- 链接
- 原型设计
- AI与原型设计实现
- 【2.2.1】代码实现思路:
- 我们要从网络接口获取图片,step,swap,uuid信息,并且通过接口返回我们代码的运行结果,最终服务器端会将我们提交的结果进行评测,返回排名,耗时,True或者Flase等信息
- 首先我将这个代码实现分为三个部分:
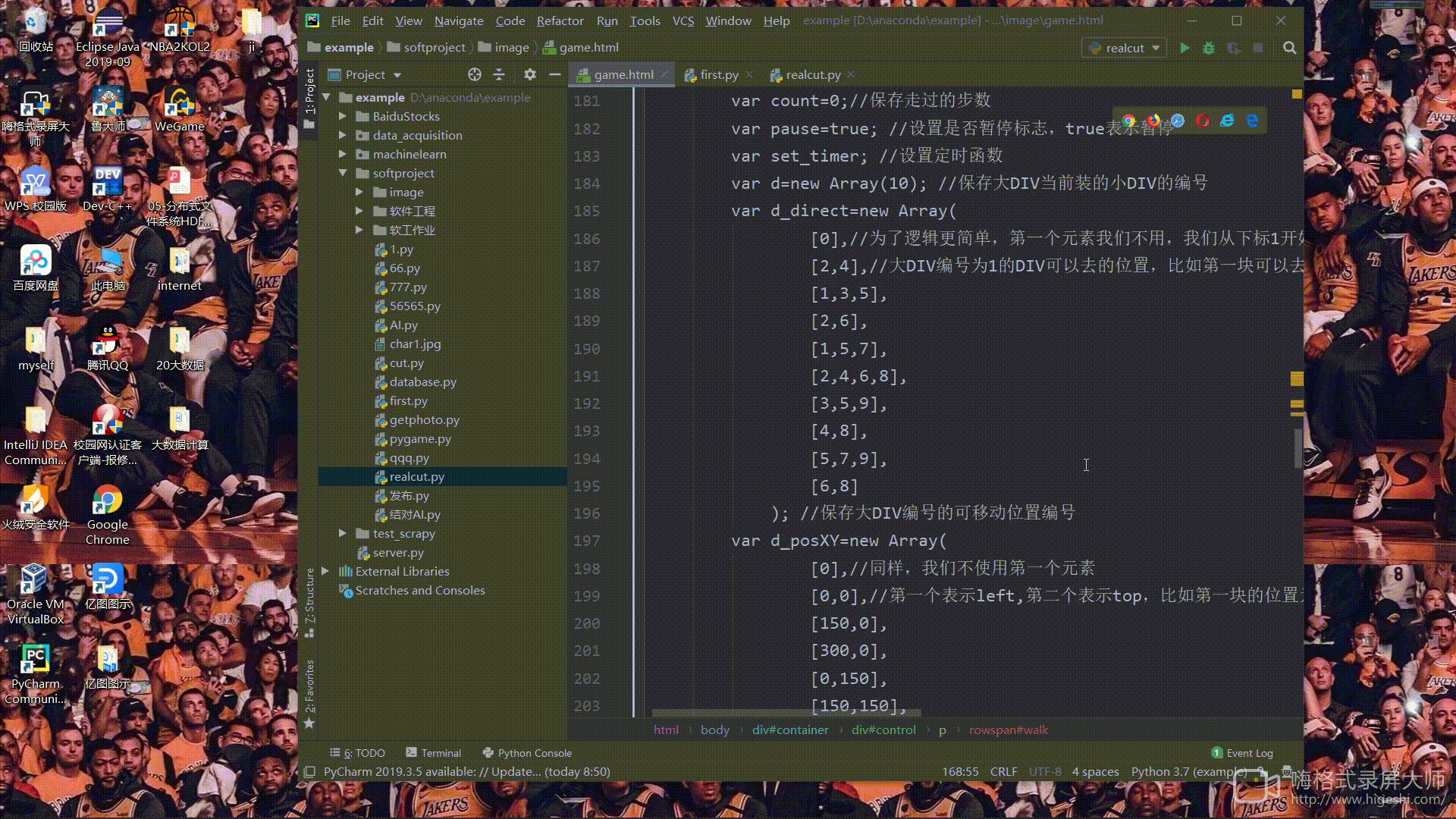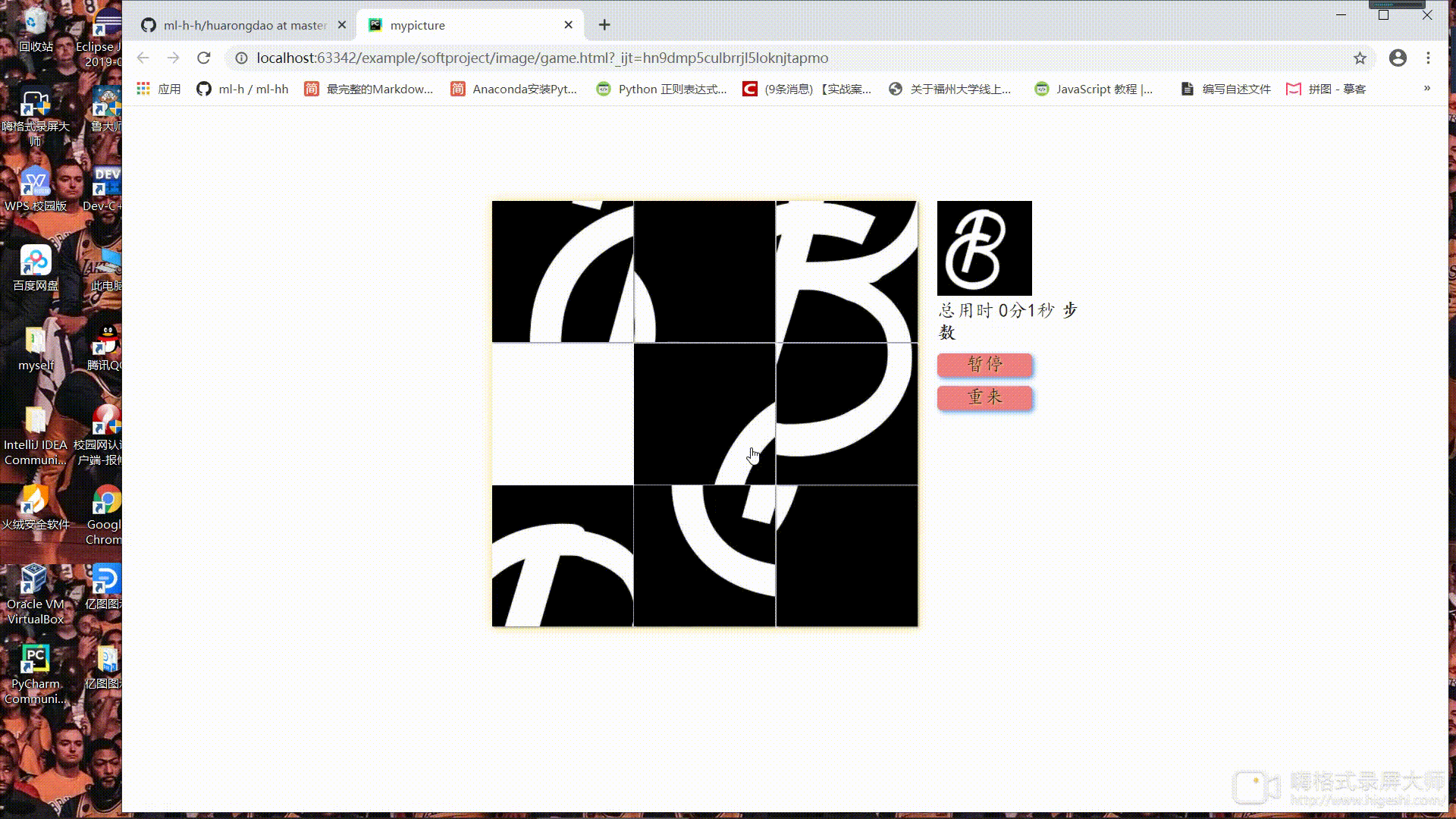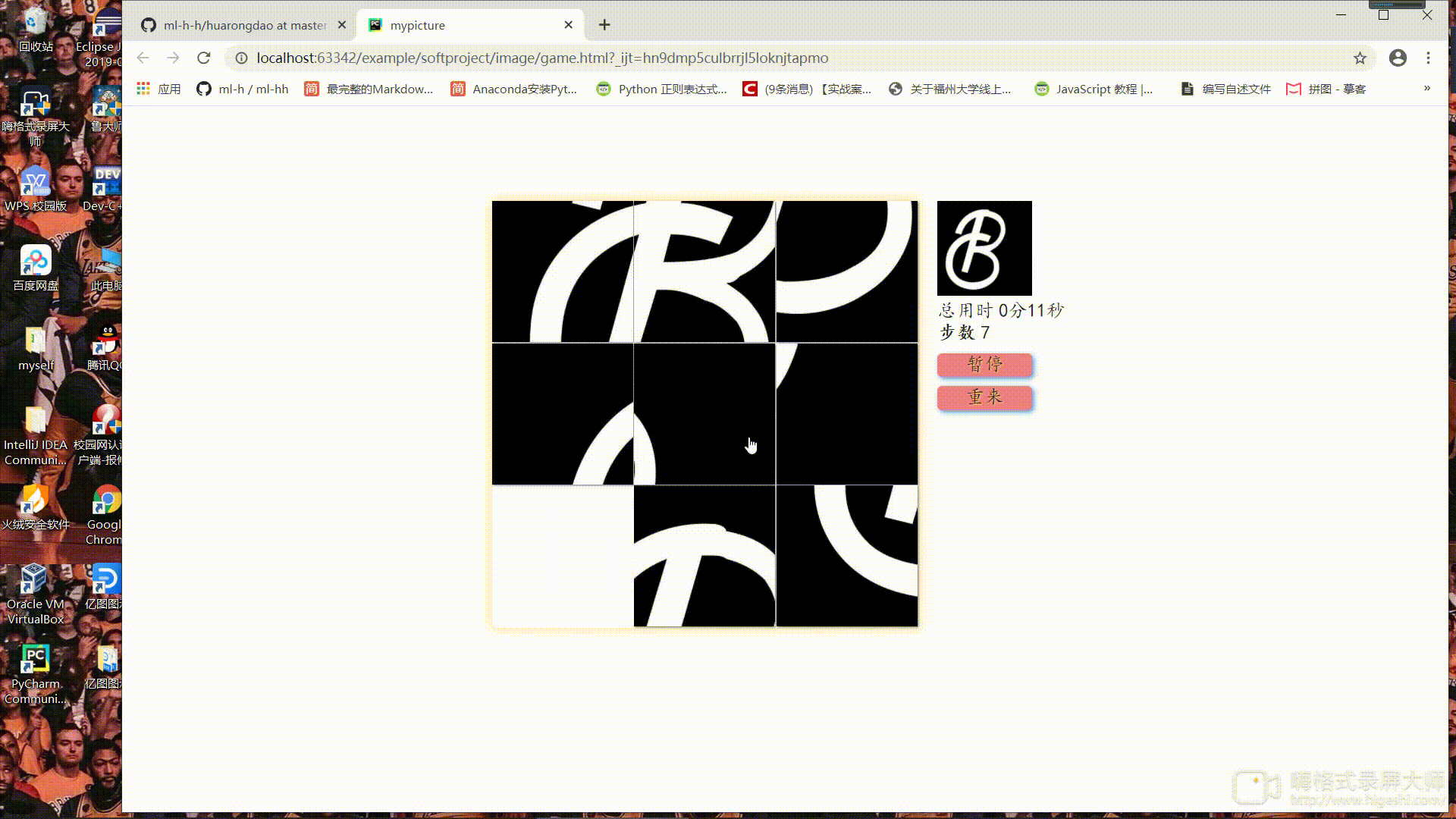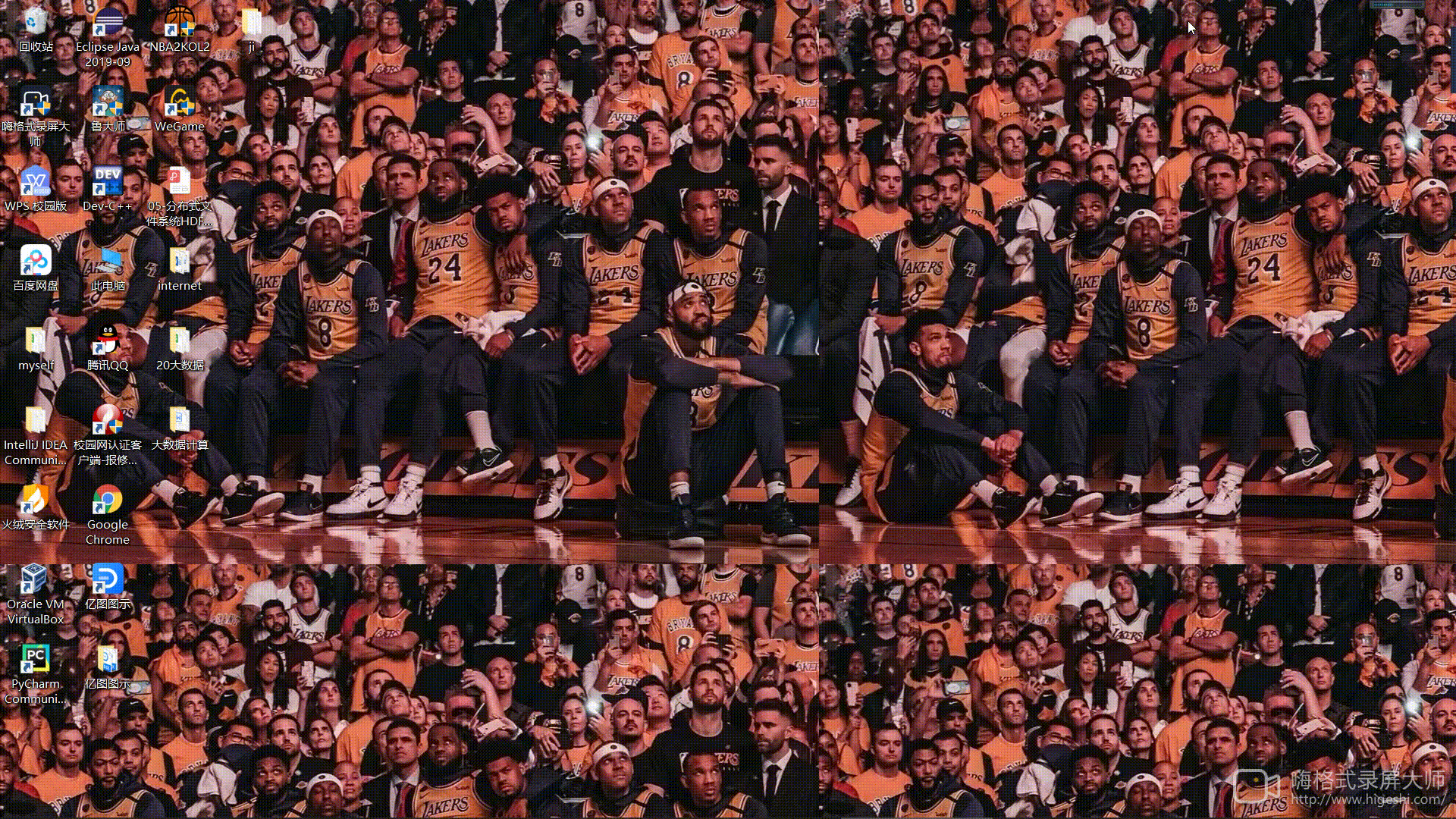
- 第一:将乱图均分切割成九张小图,识别出原来的图片,然后给每张小图添上它在原图的位置0-8,组成一个3*3的列表。
- 第二:我通过循环的方法移动空白块,一层一层添加遍历所有可能的情况,直到出现目标解即3*3的列表元素排列为012345678,或者达到强制交换后,交换对应位置的列表元素,退出循环,记录下此时从一开始的列表状态到达此时列表状态所有的空白块坐标移动所得到的坐标路径,并且将记录空白块移动的坐标列表转换为wsad序列
- 第三:如果在强制交换前就已经得到结果了,就直接将对应的序列提交即可。否则记录此时从一开始到达当前状态的路径以及对应的列表状态,然后将各自的当前列表状态先进行判断是否有解,我把所有的解都存到.pkl文件里面,方法是从目标状态列表,即012345678开始,根据空白快在原图的位置可分为九种情况,对于每一种情况我通过循环的方式去移动空白块,只要出现新的列表状态我就把他以及到达他的路径序列保存下来,让他一直运行,直到不再增加新的列表或者增加得比较慢,我就将所有的列表,以及到达该列表状态得最短路径以字典的形式保存下来写入到.pkl文件当中。在强制交换后存在有解和无解的列表,有解的列表直接从.pkl文件当中取出对应的序列,转换后再添加其强制交换以前的序列,就得到一个结果,这样我就将所有有解的情形以及对应的路径分别保存在两个列表当中,无解的情形其实就是列表不在存放我有解的列表当中,此时我会对每一种无解的列表进行两两互换,若互换以后有解,则将他们强制交换前的移动序列以及自由交换后有解的序列拼接起来,然后将序列以及自由交换的两个图片数字标签保存下来。最后我分别从强制交换后有解,以及强制交换后无解自由交换后有解的最短序列提取出来,然后再对比两种情况的最短序列,取较短的一种作为最终结果。
- 【2.2.2】github
- 【2.2.3】遇到的代码块异常
- 【2.2.4】评价你的队友
- 【2.2.5】Personal Software Process和学习进度条
- 【2.2.1】代码实现思路:
- 动画
链接
郝雷明的博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/lmmlm/
郝雷明负责的原型设计及代码链接:https://github.com/ml-h/ml-h-h/tree/master/huarongdao
傅智鑫的博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/fzx-123/
傅智鑫负责的AI大比拼算法链接:https://github.com/fzx-123/-21/tree/main
原型设计
【2.1.1】
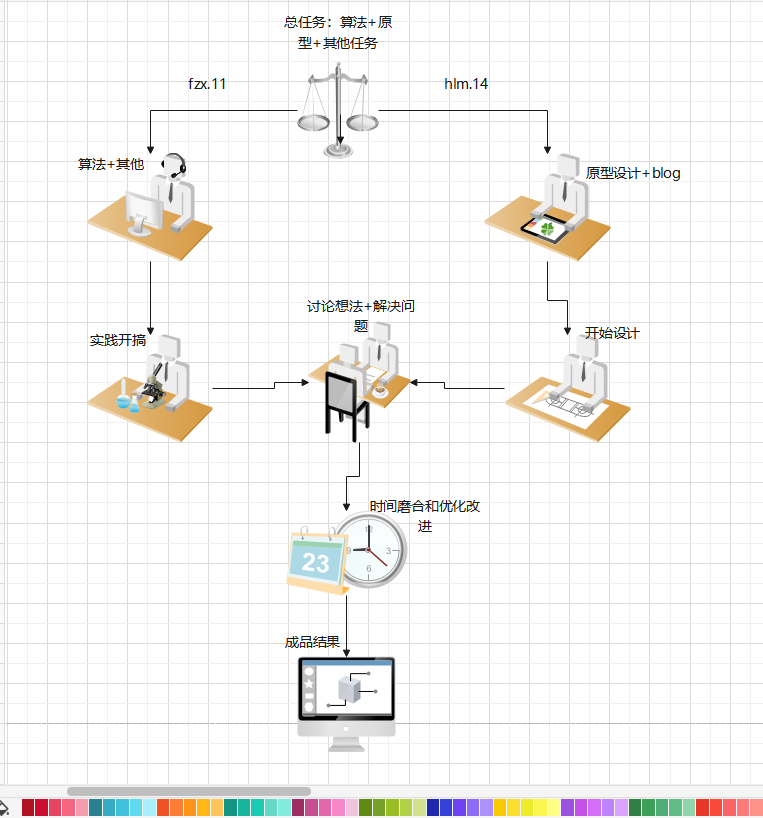
阶段1:想法
开始拿到这个题目应该说是毫无头绪,不理解题目要求做什么,后面看懂了大概后,渐渐有一点小想法,起码是要做出来一个可玩的九宫格图片拼图游戏
阶段2:概念
先从数字华容道开始了解一下,现有的数字华容道还是很多的,还有一些约束条件,看能不能从数字华容道里得到一些有用的可执行的点子
阶段3:计划
先定义目标,我们的目标是实现图片的移动拼图,但前提是我们从接口获得的图片是剪切过后乱序拼接的,所以切图是第一步,包括把原有的36张图全部切成小图,接口获得的图片也切成小图;第二步就是判断获得的图对应的原图应该是哪张,需要图片识别搞定;第三步是给每个小图进行标签并通过识别匹配原图返回对应位置的原图标签,用于后续进行移动得到正确解;第四步如果有正确解的基础上用类似广度的树进行存储来获得最优解
