1. 包含对象的类,has-a关系
c++和约束:c++包含让程序员能够限制程序结构的特性,使用explicit防止单参数构造函数的隐式转换,使用const限制方法修改数据,这么做的根本原因是:在编译阶段出现错误优于在运行阶段出现的错误。
explicit Student(const string& s) : name(s), score() {}
explicit Student(int n) : name("Nully"), score(n) {}:score()是成员对象的初始化。如果是继承关系,应该采用 : 类名(初始化量)
在第二个构造构造参数中,第一个参数是数组的元素个数,而不是数组的值。
Student doh("Homer", 10);
doh = 5; // reset name to "Nully", reset ro empty array of 5 elements
如果没有采用explicit,则将构造函数调用Student(5)将5转换成一个临时的Student对象,并将"Nully"来设置name的值。
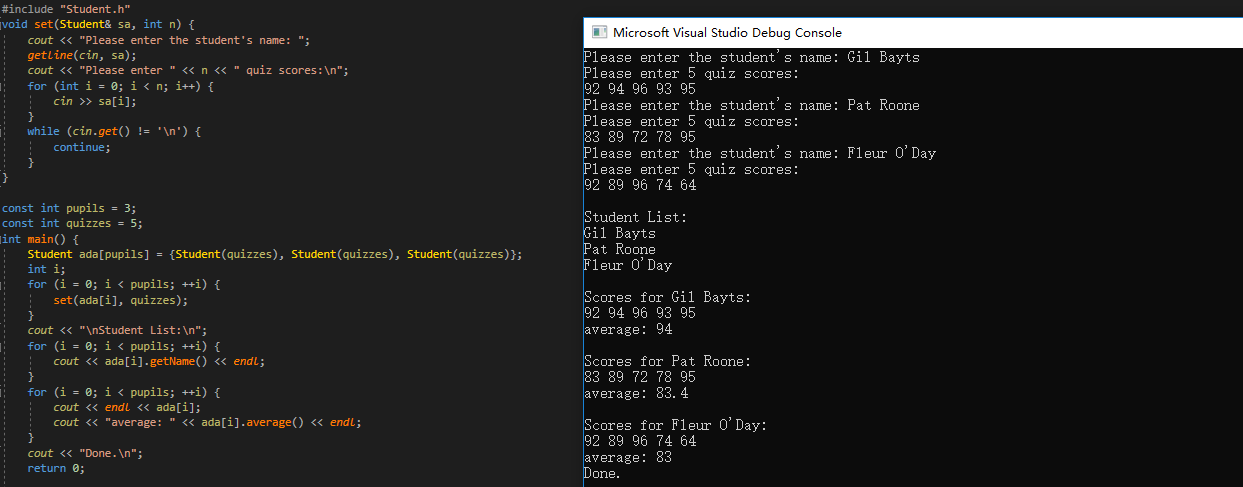
#include <iostream> #include <string.h> #include <valarray> using namespace std; class Student { private: valarray<double> scores; string name; ostream& arr_out(ostream& os) const; public: Student() : name("Null student"), scores() {} explicit Student(const string& s) : name(s), scores() {} explicit Student(int n) : name("Null student"), scores(n) {} Student(const string& s, int n) : name(s), scores(n) {} Student(const string& s, const valarray<double>& a) : name(s), scores(a) {} Student(const char* str, const double* pd, int n) : name(str), scores(pd, n) {} ~Student() {} double average() const; const string& getName() const; double &operator[](int i); double operator[](int i) const; friend istream& operator>>(istream& is, Student& stu); friend istream& getline(istream& is, Student& stu); friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Student& stu); };
#include "Student.h" #include <string> #include <iostream> using namespace std; #pragma warning(disable:4996) double Student::average() const { if (scores.size() > 0) { return scores.sum() / scores.size(); } else { return 0; } } const string& Student::getName() const { return name; } double& Student::operator[](int i) { return scores[i]; } double Student::operator[](int i) const { return scores[i]; } ostream& Student::arr_out(ostream& os) const { int i; int lim = scores.size(); if (lim > 0) { for (i = 0; i < lim; i++) { os << scores[i] << " "; if (i % 5 == 4) { os << endl; } } if (i % 5 != 0) { os << endl; } } else { os << "empty array"; } return os; } istream& operator>>(istream& is, Student& stu) { is >> stu.name; return is; } istream& getline(istream& is, Student& stu) { getline(is, stu.name); return is; } ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Student& stu) { os << "Scores for " << stu.name << ": "; stu.arr_out(os); return os; }
