字符串
python中字符串的表现形式:包含在引号(单引号,双引号,三引号)内的一串字符
用于标识:描述性的内容,如姓名,性别,国籍,种族...
name = 'fixd' #单引号
name = "apple"
name = """
这里可以写多行内容
fixd
yite
"""
单引号,双引号,多引号有什么区别?
其实单双引号没有任何区别,只有在嵌套使用引号才考虑这个问题
description = '他是一个非常 "帅" 的小伙' #双引号在内,单引号在外 print(description) description = "他是一个非常 '帅' 的小伙" #单引号在内,双引号在外 print(description) description = """她的朋友说:"他是一个非常 '帅' 的小伙" """ print(description) #单双引号在内,三引号在外
结果:
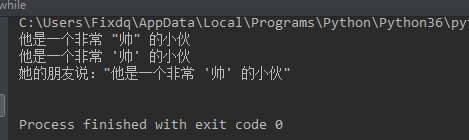
看懂这个例子,引号的嵌套应该没大问题了
字符串的内置函数
1 # 1--字母处理: 2 3 .upper() # 全部大写 4 .lower() # 全部小写 5 .swapcase() # 大小写互换 6 .capitalize() # 首字母大写,其他小写,整个字符串只有第一个字母大写 7 .title() # 首字母大写 ,整个字符串每一个单词首字母大写

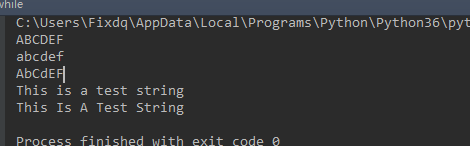
1 str = 'aBcDef' 2 print(str.upper()) # 全部大写 3 print(str.lower()) # 全部小写 4 print(str.swapcase()) # 大小写互换 5 s = "this is a test string" 6 print(s.capitalize()) # 首字母大写,其余小写 7 print(s.title()) # 首字母大写
1 # 2--格式化相关 2 3 .ljust(width) # 获取固定长度,左对齐,右边不够用空格补齐 4 .rjust(width) # 获取固定长度,右对齐,左边不够用空格补齐 5 .center(width) # 获取固定长度,中间对齐,两边不够用空格补齐 6 .zfill(width) # 获取固定长度,右对齐,左边不足用0补齐

1 a='1 2' 2 print(a.ljust(10)) # 获取固定长度,左对齐,右边不够用空格补齐 3 print(a.rjust(10)) # 获取固定长度,右对齐,左边不够用空格补齐 4 print(a.center(10)) # 获取固定长度,中间对齐,两边不够用空格补齐 5 print(a.zfill(10)) # 获取固定长度,右对齐,左边不足用0补齐 6 7 8 执行结果: 9 1 2 10 1 2 11 1 2 12 00000001 2
1 # 3--字符串搜索相关 2 3 .find() # 搜索指定字符串,没有返回-1 4 .index() # 同上,但是找不到会报错 5 .rfind() # 从右边开始查找 6 .count() # 统计指定的字符串出现的次数 7 8 # 上面所有方法都可以用index代替,不同的是使用index查找不到会抛异常,而find返回-1