阶段4:设计(WBS)

阶段5:开发
算法和原型同时开始设计和逐步实现
阶段6:测试和发布
【2.1.2】
本次所采用的原型开发工具是mockplus

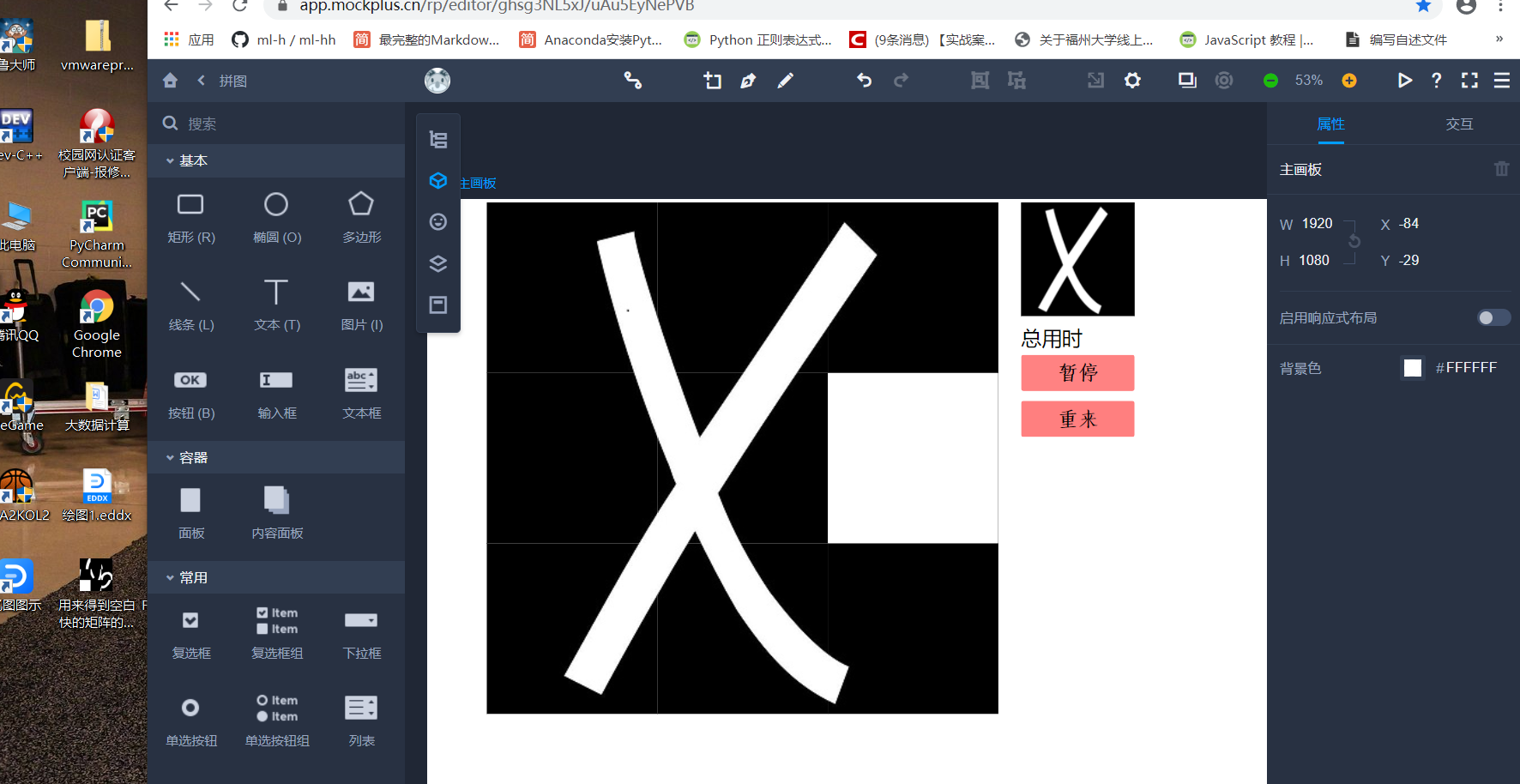
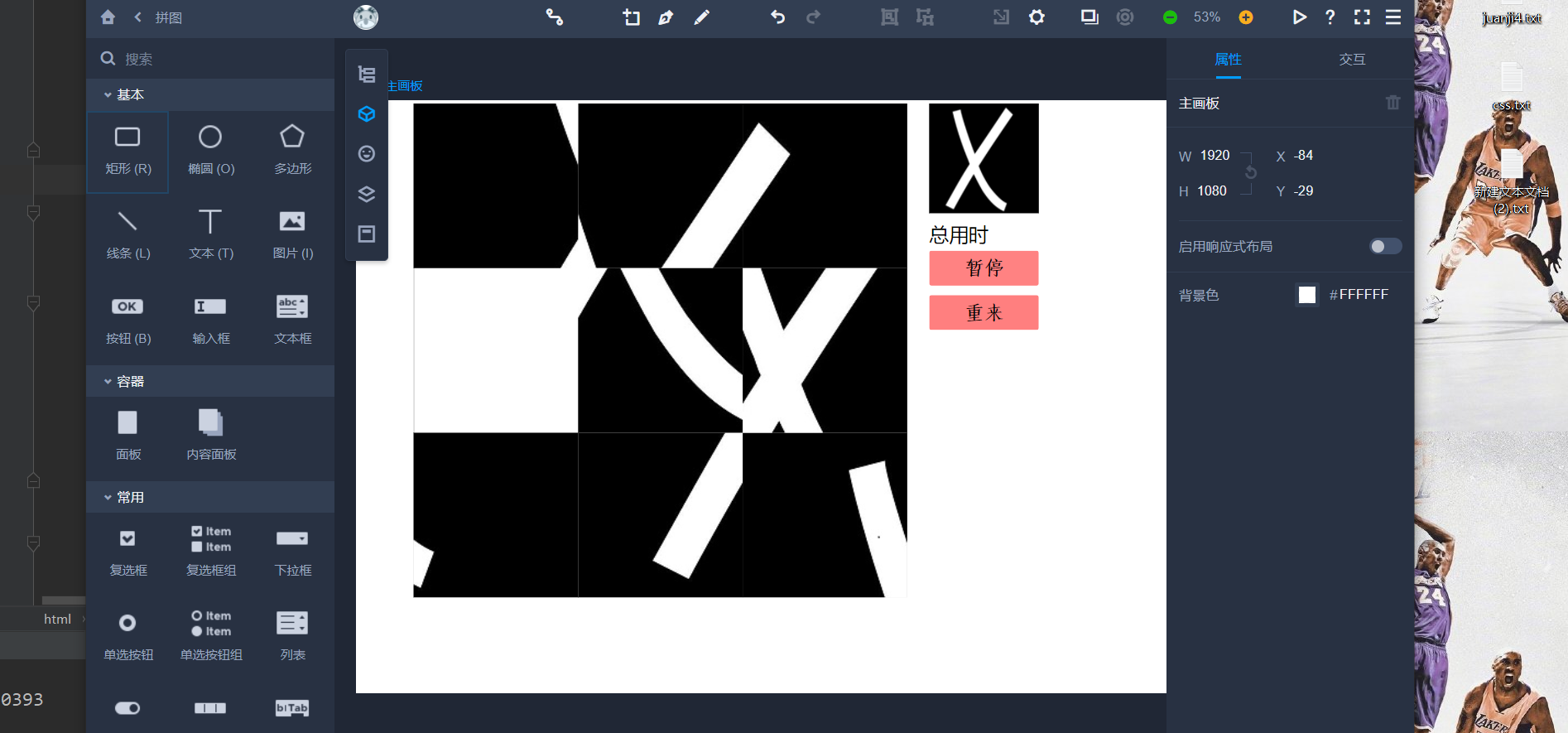
【2.1.3】
默契使然,顺利结对


【2.1.4】遇到的困难及解决方法
困难描述:
原型设计开发工具的使用问题,js的语法,css的语法,html格式等等前端知识的掌握
解决尝试:
面向百度编程,不断获取资料知识,一点点更新自己的库,一步一步增加代码功能,逐步完成
是否解决:
基本已解决,得到自己想要的东西
有何收获:
花费大量时间去获取前端的知识点,算是收获了一些知识点
AI与原型设计实现
【2.2.1】代码实现思路:
我们要从网络接口获取图片,step,swap,uuid信息,并且通过接口返回我们代码的运行结果,最终服务器端会将我们提交的结果进行评测,返回排名,耗时,True或者Flase等信息
首先我将这个代码实现分为三个部分:
第一:将乱图均分切割成九张小图,识别出原来的图片,然后给每张小图添上它在原图的位置0-8,组成一个3*3的列表。
def cut_image(image): # 将一张图片切割成九张小图,返回九张小图组成的列表
img_size = image.size
width = img_size[0] # 图片的宽度
height = img_size[1] # 图片的高度
item_width = width / 3.0
item_height = height / 3.0
item_location_list = []
image_list = []
# 将需要得到的小图的对顶坐标添加到列表,便于后续直接切割图片
for row in range(3):
for col in range(3):
item_location = (col * item_width, row * item_height, (col + 1) * item_width, (row + 1) * item_height)
item_location_list.append(item_location)
# 将切割image图片
for item_location in item_location_list:
image_list.append(image.crop(item_location)) # image.crop(item_location)是切割图片的函数
return image_list
def get_white_arr(): # 获取空白块的矩阵
image = Image.open(r'C:\Users\ASUS\Desktop\用来得到空白快的矩阵的图片.jpg') # 先从接口处下载一张乱图,切割后得到空白的图片
# image = Image.open(r'软件工程\结对作业\用来得到空白快的矩阵的图片.jpg')
char_lists = cut_image(image)
char9_list = []
for image in char_lists:
char_arr = np.array(image)
char9_list.append(char_arr)
white_arr = char9_list[6]
return white_arr
def get_35photo_list35(): # 获取36张原图的九个小图的矩阵组成的列表
list_35 = []
for i in range(35):
image = Image.open(r'C:\Users\ASUS\Desktop\无框图片\' + str(i) + '.jpg')
# image = Image.open(r'软件工程\结对作业\无框图片\' + str(i) + '.jpg')
image_list = cut_image(image)