2. 私有继承,另一种实现has-a关系的途径
使用私有继承,基类的公有成员和保护成员都将称为派生类的私有成员,意味着基类方法将不会成为派生类的一部分,但是可以在派生类的成员函数中使用它们。
包含将对象作为一个命名的成员对象添加到类中,而私有继承将对象作为一个未被命名的继承对象添加到类中,使用术语子对象来表示通过继承或包含添加的对象。
访问基类的方法:使用私有继承,只能在派生类的方法中使用基类的方法,私有继承能够使用类名和作用域解析运算符来调用基类的方法。
访问基类的对象:使用强制类型转换的方法来实现,因为子类是由父类继承而来,返回this指针的解除引用,再强制类型转换
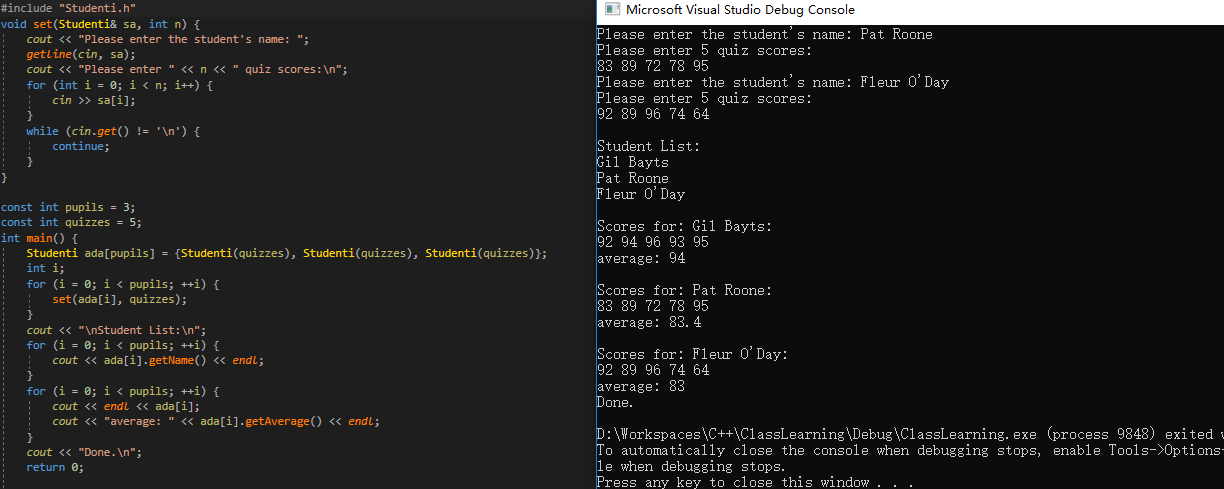
#include <string> #include <valarray> using namespace std; class Studenti : private string, private valarray<double> { private: ostream& arr_out(ostream& os) const; public: Studenti() : string("No Student"), valarray<double>() {} explicit Studenti(const string& s) : string(s), valarray<double>() {} explicit Studenti(int i) : string("Nully"), valarray(i) {} Studenti(const string& s, int n) : string(s), valarray(n) {} Studenti(const string& s, const valarray<double>& a) : string(s), valarray(a) {} Studenti(const char* str, const double* pd, int n) : string(str), valarray(pd, n) {} ~Studenti() {} double getAverage() const; double& operator[](int i); double operator[](int i) const; const string& getName() const; friend istream& operator>>(istream& is, Studenti& stu); friend istream& getline(istream& is, Studenti& stu); friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Studenti& stu); };
#include "Studenti.h" #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; double Studenti::getAverage() const { if (valarray<double>::size() > 0) { return valarray<double>::sum() / valarray<double>::size(); } else { return 0; } } const string& Studenti::getName() const { return (const string&)*this; } double& Studenti::operator[](int i) { return valarray<double>::operator[](i); } double Studenti::operator[](int i) const { return valarray::operator[](i); } ostream& Studenti::arr_out(ostream& os) const { int i = 0; int lim = valarray<double>::size(); if (lim > 0) { for (i = 0; i < lim; i++) { os << valarray<double>::operator[](i) << " "; if (i % 5 == 4) os << endl; } if (i % 5 != 0) { os << endl; } } else { os << "empty array"; } return os; } istream& operator>>(istream& is, Studenti& stu) { is >> (string&)stu; return is; } istream& getline(istream& is, Studenti& stu) { getline(is, (string&)stu); return is; } ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Studenti& stu) { os << "Scores for: " << (const string&)stu << ": "; stu.arr_out(os); return os; }
3. 使用包含还是私有继承
