Poller的存在,是为了监听事件,但具体监听什么事件呢?
这就需要用到Channel类。一个Channel对象绑定了一个fd(文件描述符),可以用来监听发生在fd上的事件,事件包括空事件(不监听)、可读事件、写完成事件。当fd上被监听事件就绪时,对应Channel对象就会被Poller放入激活队列(activeChannels_),进而在loop循环中调用封装在Channel的相应回调来处理事件。
Channel可以通过EventLoop,向Poller更新自己关心的(监听)事件(通过map Poller::channels_存储)。具体来说,对于PollPoller对象,会同步更新(poll(2))传给内核的poll事件数组pollfds_;对于EPollPoller对象,会同步更新(epoll(7))传递给内核的epoll事件数组events_;
可以这样理解,poll/epoll监听的是fd(上指定的事件pollfd.events),Poller监听的是Channel对象(上指定的事件events_),当监听到事件就绪时,将对应通道加入激活通道队列,在EventLoop的loop循环中依次调用Channel中注册的事件回调。
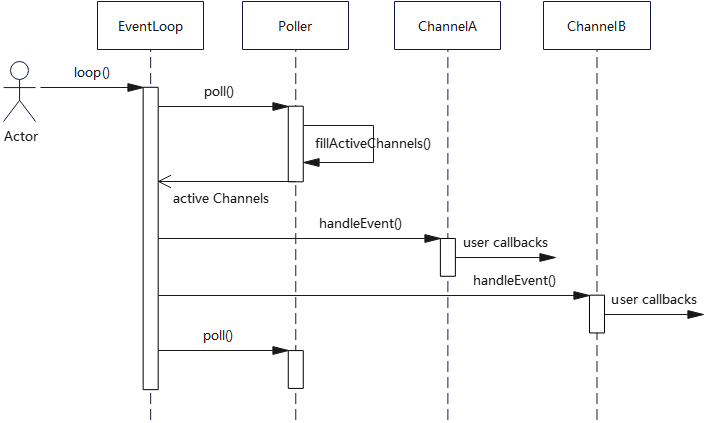
EventLoop、Poller、Channel这3个类构成了Reactor模式的核心,其时序关系如下图:
Channel 类
每个Channel对象从始至终只负责一个文件描述符(fd)的IO事件分发,但不拥有fd,也不会在析构时关闭fd。而是由诸如TcpConnection、Acceptor、EventLoop等,这样需要监听指定文件描述符上事件的类,将fd通过构造函数传递给Channel。
Channel会把不同的IO事件分发为不同的回调,如ReadCallback、WriteCallback,回调对象类型用std::function<>表示,用来定义某个可调用类型。
事件回调类型:
#include <functional>
typedef std::function<void()> EventCallback;
typedef std::function<void(Timestamp)> ReadEventCallback;
Channel成员函数主要包括:
1)设置事件处理的回调函数setCallback(如setReadCallback);
2)使能fd关心的事件events_,可调用enable(如enableReading),该fd及关心的事件会注册到Poller中进行监听;
3)关闭fd关心的事件events_,可调用disable*(如disableReading),会更新该fd在Poller中监听的事件;
4)关闭fd关心的所有事件events_,可调用disableAll,会更新该fd在Poller中监听的事件;
5)删除对fd的监听,会将其从Poller的ChannelMap中移除;
6)Poller监听到Channel事件被激活时,将其加入到激活列表,在EventLoop中回调handleEvent。
Channel类声明
/**
* Channel绑定一个fd, 用于设置fd上要监听的事件, 以及相应的回调函数.
* Poller监听到有通道绑定的事件发生, 就会将其加入激活的通道列表,
* 然后在EventLoop::loop()中调用该Channel对应事件注册的回调函数
*/
class Channel : private noncopyable
{
public:
typedef std::function<void()> EventCallback; // 除了读事件, 用于其他事件(如写/关闭/错误)回调类型
typedef std::function<void(Timestamp)> ReadEventCallback; // 读事件回调类型
Channel(EventLoop* loop, int fd__);
~Channel()
/* 处理事件, 监听事件激活时, 由EventLoop::loop调用 */
void handleEvent(Timestamp recevieTime);
/* 设置事件回调,由Channel对象持有者配置Channel事件回调时调用 */
void setReadCallback(ReadEventCallback cb)
{ readCallback_ = std::move(cb); }
void setWriteCallback(EventCallback cb)
{ writeCallback_ = std::move(cb); }
void setCloseCallback(EventCallback cb)
{ closeCallback_ = std::move(cb); }
void setErrorCallback(EventCallback cb)
{ errorCallback_ = std::move(cb); }
/* 将shared_ptr管理的对象系到本地weak_ptr管理的tie_, 可用于保存TcpConnection指针 */
void tie(const std::shared_ptr<void>&);
int fd() const { return fd_; }
int events() const { return events_; }
void set_revents(int revt) { revents_ = revt; } // used by poller
// int revents() const { return revents_; }
bool isNoneEvent() const { return events_ == kNoneEvent; }
/* 使能/禁用 监听 可读/可写事件, 会影响Poller监听的通道列表 */
void enableReading() { events_ |= kReadEvent; update(); }
void disableReading() { events_ &= ~kReadEvent; update(); }
void enableWriting() { events_ |= kWriteEvent; update(); }
void disableWriting() { events_ &= ~kWriteEvent; update(); }
void disableAll() { events_ = kNoneEvent; update(); }
/* 判断是否请求监听 可写事件 */
bool isWriting() const { return events_ & kWriteEvent; }
/* 判断是否请求监听 可读事件 */
bool isReading() const { return events_ & kReadEvent; }
// for Poller
int index() { return index_; }
void set_index(int idx) { index_ = idx; }
// for debug
string reventsToString() const;
string eventsToString() const;
void doNotLogHup() { logHup_ = false; }
EventLoop* ownerLoop() { return loop_; }
/* 从EventLoop中移除当前通道.