list_9 = []
for image in image_list:
image_arr = np.array(image) # 将图片以数组的形式读入变量
list_9.append(image_arr)
list_35.append(list_9)
return list_35
def get_messy_pictures_list9(): # 从接口处获得一张排序混乱的图片并得到切割后九张小图的矩阵组成的列表
url = "http://47.102.118.1:8089/api/challenge/start/5ff2452f-13ea-447e-83be-b0d91346d01b"
hdata = {
"teamid": 55,
"token": "6ef4189d-40b3-476e-bcd6-ca9cd9b24ce0"
}
r = requests.post(url, json=hdata)
datadir = json.loads(r.text)
datadir2 = datadir['data']
imgdata = base64.b64decode(datadir2['img'])
step = datadir2['step']
swap = datadir2['swap']
uuid = datadir['uuid']
# path = r"C:UsersASUSDesktop软工图片\char1.jpg"
path = r"char1.jpg"
file = open(path, 'wb')
file.write(imgdata)
file.close()
img = Image.open(path)
img_list = cut_image(img)
messy_pictures_list9 = []
for image in img_list:
image_arr = np.array(image)
messy_pictures_list9.append(image_arr)
return messy_pictures_list9, step, swap, uuid
def identify_label_pictures(get_messy_pictures_list9, get_35photo_list35): # 图像识别并标号
list_label_35 = [0] * 35
white_arr = get_white_arr()
for one in get_messy_pictures_list9:
if ((one == white_arr).all()): # 如果是空白块则跳过,比较是否为同一个矩阵,需要加.all(),不然默认为比较矩阵元素内部的元素是否相等
continue
for i in range(35):
for j in range(9):
if (one == get_35photo_list35[i][j]).all():
list_label_35[i] += 1
real_indx = list_label_35.index(8) # 识别原图,得到原图在存储35张图片矩阵的位置
lable_list_9 = [] # 将原图的九个小矩阵转为在原图的位置,如
for i in range(9):
lable_list_9.append(get_35photo_list35[real_indx][i].tolist())
lable_list = [] # 存放打乱后的图片的数字标签
for i in range(9):
a = get_messy_pictures_list9[i].tolist() # 将列表中的矩阵转换为列表
if a == white_arr.tolist():
lable_list.append(10) # 先给白图一个标签10
continue
xiaotu_indx = lable_list_9.index(a)
lable_list.append(xiaotu_indx)
for i in range(9): # 将白图的数值10更改为其原来的位置标签
