源码版本: 17.0.1
1. useState在哪?
//myReact.js
import { useState } from 'react';
//reactsrcindex.js
export { useState } from './src/React';
//reactsrcReact.js
import { useState } from './ReactHooks';
//reactsrcReactHooks.js
export function useState<S>(
initialState: (() => S) | S,
): [S, Dispatch<BasicStateAction<S>>] {
const dispatcher = resolveDispatcher();
return dispatcher.useState(initialState);
}
function resolveDispatcher() {
const dispatcher = ReactCurrentDispatcher.current;
return dispatcher;
}
//reactsrcReactCurrentDispatcher.js
const ReactCurrentDispatcher = {
current: (null: null | Dispatcher),
};
//react-reconsilersrcReactInternalTypes.js
export type Dispatcher = ...
找到这里发现居然是一个type,这肯定不对,全文搜索Dispatcher关键字,最终
//react-reconcilersrcReactFiberHooks.new.js
const HooksDispatcherOnMount: Dispatcher = {
useState: mountState,
};
const HooksDispatcherOnUpdate: Dispatcher = {
useState: updateState,
};
const HooksDispatcherOnRerender: Dispatcher = {
useState: rerenderState,
};
找到三个实现?再搜
export function renderWithHooks<Props, SecondArg>(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
Component: (p: Props, arg: SecondArg) => any,
props: Props,
secondArg: SecondArg,
nextRenderLanes: Lanes,
){
...
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current =
current === null || current.memoizedState === null
? HooksDispatcherOnMount
: HooksDispatcherOnUpdate;
...
// Check if there was a render phase update
if (didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdateDuringThisPass) {
let numberOfReRenders: number = 0;
do {
didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdateDuringThisPass = false;
...
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current = __DEV__
? HooksDispatcherOnRerenderInDEV
: HooksDispatcherOnRerender;
...
} while (didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdateDuringThisPass);
}
}
居然是这样的,根据是否是第一次渲染调用不同的实现。我们暂时不考虑rerender阶段。
renderWithHooks是在Fiber中根据类型是 FunctionComponent时调用的。这里先不管Fiber的整个流程。
function mountState<S>(
initialState: (() => S) | S,
): [S, Dispatch<BasicStateAction<S>>] {
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
if (typeof initialState === 'function') {
// $FlowFixMe: Flow doesn't like mixed types
initialState = initialState();
}
hook.memoizedState = hook.baseState = initialState;
const queue = (hook.queue = {
pending: null,
dispatch: null,
lastRenderedReducer: basicStateReducer,
lastRenderedState: (initialState: any),
});
const dispatch: Dispatch<
BasicStateAction<S>,
> = (queue.dispatch = (dispatchAction.bind(
null,
currentlyRenderingFiber,
queue,
): any));
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];
}
function updateState<S>(
initialState: (() => S) | S,
): [S, Dispatch<BasicStateAction<S>>] {
return updateReducer(basicStateReducer, (initialState: any));
}
看来终于找到了
2. useState干了啥?
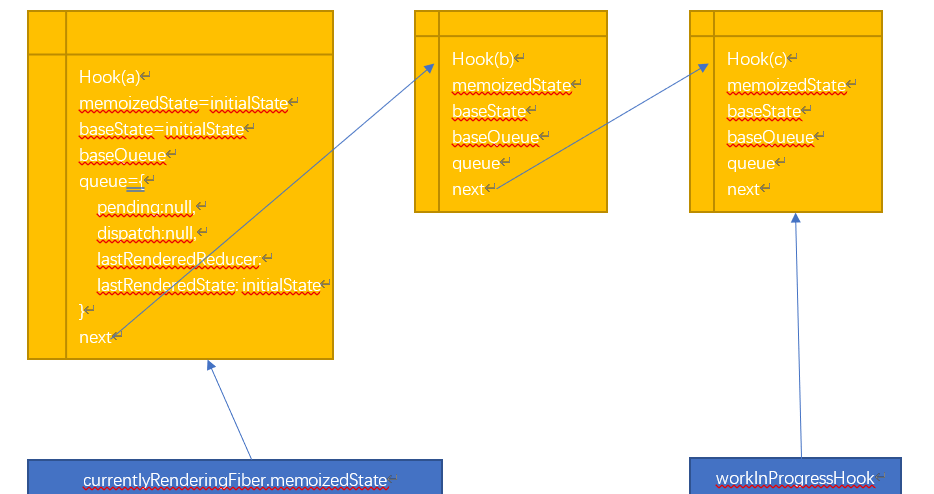
如果我们按照以下顺序调用useState,我们看看他做了什么。
const [a, setA] = useState(“a”);
const [b, setB] = useState(“b”);
const [c, setC] = useState(“c”);
根据源码来看,他生成了下面这样一个链表,然后返回了初始state(如果是函数则是计算结果)和一个叫dispatchAction的函数。
3. setXXX 干了啥?
