第一次个人编程作业
一、题目分析(tucao)
首先来看一下题目给的样例,样例选自作家余华的代表作之一——《活着》讲述了在大时代背景下,随着内战、三反五反,大跃进,文化大革命等社会变革...
(1)注意到orig文本样例的特点:①每一行之间都有一行空换行;
(2)对于样例给的其他几篇所谓的“抄袭”样本,用这样抄袭手法的人估计审核老师都不用查重就直接給零分了吧,格式完全不对,语句根本不通,还有我不认识的字。由此打消了我之前对于语义分析方面的顾虑,既然是机器随机“抄袭",只考虑文本的”物理重复率“应该就够了,因此想到了余弦相似度算法;
(3)长文本的处理方法:鉴于生成”抄袭“样本的手段极其暴力(标点符号随风飘扬),我也使用暴力的方法,②将所有的标点先去除(仅剩逗号),用逗号作为分隔符split各个文本段(经测试,以逗号分隔效果优于句号);
(4)除了奇奇怪怪的换行和标点,还有不少混淆视听的blank③去除所有多余的空格;

这些的啥我是看不懂
二、算法构思
1、数据处理,为文本相似度算法清理障碍;
2、jieba分词,对每”句“文本分别分词得到词列表;
3、余弦相似度采用基于gensim的TF-IDF算法来实现,就不重复造轮子了;
4、对每”句“文本分别计算相似度,最后求相似度期望。
算法精髓TF-IDF概要
TF-IDF是一种统计方法,用以评估一字词对于一个文件集或一个语料库中的其中一份文件的重要程度。 TF-IDF的主要思想是:如果某个词在某篇文章中出现的频率高,并且在其他文章中很少出现,则认为该词可以作为该篇文章的关键词。
计算公式
求某篇文章中某个词的TF-IDF的计算公式:
TF-IDF = TF × IDF
TF为词频,指的是该词在该文章中出现的频率;IDF为逆文档频率,衡量该词在所有文章中的出现频率。
TF的计算公式:
TF = 该词在该文章中出现次数 ÷ 该文章中的总词数
IDF的计算公式:
IDF = log[ 文章总数 ÷ (出现该词的文章数+1) ]
其中log的底数为自定义取值,一般取e。
下面通过一个简单的例子介绍利用TF-IDF计算文本相似度的原理。
假设词库中共有5个词:
dictionary = (word0,word1,word2,word3,word4)
计算其中两个文本 text1 = (word0,word1) 和 text2 = (word0,word4) 的相似度。
首先计算每个文本中每个词的tfidf权重,构成两个维度与dictionary一一对应的向量,结果如下:
text1_vec = ( 0.2,0.3 ,0,0,0 )
text2_vec = ( 0.5,0 ,0,0,0.1 )
其中,当某词的tfidf权重为0,则代表该文本中没有该词或权重非常小,可以忽略。
然后,利用余弦相似度,计算两个向量的距离,即代表两个文本的相似度。
A、B两个向量的余弦相似度计算公式如下:
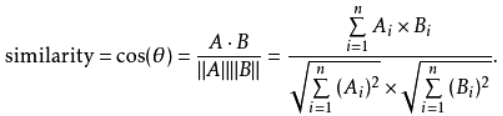
所以,sim_t1&t2 = (0.2×0.5)÷[ (0.2²+0.3²)½×(0.5²+0.1²)½ ] = 0.1149