if i not in lable_list:
white = i
# white_index = lable_list.index(10)
lable_list[lable_list.index(10)] = white
lable_list = [lable_list[0:3], lable_list[3:6], lable_list[6:9]]
for i in range(len(lable_list)):
for j in range(len(lable_list)):
if lable_list[i][j] == white:
column = j
row = i
blank_coordinate = [row, column] # 记录空白位置的坐标
return lable_list, blank_coordinate,white
第二:我通过循环的方法移动空白块,一层一层添加遍历所有可能的情况,直到出现目标解即3*3的列表元素排列为012345678,或者达到强制交换后,交换对应位置的列表元素,退出循环,记录下此时从一开始的列表状态到达此时列表状态所有的空白块坐标移动所得到的坐标路径,并且将记录空白块移动的坐标列表转换为wsad序列
def solve(lable_list, blank_coordinate, step, swap):
if lable_list == [[0, 1, 2], [3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8]]:
return
else:
# 移动空白快的主要代码
total_route_list = [] ##用来保存根节点到每个叶节点的路径
total_list = [] # 用来存放每一个叶节点当前的3*3的列表状态
total_route_list.append([blank_coordinate]) # 初始化根节点
total_list.append(lable_list) # 初始化当前3*3列表状态
middle_route_list = [] # 添加节点前与添加节点后total_route_list的中间转化列表
middle_list = [] # 添加节点前与添加节点后total_list的中间转化列表
answer_list = []
while True:
if len(total_route_list[0]) == (step + 1):
for indx in range(len(total_list)):
change_coordinate1 = [(swap[0] - 1) // 3, (swap[0] - 1) % 3] # 记录要交换的位置在3*3列表的位置
change_coordinate2 = [(swap[1] - 1) // 3, (swap[1] - 1) % 3]
t = total_list[indx][change_coordinate1[0]][change_coordinate1[1]]
total_list[indx][change_coordinate1[0]][change_coordinate1[1]] = total_list[indx][change_coordinate2[0]][change_coordinate2[1]]
total_list[indx][change_coordinate2[0]][change_coordinate2[1]] = t
# 判断交换的两个图片是否有空图,有则更新空白图片的位置
if change_coordinate1 == total_route_list[indx][-1]:
total_route_list[indx][-1] = change_coordinate2
if change_coordinate2 == total_route_list[indx][-1]:
total_route_list[indx][-1] = change_coordinate1
return total_list,total_route_list,answer_list
