Collection
首先Java中的collection都是支持泛型和类型安全
由于Java单根继承, 所以不指定, 可以在collection里面放任何对象, collection会都当作object对象, 当然这样处理, 在对象取出时, 需要自己向下转型
ArrayList apples = new ArrayList(); //默认为object apples.add(new Apple()); Apple a = (Apple)apples.get(0); //手动转型
当然也可以指定类型, 类似c++模板语法, 编译器会默认知道存放的是Apple
ArrayList<Apple> apples = new ArrayList<Apple>();
Collection接口提供的函数,
boolean add(Object obj) //添加一个Object元素 boolean addAll(Collection c) boolean contains(Object obj) //判断obj是否是调用collection的一个元素(属于) boolean containsAll(Collection c) //判断c是否是调用collection的子集(包含) boolean equals(Collection c) //判断c是否与调用collection相等 int hashCode() //返回collection的hash code boolean removeAll(Collection c) //从调用collection中去掉所有c中包含的元素(差集) boolean retainAll(Collection c) //交集
Object[] toArray() //返回collection的元素组成的数组 void clear() boolean isEmpty() int size()
完整的类图,
迭代器(Iterator)
提供对collection统一的访问方式,
Iterator iterator = collection.iterator();//得到一个迭代器 while (iterator.hasNext()) {//遍历 Object element = iterator.next(); System.out.println("iterator = " + element); }
上面已经显示iterator(), hasNext(), next()的使用方式
还有remove(), 删除由next方法返回的最后一个元素, 即先调用next, 再调用remove删除刚返回的element
Foreach
对iterator的封装, 底层仍然是调用iterator, 所以任意实现了Iterable接口的class对象, 都可以使用Foreach
Collection<String> cs = new LinkedList<String>(); for(String s : cs) System.out.print("‘" + s + "‘ ");
ListIterator
专门用于处理list的iterator, 支持双向遍历和element更新
public interface ListIterator<E> extends Iterator<E> { boolean hasNext(); E next(); boolean hasPrevious(); //支持向前遍历 E previous(); int nextIndex(); //对位置index的支持 int previousIndex(); void remove(); void set(E e); //更新最后遍历到的元素 void add(E e); //在最后遍历到的元素后add element }
List
可见对于List, 有比较老的版本, Vector和Stack, 是线程安全的, 但相应的效率较低
对于新版本, ArrayList, 基于数组实现; LinkedList, 基于链表实现, 非线程安全, 相应的效率较高, 这样当你需要考虑线程安全的时候自己加上, 更为合理.
和collection的基类相比, 增加对于位置序号的操作
void add(int index, Object element) //添加对象element到位置index上 boolean addAll(int index, Collection collection) //在index位置后添加容器collection中所有的元素 Object get(int index) //取出下标为index的位置的元素 int indexOf(Object element) //查找对象element在List中第一次出现的位置 int lastIndexOf(Object element) //查找对象element在List中最后出现的位置 Object remove(int index) //删除index位置上的元素 Object set(int index, Object element) //将index位置上的对象替换为element 并返回老的元素 List subList (int start, int end) //取出子list
LinkedList
除了支持标准的List接口, 还可以用于实现队列和栈
stack
public class Stack<T> { private LinkedList<T> storage = new LinkedList<T>(); public void push(T v) { storage.addFirst(v); } public T peek() { return storage.getFirst(); } public T pop() { return storage.removeFirst(); } public boolean empty() { return storage.isEmpty(); } public String toString() { return storage.toString(); } }
queue
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>(); //LinkedList是Queue的子类,已经包含queue的接口 offer() //插入element到队尾 peek(), element() //不移除,返回队头,区别是为空时, peek返回null, 而element会抛异常 poll(), remove() //移除并返回队头,同样为空时, poll返回null, 而remove会抛异常
PriorityQueue, 接口相同, 只不过基于最小堆实现
deque, 双向队列
public class Deque<T> { private LinkedList<T> deque = new LinkedList<T>(); public void addFirst(T e) { deque.addFirst(e); } public void addLast(T e) { deque.addLast(e); } public T getFirst() { return deque.getFirst(); } public T getLast() { return deque.getLast(); } public T removeFirst() { return deque.removeFirst(); } public T removeLast() { return deque.removeLast(); } public int size() { return deque.size(); } public String toString() { return deque.toString(); } }
Map
Object put(Object key,Object value) Object remove(Object key) void putAll(Map mapping) //将另外一个Map中的元素存入当前的Map中 Object get(Object key) boolean containsKey(Object key) //判断Map中是否存在某键(key) boolean containsValue(Object value) //判断Map中是否存在某值(value) public Set keySet() //返回所有的键(key), 用set, 不可重复 public Collection values() //返回所有的值(Value),用Collection, 可以重复 public Set entrySet() //返回一个实现 Map.Entry 接口的元素 Set
Set, 基于Map实现
和数学上的set概率是相同的, 最大特性是不允许有重复元素
所以可以用来查同, 过滤等, 当然实现机制用hash来实现
Set的接口等同于collection的接口
常用的set操作,
Union, s1.addAll(s2)
Intersection, s1.retainAll(s2)
补集, all.removeAll(set)
几种不同的set实现只是在于遍历顺序不同,
HashSet, 基于HashMap实现
最常见的set, 遍历时无序
TreeSet, 基于红黑树实现
遍历时, 元素有序, 所以成员要求实现Comparable接口,或者使用Comparator构造TreeSet
LinkedHashSet, 基于hash实现, 但是使用链表维护插入顺序
可以以插入序进行遍历
Collection Utilities
java.util.Collections的静态方法
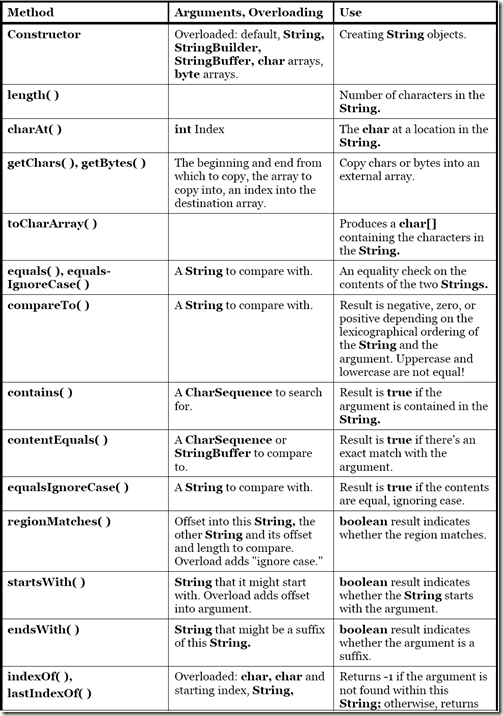
String
String的不可变性, 任何更改操作, 其实都是创建新的String对象
String和char, int转化
String s = new String("asdfds"); char [] ch = s.toCharArray(); String s1 = ch.toString(); Integer i = new Integer (3); s1 = i.toString(); int a = Integer.parseInt(s1);