三、主要代码
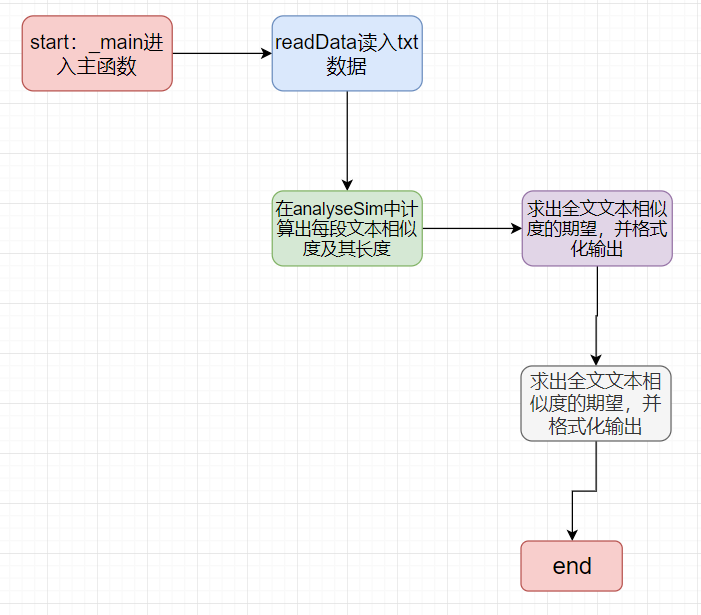
流程图
1.数据处理模块说明
①消除换行
②消除空格
③除去所有除逗号以外的标点符号
④以逗号为分隔符,划分为若干”句子“
def readData(textPath):
data = []
te = ""
with open(textPath, "r", encoding='utf-8') as org:
for line in org.readlines():
te += line # lines to line
# 应当先除换行,再解决空格,去除除了逗号以外所有标点,最后用逗号split
# print(te)
te = te.replace("
", "")
te = te.replace(" ", "")
###
te = te.replace("、", "")
te = te.replace(":", "")
te = te.replace("“", "")
te = te.replace("”", "")
te = te.replace(";", "")
te = te.replace("。", "")
###
temp = te.split("。")
for i in temp:
data.append(i.split(","))
data = sum(data, [])
return data
2.计算模块接口的设计与实现过程
def analyse(base_data, target_data):
'''
parameters:
base_data:Union[list[str],]
target_data:Union[list[str],]
'''
# 1.walk through all datas of "base_data" and split them by word of Chinese
base_data = [base_data, " "]
print(base_data[0])
base_items = [[i for i in jieba.lcut(item)] for item in base_data]
print(base_items[0])
# 2.create a dictionary
dictionary = corpora.Dictionary(base_items)
# 3.create a corpus by sparse vector from doc2bow
corpus = [dictionary.doc2bow(item) for item in base_items]
# 4.with tf-idf
tf = models.TfidfModel(corpus)
# 5.get features by token2id
num_features = len(dictionary.token2id.keys())