一般情况选择包含关系,因为实现更加简单
如果新类需要访问原有类的保护成员,或者需要重新定义虚函数,则应当使用私有继承。
4. 私有继承如何重新定义访问权限的两种方法(如何让对象能够使用基类的方法):
a. 定义一个使用基类方法的派生方法
double Student::sum() const{
return valarray<double>::sum(); // use privately-inherited method
}
b. 将函数包装在另一个函数的调用中,即使用一个using声明来指出派生类是可以使用特定的基类成员,即使使用的是私有派生,加入希望通过Student类能够使用valarray方法的min()和max()方法
class Student : private string, private valarray<double>{
public:
using valarray<double> min;
using valarray<double> max;
}
上面的using声明使得valarray<double>::min()和valarray<double>::max()可用,就像它们是Student的公有方法一样
5. protected继承:继承父类的公有方法成为子类的保护方法。
6. 多重继承(MI)
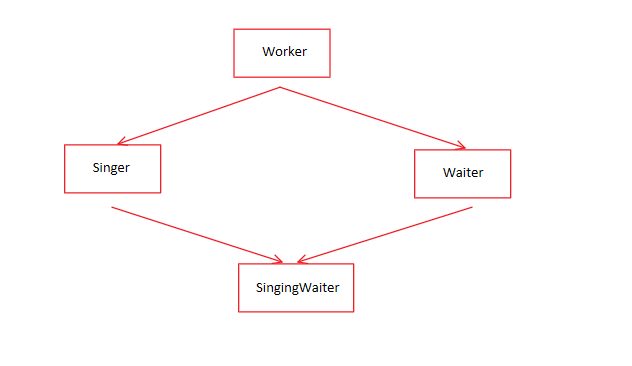
根据上图的继承关系,对于SiingingWaiter有两个Worker,因此引入虚基类
SingingWaiter ed;
Worker* pw = &ed;存在二义性
正确的访问方式:Worker* pw1 = (Waiter*) &ed; Worker* pw2 = (Singer*) &ed;
虚基类:使得多个类(它们的基类相同),派生出的类只继承一个基类对象。通过在类中声明virtual可以使Singer和Waiter的虚基类。
虚基类的特性:在定义基类是虚的时候,禁止信息通过中间类自动传递给基类。需要显示的调用基类的构造函数。一般的继承关系可以通过中间类传递给基类,对于非虚基类,显示调用两层关系的基类非法。
#include <string> using namespace std; class Worker { private: string fullname; long id; protected: virtual void data() const; virtual void get(); public: Worker() : fullname("no one"), id(0L) {}; Worker(const string& s, long n) : fullname(s), id(n) {} virtual ~Worker() = 0; virtual void set() = 0; virtual void show() const = 0; }; class Waiter : virtual public Worker { private: int panache; protected: void data() const; void get(); public: Waiter() : Worker(), panache(0) {} Waiter(const string& s, long n, int p = 0) : Worker(s, n), panache(0) {} Waiter(const Worker& wk, int p = 0) : Worker(wk), panache(p) {} void set(); void show() const; }; class Singer : virtual public Worker { protected: enum { other, alto, contralto, soprano, bass, baritone, tenor }; enum { Vtype = 7 }; void data() const; void get(); private: static char *pv[Vtype]; int voice; public: Singer() : Worker(), voice(other) {} Singer(const string& s, long n, int v = other) : Worker(s, n), voice(v) {} Singer(const Worker& wk, int v = other) : Worker(wk), voice(v) {} void set(); void show() const; };