* 建议在移除前禁用所有事件
*/
void remove();
private:
/* 将fd对应事件转化为字符串 */
static string eventsToString(int fd, int ev);
/* update()将调用EventLoop::updateChannel更新监听的通道 */
void update();
/* 根据不同的事件源激活不同的回调函数,来处理事件 */
void handleEventWithGuard(Timestamp receiveTime);
static const int kNoneEvent;
static const int kReadEvent;
static const int kWriteEvent;
EventLoop* loop_;
const int fd_; // file descriptor
int events_; // request events, set by user
int revents_; // returned events, current active events, set by EventLoop/Poller
// used by Poller
// PollPoller: index of poll fds array mapped to fd_
// EPollPoller: operation type for fd: kNew, kAdded, kDeleted
int index_;
bool logHup_;
/* 使用weak_ptr指向shared_ptr所指对象, 防止循环引用. 通常是生命周期不确定的对象, 如TcpConnection */
std::weak_ptr<void> tie_;
bool tied_; /* weak_ptr tie_绑定对象的标志 */
bool eventHandling_; /* 正在处理事件的标志 */
bool addedToLoop_; /* 加入到loop中, 被监听/处理的标志 */
ReadEventCallback readCallback_; /* 可读事件回调 */
EventCallback writeCallback_; /* 可写事件回调 */
EventCallback closeCallback_; /* 关闭事件回调 */
EventCallback errorCallback_; /* 错误事件回调 */
};
Channel中的几个重要函数:
handleEvent 处理事件
处理激活的Channel事件,由Poller更新激活的Channel列表,EventLoop::loop()根据激活Channel列表,逐个执行Channel中已注册好的相应回调。实际事件处理工作,由handleEventWithGuard完成。
/**
* 处理激活的Channel事件
* @details Poller中监听到激活事件的Channel后, 将其加入激活Channel列表,
* EventLoop::loop根据激活Channel回调对应事件处理函数.
* @param recevieTime Poller中调用epoll_wait/poll返回后的时间. 用户可能需要该参数.
*/
void Channel::handleEvent(Timestamp recevieTime)
{
/*
* shared_ptr通过RAII方式管理对象资源guard
* weak_ptr::lock可将weak_ptr提升为shared_ptr, 引用计数+1
*/
std::shared_ptr<void> guard;
if (tied_)
{
/*
* 为什么使用 tie?
* 确保在执行事件处理动作时, 所需的对象不会被释放, 但又不能用shared_ptr,
* 否则可能导致循环引用. 最好使用weak_ptr, 然后lock提升为shared_ptr, 这样更安全.