# 6.calculate the similarity of sparse matrix and an index is established
index = similarities.MatrixSimilarity(tf[corpus], num_features=num_features)
# 7.process the testText
test_words = [word for word in jieba.cut(target_data)]
print(test_words)
# 8.the sparse vector of testText
new_vec = dictionary.doc2bow(test_words)
# 9.get the sims
sims = index[tf[new_vec]]
print(list(sims)[0])
return list(sims)[0]
3.文章相似度的期望求法
# analyse
size = analyseSim(origText, testText)
similarity = np.vdot(weight, value)/size
print("Final similarity:{}".format(similarity))
out_path = "./result/"
with open(out_path + 'res.txt', "w", encoding='utf-8') as res:
res.write(str(similarity))
其中weight是每个”句子“长度组成的矩阵;
value是每个”句子“对应的相似度组成的矩阵;
size为文章总长度;
通过numpy.vdot快速进行矩阵内积,除以总size的到相似度期望。
四、性能分析
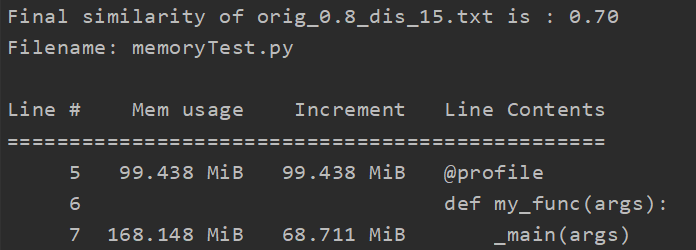
1.内存占用:
分析方法:调用memory_profiler库,在命令行中输入python -m memory_profiler memory_profiler_test.py
分析结果:(对于单个测试文件)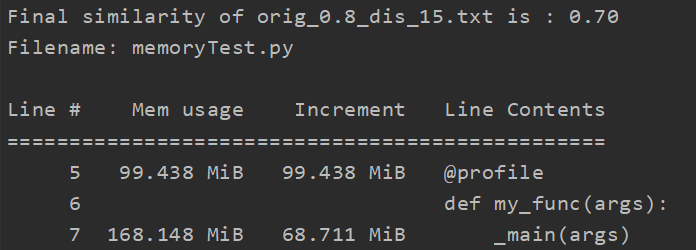
显然占用内存大小符合预期
2.单元测试:
分析方法:
使用unittest,直接运行python -m test_v2.py
(请注意修改相关路径)
import unittest
from main import readData, analyseSim
import numpy as np
base_path = "C:\Users\Breeze\Desktop\soft_engi\textSimilarity\textSimilarity\041801420\data\sim_\"
class TestForAllTextTfIdf(unittest.TestCase):
@classmethod
def setUp(self):
print("call setup……")
@classmethod
def tearDown(self):
print("call teardown")