# 对每一条从根节点到叶节点的路径继续添加子节点
for indx in range(len(total_route_list)):
blank_coordinate = total_route_list[indx][-1] # 新添加的子节点的父节点
if len(total_route_list[indx]) > 1:
parent_blank_coordinate = total_route_list[indx][-2] # 新添加子节点的爷爷节点,主要是防止空白块移动重复
# 得到可以与当前空白块移动的位置坐标
child_coordinate_list = []
if blank_coordinate == [0,0]:
child_coordinate_list = [[0,1],[1,0]]
elif blank_coordinate == [0,1]:
child_coordinate_list = [[0,0],[0,2],[1,1]]
elif blank_coordinate == [0,2]:
child_coordinate_list = [[0,1],[1,2]]
elif blank_coordinate == [1,0]:
child_coordinate_list = [[0,0],[1,1],[2,0]]
elif blank_coordinate == [1,1]:
child_coordinate_list = [[0,1],[1,0],[1,2],[2,1]]
elif blank_coordinate == [1,2]:
child_coordinate_list = [[0,2],[1,1],[2,2]]
elif blank_coordinate == [2,0]:
child_coordinate_list = [[2,1],[1,0]]
elif blank_coordinate == [2,1]:
child_coordinate_list = [[2,0],[1,1],[2,2]]
else:
child_coordinate_list = [[2,1],[1,2]]
if len(total_route_list) > 1: # 只要有多余一个节点,则每条路径都至少有两个节点存在
child_coordinate_list.remove(parent_blank_coordinate)
for child_coordinate in child_coordinate_list:
# a = list.copy(total_route_list[indx])#得到一个新节点路径,保存着之前与当前空白块的移动位置
a = copy.deepcopy(total_route_list[indx]) #采用深复制,使得total_route_list[index]内部列表元素不被更改
a.append(child_coordinate)
middle_route_list.append(a)
# 更新当前叶节点的3*3列表的状态
b = copy.deepcopy(total_list[indx])
t = 0
t = b[blank_coordinate[0]][blank_coordinate[1]]
b[blank_coordinate[0]][blank_coordinate[1]] = b[child_coordinate[0]][child_coordinate[1]]
b[child_coordinate[0]][child_coordinate[1]] = t
middle_list.append(b)
# 若当前列表状态为[[0,1,2],[3,4,5],[6,7,8]],将路径保存在答案列表当中
if b == [[0, 1, 2], [3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8]]:
total_route_list = middle_route_list.copy()
