option(2, b[i].x - b[i].y, b[i].x + b[i].y, b[i].v); } // maxflow int pn = n + m; sort(p+1, p+pn+1); s.clear(); for (int i=pn; i; --i) { if(p[i].op == 1) s.insert(pa(p[i].x, p[i].y, p[i].v)); else { int cv = p[i].v; pa r = pa(inf, p[i].y, cv), t; while(cv && s.size()) { it = s.upper_bound(r); if(it == s.begin()) break; --it; t = *it; s.erase(it); int tmp = min(t.v, cv); cv -= tmp, t.v -= tmp; ans -= tmp; if(t.v > 0) s.insert(t); } } } cout << ans; return 0; }