#include "Workermi.h" #include <iostream> using namespace std; Worker::~Worker() {} void Worker::data() const { cout << "Name: " << fullname << endl; cout << "Employee ID: " << id << endl; } void Worker::get() { getline(cin, fullname); cout << "Enter worker's ID: "; cin >> id; while (cin.get() != ' ') continue; } void Waiter::set() { cout << "Enter waiter's name: "; Worker::get(); get(); } void Waiter::show() const { cout << "Category: waiter "; Worker::data(); data(); } void Waiter::data() const { cout << "Panache rating: " << panache << endl; } void Waiter::get() { cout << "Enter waiter's panache rating: "; cin >> panache; while (cin.get() != ' ') continue; } char* Singer::pv[Singer::Vtype] = {"other", "alto", "contralto", "soprano", "brass", "baritone", "tenor"}; void Singer::set() { cout << "Enter singer's name:"; Worker::get(); get(); } void Singer::show() const { cout << "Categor: singer "; Worker::data(); data(); } void Singer::data() const { cout << "Vocal range: " << pv[voice] << endl; } void Singer::get() { cout << "Enter number for singer's vocal range: "; int i; for (i = 0; i < Vtype; i++) { cout << i << ": " << pv[i] << " "; if (i % 4 == 3) { cout << endl; } } if (i % 4 != 0) cout << ' '; cin >> voice; while (cin.get() != ' ') continue; } void SingingWaiter::data() const { Singer::data(); Waiter::data(); } void SingingWaiter::get() { Waiter::get(); Singer::get(); } void SingingWaiter::set() { cout << "Enter singing waiter's name: "; Worker::get(); get(); } void SingingWaiter::show() const { cout << "Category: singing watier "; Worker::data(); data(); }
#include "Workermi.h" #include <cstring> const int SIZE = 5; using namespace std; int main() { Worker* lolas[SIZE]; int ct; for (ct = 0; ct < SIZE; ct++) { char choice; cout << "Enterk the employee category: " << "w: waiter s: singer " << "t: singing waiter q:quit "; cin >> choice; while (strchr("wstq", choice) == NULL) { cout << "Please enter a w, s, t, or q: "; cin >> choice; } if (choice == 'q') break; switch (choice) { case 'w': lolas[ct] = new Waiter; break; case 's': lolas[ct] = new Singer; break; case 't': lolas[ct] = new SingingWaiter; break; } cin.get(); lolas[ct]->set(); } cout << " Here is your staff: "; int i; for (i = 0; i < ct; i++) { cout << endl; lolas[i]->show(); } for (i = 0; i < ct; i++) { delete lolas[i]; } cout << "Bye. "; return 0;
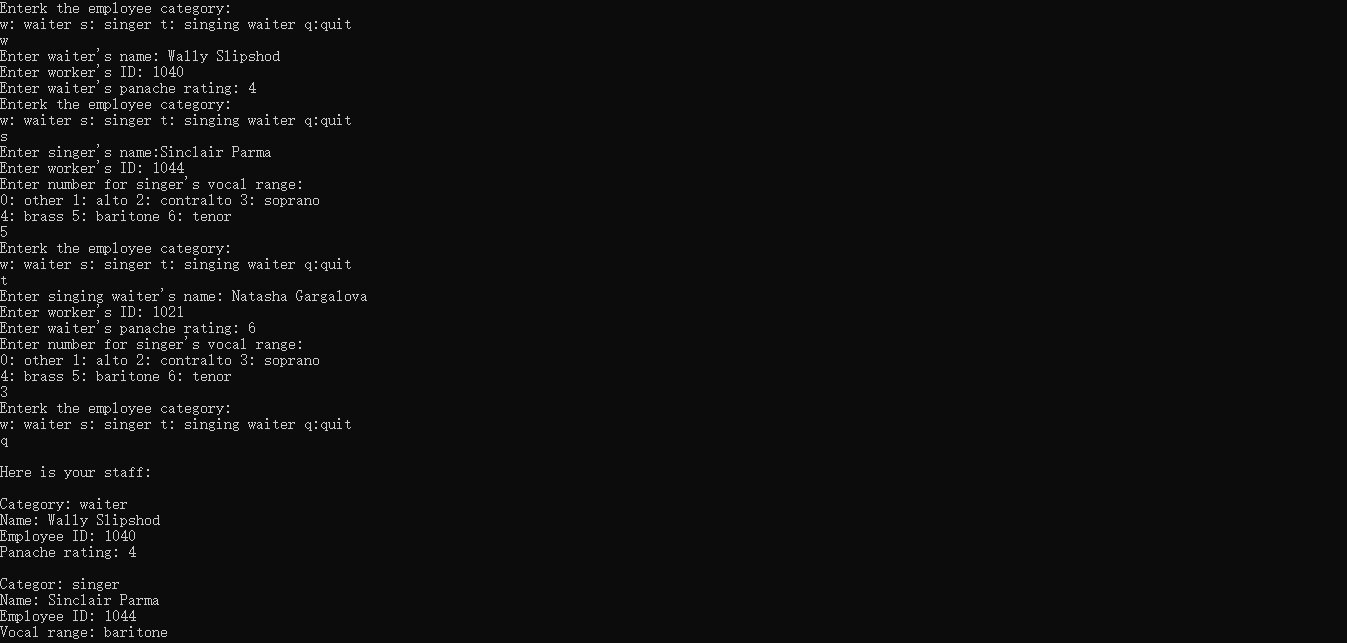

多继承如果两个父类都存在同一函数,子类不重新定义该函数,将会出现二义性。ambiguous
7. 虚基类和支配。
如果类从不同的类继承了两个或者多个同名成员,使用这个成员名时候,如果没有用类名限定,将导致二义性。
虚基类:虚二义性,即如果名称优先于其它所有的名称(继承父类名称优先于子类名称,与继承的层数无关),则使用它的时候,不适用限定符,也不会导致二义性,同时虚二义性规则与访问规则无关。
8. 模板类
如果想声明一个类是模板类,只需要在类定义前加入:template <typename T>即可,仅在程序中包含模板不能生成模板类,必须请求实例化。