def test_self_tfidf(self):
print("正在载入orig.txt")
_main("orig.txt",
"orig.txt")
def test_add_tfidf(self):
print("正在载入orig.txt")
_main("orig.txt",
"orig_0.8_dis_10.txt")
def test_del_tfidf(self):
print("正在载入orig.txt")
_main("orig.txt",
"orig_0.8_dis_10.txt")
def test_dis_1_tfidf(self):
print("正在载入orig_0.8_dis_1.txt")
_main("orig.txt",
"orig_0.8_dis_1.txt")
def test_dis_3_tfidf(self):
print("正在载入orig_0.8_dis_3.txt")
_main("orig.txt",
"orig_0.8_dis_3.txt")
def test_dis_7_tfidf(self):
print("正在载入orig_0.8_dis_7.txt")
_main("orig.txt",
"orig_0.8_dis_7.txt")
def test_dis_11_tfidf(self):
print("正在载入orig_0.8_dis_10.txt")
_main("orig.txt",
"orig_0.8_dis_10.txt")
def test_dis_15_tfidf(self):
print("正在载入orig_0.8_dis_15.txt")
_main("orig.txt",
"orig_0.8_dis_15.txt")
def test_dis_mix_tfidf(self):
print("正在载入orig_0.8_mix.txt")
_main("orig.txt",
"orig_0.8_mix.txt")
def test_dis_rep_tfidf(self):
print("正在载入orig_0.8_rep.txt")
_main("orig.txt",
"orig_0.8_rep.txt")
def _main(origText_path, testText_path):
_path = testText_path
origText_path = base_path + origText_path
testText_path = base_path + testText_path
weight = []
value = []
origText = readData(origText_path)
# print(len(origText))
testText = readData(testText_path)
# print(len(testText))
# analyse
size = analyseSim(origText, testText, weight, value)