*/
guard = tie_.lock();
if (guard)
{
handleEventWithGuard(recevieTime);
}
}
else
{
handleEventWithGuard(recevieTime);
}
}
handleEventWithGuard 识别事件并回调
根据不同的激活原因,调用不的回调函数。这些回调函数,是在持有Channel对象,需要进行事件监听的class中进行设置,比如TcpConnection,EventLoop,Acceptor,TimerQueue等。而有些回调函数,经过层层传递,会呈现可网络库的调用者,比如TcpConnection会将处理一个socket fd的读事件回调(新建连接请求),传递给TcpServer::newConnection,这样用户就能通过TcpServer::setConnectionCallback设置其回调。
/**
* 根据不同的激活原因, 调用不同的回调函数
*/
void Channel::handleEventWithGuard(Timestamp receiveTime)
{
eventHandling_ = true; // 正在处理事件
LOG_TRACE << reventsToString(); // 打印fd及就绪事件
if ((revents_ & POLLHUP) && !(revents_ & POLLIN))
{ // fd挂起(套接字已不在连接中), 并且没有数据可读
if (logHup_)
{ // 打印挂起log
LOG_WARN << "fd = " << fd_ << " Channel::handle_event() POLLHUP";
}
// 调用关闭回调
if (closeCallback_) closeCallback_();
}
if (revents_ & POLLNVAL) // 无效请求, fd没打开
{ // fd dont be opened
LOG_WARN << "fd = " << fd_ << " Channel::handle_event() POLLNVAL";
}
if (revents_ & (POLLERR | POLLNVAL)) // 错误条件, 或 无效请求, fd没打开
{ // error or fd dont be opened
if (errorCallback_) errorCallback_();
}
if (revents_ & (POLLIN | POLLPRI | POLLRDHUP)) // 有待读数据, 或 紧急数据(e.g. TCP带外数据), 或流套接字对端关闭连接/写半连接
{ // there is data, urgent data, to be read
if (readCallback_) readCallback_(receiveTime);
}
if (revents_ & POLLOUT)
{
if (writeCallback_) writeCallback_();
}
eventHandling_ = false;
}
update 更新通道
通过EventLoop对象,传递给Poller对象,然后更新其监听的通道列表中对应通道。支持ADD/MOD操作。
void Channel::update()
{
addedToLoop_ = true;
loop_->updateChannel(this);
}
void EventLoop::updateChannel(Channel *channel)
{
assert(channel->ownerLoop() == this);
assertInLoopThread();
poller_->updateChannel(channel);
}
/**
* Update array pollfds_
*
* O(logN)
*/
void PollPoller::updateChannel(Channel *channel)
{
Poller::assertInLoopThread();
LOG_TRACE << "fd = " << channel->fd() << " events = " << channel->events();
if (channel->index() < 0)
{ // a new one, add to pollfds_
// ensure channel point to a new one
assert(channels_.find(channel->fd()) == channels_.end());
struct pollfd pfd;
pfd.fd = channel->fd();
pfd.events = static_cast<short>(channel->events());
pfd.revents = 0;
pollfds_.push_back(pfd);
int idx = static_cast<int>(pollfds_.size()) - 1;
channel->set_index(idx);
channels_[pfd.fd] = channel; // insert (fd, channel)
}
else
{ // update existing one
assert(channels_.find(channel->fd()) != channels_.end());
assert(channels_[channel->fd()] == channel);
int idx = channel->index();
// ensure channel does exist in pollfds_
assert(0 <= idx && idx < static_cast<int>(pollfds_.size()));
struct pollfd& pfd = pollfds_[idx];
assert(pfd.fd == channel->fd() || pfd.fd == -channel->fd() - 1);
pfd.fd = channel->fd();
pfd.events = static_cast<short>(channel->events());
pfd.revents = 0;
if (channel->isNoneEvent())
{
// ignore this pollfd
pfd.fd = -channel->fd() - 1;
}
}
}
remove 移除通道
与update类似,也是通过EventLoop传递给Poller对象,将当前通道从Poller的事件列表中删除。支持DEL操作。
void Channel::update()
{
addedToLoop_ = true;
loop_->updateChannel(this);
}
void EventLoop::updateChannel(Channel *channel)
{
assert(channel->ownerLoop() == this);
assertInLoopThread();
poller_->updateChannel(channel);
}
/**
* 从监听的通道数组channels_中, 移除指定通道
*/
void PollPoller::removeChannel(Channel *channel)
{
Poller::assertInLoopThread();
LOG_TRACE << "fd = " << channel->fd();
assert(channels_.find(channel->fd()) != channels_.end());
assert(channels_[channel->fd()] == channel);
assert(channel->isNoneEvent());
int idx = channel->index();
assert(0 <= idx && idx < static_cast<int>(pollfds_.size()));
const struct pollfd& pfd = pollfds_[idx]; (void)pfd;
// ensure remove one invalid channel from channels_
assert(pfd.fd == -channel->fd() - 1 && pfd.events == channel->events());
size_t n = channels_.erase(channel->fd());
assert(n == 1); (void)n;
// remove pollfd from pollfds_ by index
if (implicit_cast<size_t>(idx) == pollfds_.size() - 1)
{ // last of pollfds_
pollfds_.pop_back();
}
else
{
// swap the pollfd to be removed with the last of pollfds_,
// then remove the last
int channelAtEnd = pollfds_.back().fd;
iter_swap(pollfds_.begin() + idx, pollfds_.end() - 1);
if (channelAtEnd < 0)
{
channelAtEnd = -channelAtEnd - 1;
}
channels_[channelAtEnd]->set_index(idx);
pollfds_.pop_back();
}
}
参考
https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_35261315/article/details/78322176