我们通常使用的setXXX就是调用的dispatchAction函数,那我们看看他干了什么。
function dispatchAction<S, A>(
fiber: Fiber,
queue: UpdateQueue<S, A>,
action: A,
) {
const update: Update<S, A> = {
lane,
action,
eagerReducer: null,
eagerState: null,
next: (null: any),
};
// Append the update to the end of the list.
const pending = queue.pending;
if (pending === null) {
// This is the first update. Create a circular list.
update.next = update;
} else {
update.next = pending.next;
pending.next = update;
}
queue.pending = update;
...
scheduleUpdateOnFiber(fiber, lane, eventTime);
}
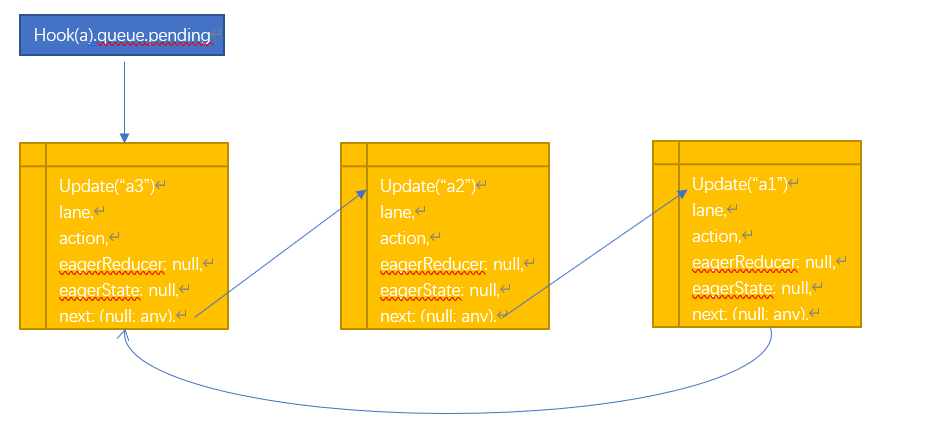
看起来有点绕,其实就是将我们的setXXX放入循环链表队列,然后等待执行。
如果我们按以下顺序调用setA
setA(“a1);
setA(“a2);
setA(“a3);
将会生成如下的链表,然后等待Fiber调度重新渲染。
4. 我的state是怎么被更新的?
现在就等Fiber调度更新了,我们知道他会再次调用renderWithHooks,但是这次会使用HooksDispatcherOnUpdate的实现,因此源码如下:
function basicStateReducer<S>(state: S, action: BasicStateAction<S>): S {
// $FlowFixMe: Flow doesn't like mixed types
return typeof action === 'function' ? action(state) : action;
}
function updateState<S>(
initialState: (() => S) | S,
): [S, Dispatch<BasicStateAction<S>>] {
return updateReducer(basicStateReducer, (initialState: any));
}
function updateReducer<S, I, A>(
reducer: (S, A) => S,
initialArg: I,
init?: I => S,
): [S, Dispatch<A>] {
const hook = updateWorkInProgressHook();
const queue = hook.queue;
queue.lastRenderedReducer = reducer;
const current: Hook = (currentHook: any);
let baseQueue = current.baseQueue;
// 把上图中的pending链表挂载到baseQueue上,pending链表置空
const pendingQueue = queue.pending;
if (pendingQueue !== null) {
// 把未被处理的更新也放入到baseQueue上
if (baseQueue !== null) {
const baseFirst = baseQueue.next;
const pendingFirst = pendingQueue.next;
baseQueue.next = pendingFirst;
pendingQueue.next = baseFirst;
}
current.baseQueue = baseQueue = pendingQueue;
queue.pending = null;
}
if (baseQueue !== null) {
const first = baseQueue.next;
let newState = current.baseState;
let newBaseState = null;
let newBaseQueueFirst = null;
let newBaseQueueLast = null;
let update = first;
// 把链表中的所有更新依次执行完成
do {
const updateLane = update.lane;
if (!isSubsetOfLanes(renderLanes, updateLane)) {
...
} else {
...
// 处理更新
if (update.eagerReducer === reducer) {
newState = ((update.eagerState: any): S);
} else {
const action = update.action;
//reducer会判断是否是函数还是值,如果传入setXXX的是函数,则进行计算结果
newState = reducer(newState, action);
}
}
update = update.next;
} while (update !== null && update !== first);
...
hook.memoizedState = newState;
hook.baseState = newBaseState;
hook.baseQueue = newBaseQueueLast;
queue.lastRenderedState = newState;
}
const dispatch: Dispatch<A> = (queue.dispatch: any);
//返回新的state值和缓存的dispatch函数
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];
}
我们排除一些干扰代码和rerender相关的代码。现在知道了,原来是这样的。
5. 为什么setXXX不会被改变?
Note
React guarantees that
setStatefunction identity is stable and won’t change on re-renders. This is why it’s safe to omit from theuseEffectoruseCallbackdependency list.
官方文档上有这么一句话,setState方法在重新渲染的时候不会被改变。为什么?
还记得第一节的mountState中有这么一句话,把当前Fiber和queue绑定到dispatchAction上并赋值给queue。
const dispatch: Dispatch<
BasicStateAction<S>,
> = (queue.dispatch = (dispatchAction.bind(
null,
currentlyRenderingFiber,
queue,
): any));
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];
然后在update的时候,使用的是当前hook的queue上dispatch方法返回,所以我们使用的setXXX是不会变的。
const dispatch: Dispatch<A> = (queue.dispatch: any);
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];