similarity = np.vdot(weight, value) / size
print(("Final similarity of {} is : %.2f" % similarity).format(_path))
out_path = "C:\Users\Breeze\Desktop\soft_engi\textSimilarity\textSimilarity\041801420\result\"
with open(out_path + 'res.txt', "a+", encoding='utf-8') as res:
res.write(("%.2f"%(similarity))+'
')
res.close()
return similarity
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
测验结果:
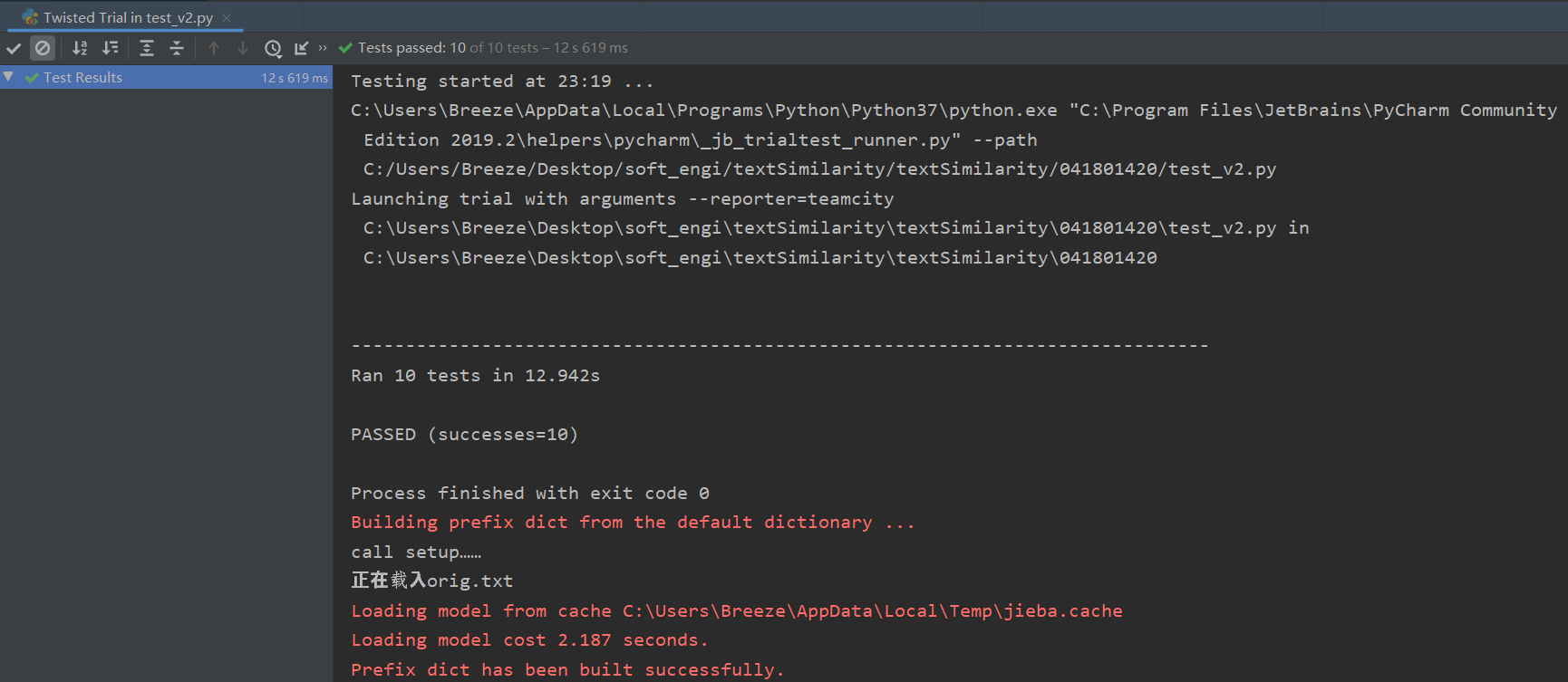
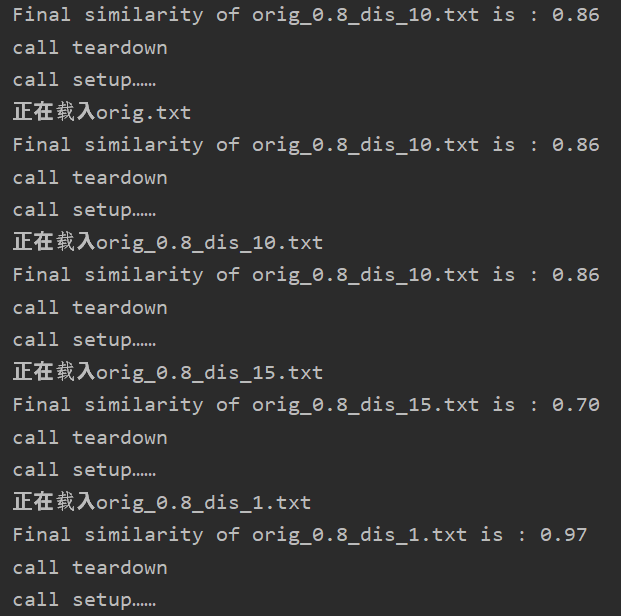
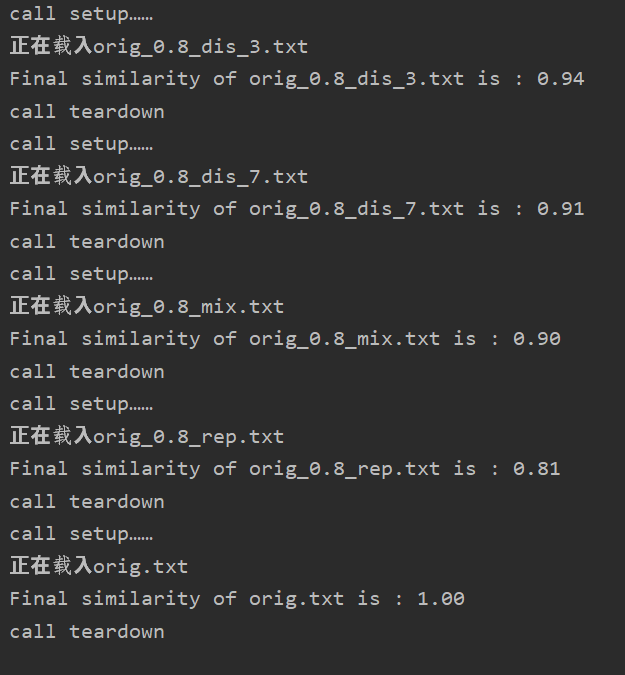
结果分析:
特地加入了原文章与原文查重的例子,检测结果为1.00;
效果符合我的预期;但是该算法的泛化能力实际上是有限的,比如对于语义上的修改,可能导致无法视为抄袭,因为只是在“物理层次”上进行查重。
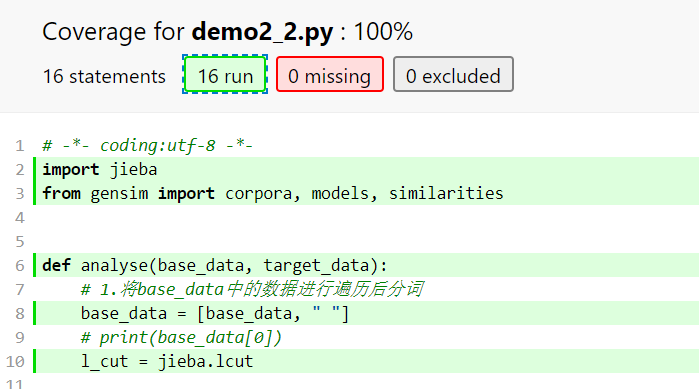
测试覆盖率:使用coverage库(苦逼poorman没有professional pycharm)
3.性能改进:
在for循环中,运用了一个小trick,把需要从库里面找的函数先“复制”出来
l_cut = jieba.lcut
base_items = [[i for i in l_cut(item)] for item in base_data]
doctobow = dictionary.doc2bow
corpus = [doctobow(item) for item in base_items]
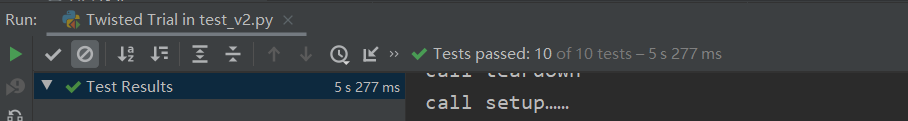
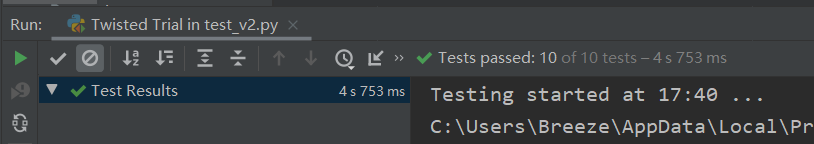
看上去节省了一点时间;有时间再补一下多进程的方法
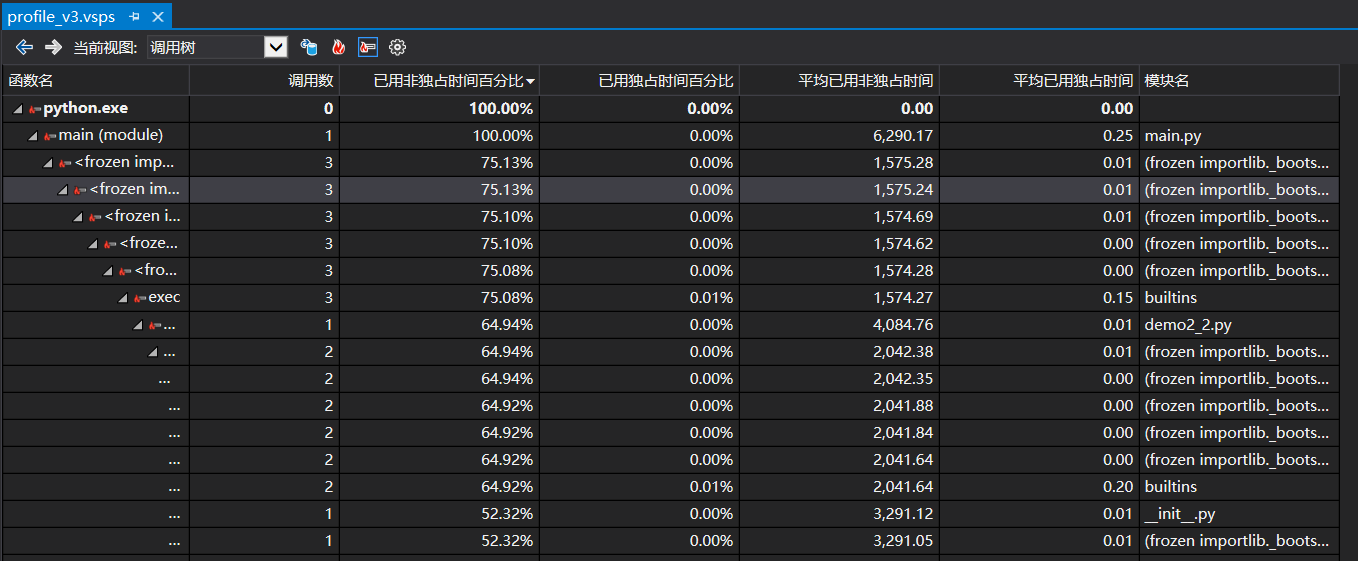
下图为VS2019生成的性能分析图
4.异常处理
对空文本进行了异常处理:
class NonetextError(ValueError):
pass
........................................
if len(te) == 0:
raise NonetextError("the text with path of '{}' is none".format(textPath))
五、PSP表格