total_list = middle_list.copy()
answer_list.append(a)
return total_list,total_route_list,answer_list
total_route_list = middle_route_list.copy()
total_list = middle_list.copy()
middle_route_list = []
middle_list = []
def get_sequence(blank_move_list):
sequence = ""
for i in range(len(blank_move_list) - 1):
row1 = blank_move_list[i][0]
col1 = blank_move_list[i][1]
row2 = blank_move_list[i + 1][0]
col2 = blank_move_list[i + 1][1]
if row2 - row1 == 1:
sequence += "s"
elif row2 - row1 == -1:
sequence += "w"
elif col2 - col1 == 1:
sequence += "d"
else:
sequence += "a"
return sequence
第三:如果在强制交换前就已经得到结果了,就直接将对应的序列提交即可。否则记录此时从一开始到达当前状态的路径以及对应的列表状态,然后将各自的当前列表状态先进行判断是否有解,我把所有的解都存到.pkl文件里面,方法是从目标状态列表,即012345678开始,根据空白快在原图的位置可分为九种情况,对于每一种情况我通过循环的方式去移动空白块,只要出现新的列表状态我就把他以及到达他的路径序列保存下来,让他一直运行,直到不再增加新的列表或者增加得比较慢,我就将所有的列表,以及到达该列表状态得最短路径以字典的形式保存下来写入到.pkl文件当中。在强制交换后存在有解和无解的列表,有解的列表直接从.pkl文件当中取出对应的序列,转换后再添加其强制交换以前的序列,就得到一个结果,这样我就将所有有解的情形以及对应的路径分别保存在两个列表当中,无解的情形其实就是列表不在存放我有解的列表当中,此时我会对每一种无解的列表进行两两互换,若互换以后有解,则将他们强制交换前的移动序列以及自由交换后有解的序列拼接起来,然后将序列以及自由交换的两个图片数字标签保存下来。最后我分别从强制交换后有解,以及强制交换后无解自由交换后有解的最短序列提取出来,然后再对比两种情况的最短序列,取较短的一种作为最终结果。
以下代码是用来得到空白块在原图的位置为0的所有解
import copy,json
import pickle
from time import *
def get_sequence(blank_move_list):
sequence = ""
for i in range(len(blank_move_list) - 1):
row1 = blank_move_list[i][0]
col1 = blank_move_list[i][1]
row2 = blank_move_list[i + 1][0]
col2 = blank_move_list[i + 1][1]
if row2 - row1 == 1:
sequence += "w"
elif row2 - row1 == -1:
sequence += "s"
elif col2 - col1 == 1:
sequence += "a"
else:
sequence += "d"
return sequence
all_route_list = []
all_list = []
total_route_list = []
blank_coordinate = [0,0]
total_route_list.append([blank_coordinate])
total_list = []
lable_list= [[0,1,2],[3,4,5],[6,7,8]]
total_list.append(lable_list)
