1.

public class test5 { public static void main(String[] args) { Foo obj1=new Foo(); Foo obj2=new Foo(); Foo obj3=obj1; System.out.println(obj1==obj2); System.out.println(obj1==obj3); } } class Foo { int value=100; }
输出结果:

当“==”施加于原始数据类型变量时,是比较变量所保存的数据是否相等。
而施加于引用类型变量时,是比较两个变量是否引用同一个对象。
引用代表地址值,所以“==”实际上是比较对象的地址是否相等。
obj1,obj2都开辟了一个空间所以地址值不同,
obj3的地址实际指向obj1,所以为true。
2.

public class test5 { public static void main(String[] args) { Foo obj1=new Foo(); } } class Foo { int value; public Foo(int initValue) { value=initValue; } public Foo() {} }
由于Foo定义了构造方法,所以系统不会再提供默认构造方法,
所以必须定义Foo的无参构造方法。
3.

代码如下:
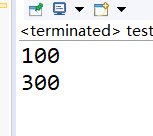
public class test5 { public static void main(String[] args) { InitializeBlockClass obj=new InitializeBlockClass(); System.out.println(obj.field); obj=new InitializeBlockClass(300); System.out.println(obj.field); } } class InitializeBlockClass { { field=200; } public int field=100; public InitializeBlockClass(int value) { this.field=value; } public InitializeBlockClass() { } }
运行结果:
我们可以调整
{
field=200;
}
的位置观察结果

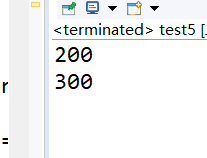

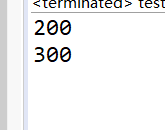
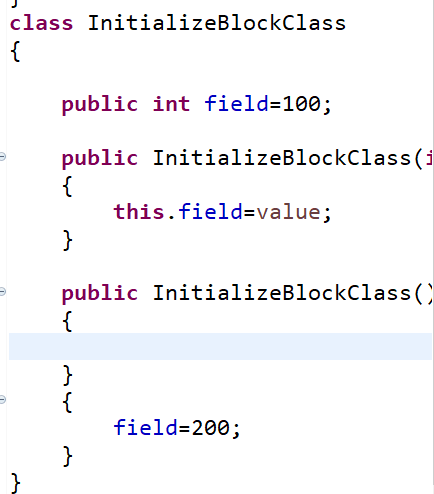
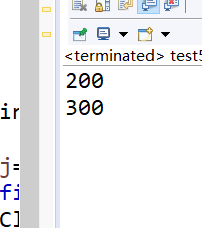


从这几个实验中不难看出规律;
对于对象的无参构造,field最终的值与初始化类字段的位置有关,即是按照线性顺序执行初始化类字段与其他语句的。
但对于对象的有参数的构造,field的值与初始化类字段无关至于有参构造方法有关。
4.

class Root { static { System.out.println("Root的静态初始化块"); } { System.out.println("Root的普通初始化块"); } public Root() { System.out.println("Root的无参数的构造器"); } } class Mid extends Root { static { System.out.println("Mid的静态初始化块"); } { System.out.println("Mid的普通初始化块"); } public Mid() { System.out.println("Mid的无参数的构造器"); } public Mid(String msg) { //通过this调用同一类中重载的构造器 this(); System.out.println("Mid的带参数构造器,其参数值:" + msg); } } class Leaf extends Mid { static { System.out.println("Leaf的静态初始化块"); } { System.out.println("Leaf的普通初始化块"); } public Leaf() { //通过super调用父类中有一个字符串参数的构造器 super("Java初始化顺序演示"); System.out.println("执行Leaf的构造器"); } } public class TestStaticInitializeBlock { public static void main(String[] args) { new Leaf(); }
运行结果

创建子类对象时会导致父类的初始化块执行,且静态初始化块由于普通初始化块的执行。
静态初始化块只执行一次.
5.

package test; public class TestStaticInitializeBlock { public static void main(String[] args) { new Test().showFlag(); } } class Test { public int flag=100; public static void showFlag() { Test test=new Test(); System.out.println(test.flag); } }
运行结果

可以再静态方法中创建一个对象,通过对象调用非静态成员。
6.

public class StrangeIntegerBehavior { public static void main(String[] args) { Integer i1=100; Integer j1=100; System.out.println(i1==j1); Integer i2=129; Integer j2=129; System.out.println(i2==j2); } }
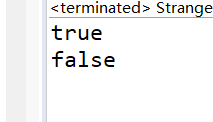
运行结果
private static class IntegerCache { static final int low = -128; static final int high; static final Integer[] cache; static Integer[] archivedCache; static { // high value may be configured by property int h = 127; String integerCacheHighPropValue = VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high"); if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) { try { h = Math.max(parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue), 127); // Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE h = Math.min(h, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low) -1); } catch( NumberFormatException nfe) { // If the property cannot be parsed into an int, ignore it. } } high = h; // Load IntegerCache.archivedCache from archive, if possible VM.initializeFromArchive(IntegerCache.class); int size = (high - low) + 1; // Use the archived cache if it exists and is large enough if (archivedCache == null || size > archivedCache.length) { Integer[] c = new Integer[size]; int j = low; for(int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) { c[i] = new Integer(j++); } archivedCache = c; } cache = archivedCache; // range [-128, 127] must be interned (JLS7 5.1.7) assert IntegerCache.high >= 127; } private IntegerCache() {} }
上面的代码就是Integer.class的原码,可以看到Integer对-128~127范围内的进行装箱指向同一位置,范围外的装箱指向不同位置,所以129显示false。