其实这个部分如果要做的详细,可能得用Project Professional或者禅道(下次一定)
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 30 | 20 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 30 | 10 |
| Development | 开发 | 60 | 30 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 300 | 360 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 60 | 360 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 | 60 | 120 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 120 | 120 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 60 | 100 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 180 | 200 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 120 | 100 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 120 | 420 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 120 | 60 |
| · Test Repor | · 测试报告 | 60 | 60 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 30 | 30 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 60 | 60 |
| · 合计 | 1410 | 2050 |
六、总结
第一次经历这样的软工实践作业,特别是第一次写单元测试,搞了好久才明白啥意思。。
整个项目下来,单元测试、性能分析差不多占了70%的时间,因为在打单元测试的代码时,发现有的函数接口还得修改,头大。
新接触了unittest库,还有好多性能分析的库;用vs分析过,数据惨不忍睹,应该是vs太重了,在那边测试一篇文章查重要花6s+,而在pycharm里面测试十篇才不到5s;
展望:
还是需要多练习,提高python的熟练度,希望能有一天不要天天咋咋都百度Google;另一方面就是在软件开发方面,要注重代码的质量。平时不要总是想着调包炼丹,做代码搬运工的同时也应该静下心来仔细分析冷静学习。
备注:
corpora 语料库
sparse vectors 稀疏向量
transformation 转换,指由稀疏向量组成的稀疏矩阵生成某个向量空间模型。