middle_list =[]
middle_route_list = []
print(len(total_route_list))
for i in range(29):
print(i)
b1 =time()
for indx in range(len(total_route_list)):
# print(len(total_route_list))
blank_coordinate = total_route_list[indx][-1] # 新添加的子节点的父节点
# print(blank_coordinate)
if len(total_route_list[indx]) > 1:
parent_blank_coordinate = total_route_list[indx][-2] # 新添加子节点的爷爷节点,主要是防止空白块移动重复
# 得到可以与当前空白块移动的位置坐标
if blank_coordinate == [0,0]:
child_coordinate_list = [[0,1],[1,0]]
elif blank_coordinate == [0,1]:
child_coordinate_list = [[0,0],[0,2],[1,1]]
elif blank_coordinate == [0,2]:
child_coordinate_list = [[0,1],[1,2]]
elif blank_coordinate == [1,0]:
child_coordinate_list = [[0,0],[1,1],[2,0]]
elif blank_coordinate == [1,1]:
child_coordinate_list = [[0,1],[1,0],[1,2],[2,1]]
elif blank_coordinate == [1,2]:
child_coordinate_list = [[0,2],[1,1],[2,2]]
elif blank_coordinate == [2,0]:
child_coordinate_list = [[2,1],[1,0]]
elif blank_coordinate == [2,1]:
child_coordinate_list = [[2,0],[1,1],[2,2]]
else:
child_coordinate_list = [[2,1],[1,2]]
if len(total_route_list) > 1: # 只要有多余一个节点,则每条路径都至少有两个节点存在
child_coordinate_list.remove(parent_blank_coordinate)
for child_coordinate in child_coordinate_list:
## a = list.copy(total_route_list[indx])#得到一个新节点路径,保存着之前与当前空白块的移动位置
a = copy.deepcopy(total_route_list[indx])
a.append(child_coordinate)
# 更新当前叶节点的3*3列表的状态
b = copy.deepcopy(total_list[indx])
t = 0
t = b[blank_coordinate[0]][blank_coordinate[1]]
b[blank_coordinate[0]][blank_coordinate[1]] = b[child_coordinate[0]][child_coordinate[1]]
b[child_coordinate[0]][child_coordinate[1]] = t
middle_route_list.append(a)
middle_list.append(b)
# if b not in total_list:
# middle_route_list.append(a) #使用这些筛选代码用时会非常的长
# middle_list.append(b)
if b not in all_list:
all_list.append(b)
