Reference Book: <<Engineering long-lasting software>>
http://saasbook.info
Chapter One Engineering Software is Different from Engineering Hardware
https://www.coursera.org/saas/lecture/preview
1.1-1.2 - Introduction - Engineering Software is Different from Engineering Hardware
Why so man SW disasters and no HW disaters?
Ariane 5 rocket explosion
Therac-25 lethal radiation overdose
Mars Climate Orbiter disintegration
FBI Virtual Case File project abandonment
Independent Product vs Continuous Improvement
Cose of field upgrade
HW=∞
HW designs must be finished before manufactured and shipped
Bugs: Return HW (lose if many returns)
SW=0
Expect SW gets better over time
Bugs: Wait for upgrade
HW decays, SW long lasting
Legacy SW vs Beautiful SW
Legacy code: old SW that continues to meet customers' needs, but difficult to evolve due to design inelegance or antiquated technology
60% SW maintenance costs adding new functionality to legacy SW
17% for fixing bugs
Beautiful code: meets customers' needs and easy to evolve
1.3 Development Processes: Waterfall vs. Agile
Waterfall: Big Design Up Front
Requirements analysis and specification
Architectural design
Implementation and integration
Verification
Operation and maintenance
Complete one phase before start next one
Waterfall process works well for software with specs that won't change,
But often when customer sees result, wants big changes
But often after build first one, developers learn right way they should have built it
" Plan to throw one [Implementation] away, you will, anyhow."----Fred Brooks, Jr.
If a problem has no solution, it may not be a problem, but a fact, not to be solved, but to be coped with over time. ----Shimon Peres
Agile Manifesto 2001
"We are uncovering better ways of developing SW by doing it and helping others do it. Through this work we have come to value
- Individuals and interactions over processes & tools
- Working software over comprehensive documentation
- Customers collaboration over contract negotiation
- Responding to change over following a plan
That is, while there is a value in the items on the right, we value the items on the left more."
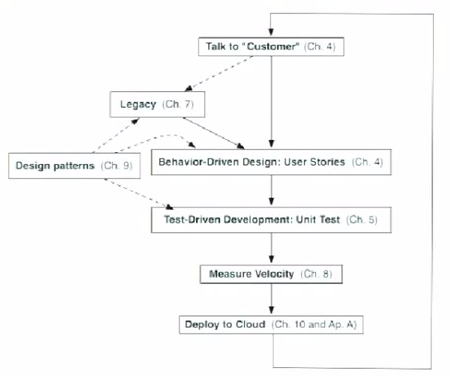
Agile lifecycle
- Embraces change as a fact of life: continuous improvement vs. phases
- Developers continuously refine working but incomplete prototype until customers happy, with customer feedback on each iteration ( every 2 weeks)
- Agile emphasize Test-Driven Development (TDD) to reduce mistakes, User Stories to reach agreement and validate customer requirements, Velocity to measure progress
1.4 Assurance
Verification: Did you build the thing right? Meet the specification?
Validation: Did you build the right thing? Is this what the customer wants? Is the specification correct?
Hardware focus generally verification
Software focus generally validation
Testing
Exhaustive testing infeasible
Divide and conquer: perform different tests at different phases of SW development
- Upper level doesn't redo tests of lower level
- System or acceptance test: integrated program meets its specifications
- Integration test: interfaces between units have consistent assumptions, communicate correctly
- Module or functional test: across individual units
- Unit Test: Single method does what was expected
More testing:
Coverage
Regression Testing
Continuous Integration Testing
Agile=> Test Driven Design: write tests before you write the code
Limits of Testing: Program testing can be used to show the presence of bugs, but never to show their absence! ( Edsger W. Dijkstra )
Formal Methods
Start with formal specification & prove program behavior follows spec. Options:
Human does proof
Computer via automatic theorem proving
Computer via model checking
Computationally expensive, so use only if
- Small, fixed function
- Expensive to repair, very hard to test
- E.g., network protocols, safety critical SW
1.5 Productivity
Moore's Law => 2X transistors/18 months
- HW designs get bigger
- Faster processers and bigger memories
- SW designs get bigger
- Must improve HW & SW productivity
Techniques
- Clarity via conciseness
- Shorter and easier to read
- Raise the level of abstraction
- Synthesis
- Reuse
- Procedures and functions
- Standardized libraries
- Object oriented programming
- Design patterns
- Automation and Tools
Don't Repeat Yourself (DRY)
Don't copy and paste code
1.6 Software as a Service
SaaS: delivers SW and data as service over internet via thin program (e.g., browser)
Reasons for SaaS:
- No install worries about HW capability, OS
- No worries about data loss
- Easy for groups to interact with same data
- If data is large or changed frequently, simpler to keep 1 copy at central site
- 1 copy of SW, controlled HW environment => no compatibility hassles for developers
- 1 copy => simplifies upgrade for developers and no user upgrade requests
SaaS Loves Agile & Rail
- Frequent upgrades matches Agile lifecycle
- Many frameworks for Agile/SaaS
- This course use Ruby on Rails