复习数据结构的时候看到指针的引用,两年前学的细节确实有点想不起来,于是查了一下网上的资料,并且自己实践了一下,总结了一句话就是:
指针作为参数传给函数,函数中的操作可以改变指针所指向的对象和对象的值,但函数结束后还是会指向原来的对象,若要改变,可用指针的指针或者指针的引用。
ps:对原po的代码稍作修改,看上去更直观些。
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 void foo(int *&t, int *y)//此处是int *t还是int *&t,决定了调用该函数的指针本身会不会被修改。分别跑一下程序即可知。 5 { 6 t = y; 7 //*t = 4; 8 cout << "foo1:" << t << endl; 9 cout << "foo2:" << y << endl; 10 } 11 12 int main() 13 { 14 int num = 4; 15 int num2 = 5; 16 int *p = # 17 int *q = &num2; 18 cout <<"p: "<< p << endl; 19 cout <<"q: "<< q << endl; 20 foo(p, q); 21 cout << "after foo" << endl; 22 cout <<"p: "<< p << endl; 23 cout <<"q: "<< q << endl; 24 cout <<"*p: "<< *p << endl; 25 cout <<"*q: "<< *q << endl; 26 cout << "************" << endl; 27 cout<<"num: "<< num<<endl<<"num2: "<<num2<<endl; 28 }
未加&时: 加了&时


可以看出,未加&时,指针在函数中值被修改(即指向了其他对象),但从函数中返回后仍然指向原来对象(值未被修改)。
而加了&时,指针在函数中值被彻底修改,返回后也是被修改的状态,指向了其他对象。
本质上和一个int a与int& a的区别一样。
===================================================================================================
下面是代码和截图:
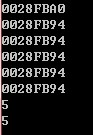
1、首先是传递指针
#include<iostream>using namespace std;void foo(int *t,int *y);int main(){ int num = 4; int num2 = 5; int *p = # int *q = &num2; cout<<p<<endl; cout<<q<<endl; foo(p,q); cout<<p<<endl; cout<<q<<endl; cout<<*p<<endl; cout<<*q<<endl; cin>>num;}void foo(int *t,int *y){ t = y; *t = 4; cout<<t<<endl; cout<<y<<endl;} |
q所指向的值改变,但最后p,q都还指向原来的对象
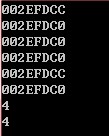
2、传递指针的引用
#include<iostream>using namespace std;void foo(int *&t,int *y);int main(){ int num = 4; int num2 = 5; int *p = # int *q = &num2; cout<<p<<endl; cout<<q<<endl; foo(p,q); cout<<p<<endl; cout<<q<<endl; cout<<*p<<endl; cout<<*q<<endl; cin>>num;}void foo(int *&t,int *y){ t = y; *t = 4; cout<<t<<endl; cout<<y<<endl;} |
函数执行后p和q指向同一对象。
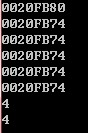
3、指针的指针
差点被绕晕了,指针的引用还好理解,传递参数的时候直接传递指针就好,但是指针的指针就需要把那参数的几种形式理解清楚:t是传递的指针的地址,相当于foo函数中的&y,*t是指针的值,也就是所指向的对象的地址,所以我下面代码里改变他所指向的对象是用*t = y;**t就和*y表示的意思一样了,就是指向对象的值。
#include<iostream>using namespace std;void foo(int **t,int *y);int main(){ int num = 4; int num2 = 5; int *p = # int *q = &num2; cout<<p<<endl; cout<<q<<endl; foo(&p,q); cout<<p<<endl; cout<<q<<endl; cout<<*p<<endl; cout<<*q<<endl; cin>>num;}void foo(int **t,int *y) //t是指针的地址,*t是指针的值,也就是指向的对象的地址{ *t = y; cout<<*t<<endl; cout<<y<<endl;} |