all_route_list.append(a)
if i >= 15 :
begin_time1 = time()
# res = [middle_list.index(x) for x in set(middle_list)]
middle_m_list = [str(i) for i in middle_list]
se = set(middle_m_list)
res = []
# res = [middle_list.index(x) for eval(x) in se]
for i in range(len(se)):
a = middle_list.index(eval(list(se)[i]))
res.append(a)
del_res = {i for i in range(len(middle_list))} - set(res)
count = 0
y = list(del_res)
y.sort()
for j in y :
del middle_list[j-count]
del middle_route_list[j-count]
count += 1
total_route_list = middle_route_list.copy()
total_list = middle_list.copy()
print(len(total_route_list))
print(len(all_list))
middle_route_list = []
middle_list = []
if len(all_list) > 177000:
break
all_sentence = []
print(len(all_list))
for i in range(len(all_route_list)):
sentence = get_sequence(all_route_list[i])
sentence = sentence[::-1]
all_sentence.append(sentence)
print(len(all_sentence))
str_all_list = []
for i in range(len(all_route_list)):
str_all_list.append(str(all_list[i]))
dic =dict()
for i in range(len(str_all_list)):
key = str_all_list[i]
dic[key] = all_sentence[i]
with open("00.pkl", 'wb') as t: # 将数据写入pkl文件
pickle.dump(dic, t)
【2.2.2】github
https://github.com/fzx-123/-21/tree/main
【2.2.3】遇到的代码块异常
问题描述:在判断列表是否在我存放的解集当中的时候,列表以及对应的序列我以字典的形式存放到文件当中,在判断列表是否有解的时候我直接将列表当作键去取对应的序列,直接就抛出了错误。
解决尝试:我将列表转换为字符串形式,用列表对应的字符串当做键,去判断该键是否在字典当中
是否解决:解决了
有何收获:更加熟悉对字典的键的使用,相信自己以后不会犯相同的错误了
【2.2.4】评价你的队友
在编写代码遇到困难的时候,我队友会很积极的帮我在网上找解决办法,虽然到测试前一天晚上测试的时候发现我的算法有问题,测试返回结果几乎都是false,但是我队友丝毫没有抱怨的意思,而是尽力的帮我找解决办法,很感动。尽管后来用了两天的时间解决了这个问题,但是我们组却少做了两天的题目,基本测试分都拿不全,只能靠最后一天的测试让排名往前挤一挤,我感觉挺愧疚的。和你一起完成这次作业虽让很艰难(我的编程太弱了),但是很愉快。而且博客也几乎是我队友完成的,看上去挺花里胡哨的,优秀!
【2.2.5】Personal Software Process和学习进度条
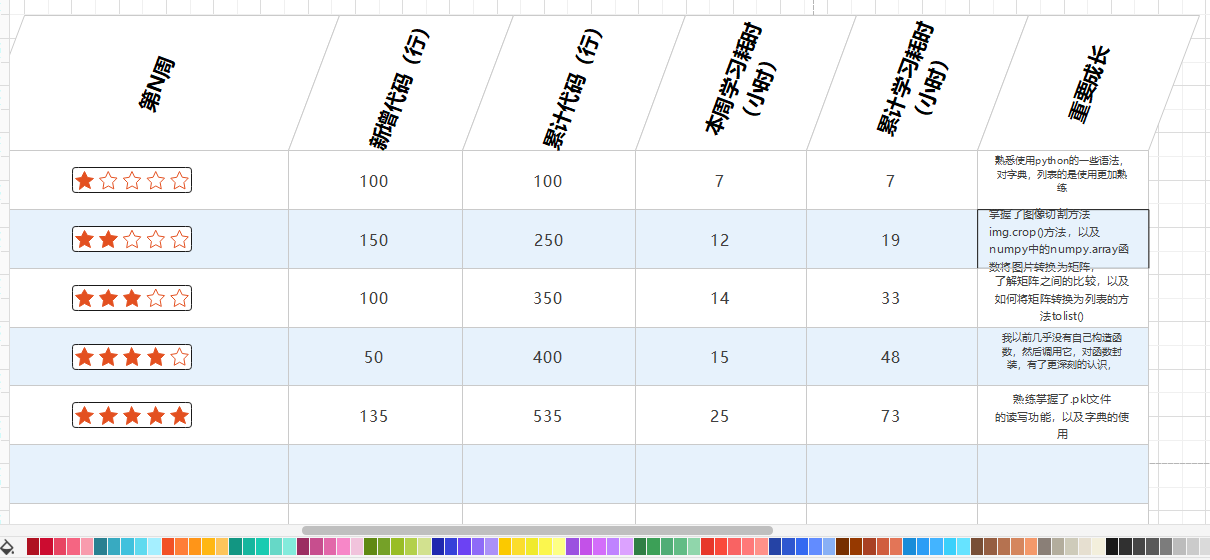
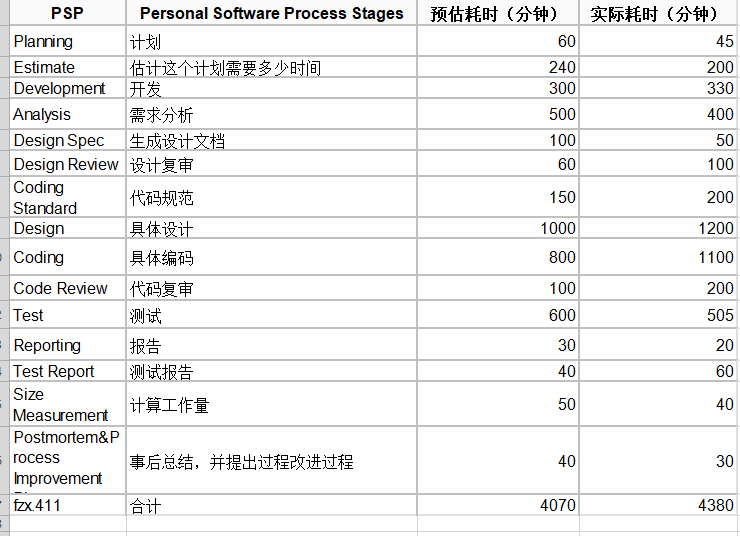
动画