1 s='hello world' 2 print(s.find('e')) # 搜索指定字符串,没有返回-1 3 print(s.find('w',1,2)) # 顾头不顾尾,找不到则返回-1不会报错,找到了则显示索引 4 print(s.index('w',1,2)) # 同上,但是找不到会报错 5 print(s.count('o')) # 统计指定的字符串出现的次数 6 print(s.rfind('l')) # 从右边开始查找
1 # 4--字符串替换 2 3 .replace('old','new') # 替换old为new 4 .replace('old','new',次数) # 替换指定次数的old为new 5 6 7 s='hello world' 8 print(s.replace('world','python')) 9 print(s.replace('l','p',2)) 10 print(s.replace('l','p',5)) 11 12 #执行结果: 13 hello python 14 heppo world 15 heppo worpd
1 # 5--字符串去空格及去指定字符 2 3 .strip() # 去两边空格 4 .lstrip() # 去左边空格 5 .rstrip() # 去右边空格 6 7 .split() # 默认按空格分隔 8 .split('指定字符') # 按指定字符分割字符串为数组 9 10 11 s=' h e-l lo ' 12 print(s) 13 print(s.strip()) 14 print(s.lstrip()) 15 print(s.rstrip()) 16 print(s.split('-')) 17 print(s.split())
1 # 6--字符串判断相关 2 3 .startswith('start') # 是否以start开头 4 .endswith('end') # 是否以end结尾 5 .isalnum() # 是否全为字母或数字 6 .isalpha() # 是否全字母 7 .isdigit() # 是否全数字 8 .islower() # 是否全小写 9 .isupper() # 是否全大写 10 .istitle() # 判断首字母是否为大写 11 .isspace() # 判断字符是否为空格
补充1:
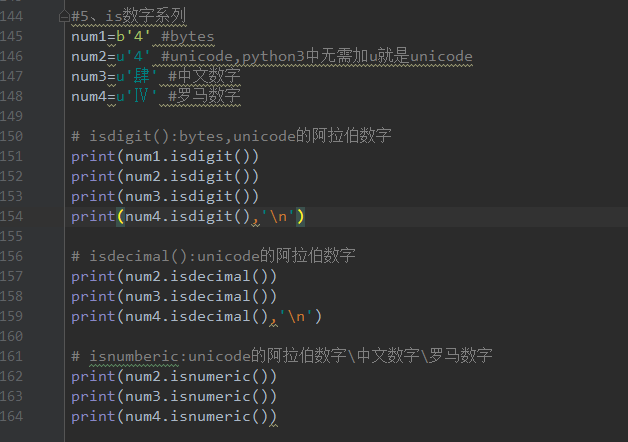
isdigit() #判断字符串内是否为数字( 1234...)
isnumberic() #判断字符串内是否为数字(常用数字(1234 ...),中文数字(壹贰叁肆...),罗马数字(Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ...))
eg
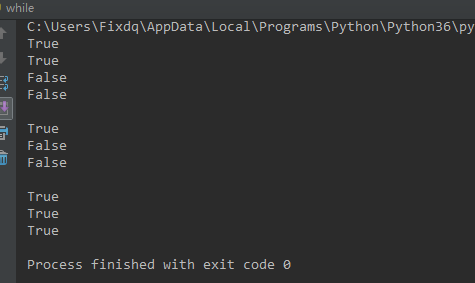
结果:
补充2:
':'.join( 列表 ) 以 :为连接符将其他字符串序列连接成一个新的字符串(冒号可以用任意其他字符)
eg:
1 old_str = ['name','jpg','rwx'] 2 new_str = ':'.join(old_str) 3 print(new_str)
注意:join方法传入的列表必须只包含str类型的元素
字符串格式化(format)
占位符 %s
#使用 %s 占位符的方式 str = 'my name is %s,my age is %s' % ('Fixd',18) print(str)

format(三种玩法)
1.使用 {} 占位符的方式
str = 'my name is {},my age is {}'.format('Fixd',18) #一般的使用方法 print(str) #format 参数个数 > 占位符个数 str = 'my name is {},my age is {}'.format('Fixd',18,25,'yite') #多余的参数不会显示,但不会报错 print(str) #format 参数个数 < 占位符个数 str = 'my name is {},my age is {}'.format('Fixd') #这种情况就会报错,看下图 print(str)
结果:

报错的结果:
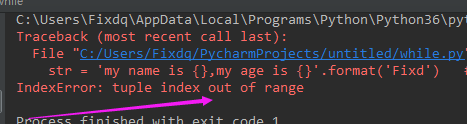
2.使用 {索引} 占位符的方式
#format 对应参数 str = 'my name is {0},my age is {1}'.format('Fixd',18) print(str) #format 多个参数,可根据索引取对应的参数 str = 'my name is {0},my age is {1}'.format('Fixd',18,45,'yite') print(str) str = 'my name is {3},my age is {2}'.format('Fixd',18,25,'yite') print(str)
结果:

3.使用 {key} 占位符的方式
#format 对应参数 str = 'my name is {name},my age is {age}'.format(name= 'Fixd',age = 18) print(str)

字符串的取值
http://www.cnblogs.com/fixdq/p/8606768.html
