前言
许多个人计算机和工作站都有多个CPU核心,可以同时执行多个线程。利用硬件的特性,使用并行化代码以在多个处理器之间分配工作。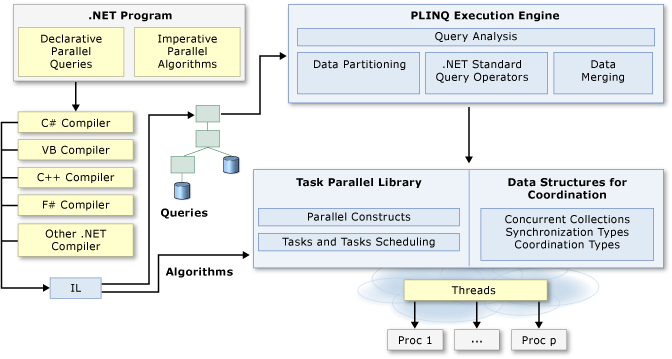
应用场景
- 文件批量上传
并行上传单个文件。也可以把一个文件拆成几段分开上传,加快上传速度。
- 数据分批计算
如几百万数据可以拆成许多无关联的部分,并行计算处理。最后聚合。
- 数据推送
也是需要将数据拆解后,并行推送。
任务并行库-数据并行
如果在一个循环内在每次迭代只执行少量工作或者它没有运行多次迭代,那么并行化的开销可能会导致代码运行的更慢。使用并行之前,应该对线程(锁,死锁,竞争条件)应该有基本的了解。
Parallel.For
/// <summary>
/// 正常循环
/// </summary>
public void FormalDirRun()
{
long totalSize = 0;
var dir = @"E:LearnWallorleans";//args[1];
String[] files = Directory.GetFiles(dir);
stopwatch.Restart();
for (var i = 0; i < files.Length; i++)
{
FileInfo fi = new FileInfo(files[i]);
long size = fi.Length;
Interlocked.Add(ref totalSize, size);
}
stopwatch.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"FormalDirRun------{files.Length} files, {totalSize} bytes,time:{stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds},Dir:{dir}");
}
/// <summary>
/// 并行循环
/// </summary>
public void ParallelForDirRun()
{
long totalSize = 0;
var dir = @"E:LearnWallorleans";//args[1];
String[] files = Directory.GetFiles(dir);
stopwatch.Restart();
Parallel.For(0, files.Length,
index =>
{
FileInfo fi = new FileInfo(files[index]);
long size = fi.Length;
Interlocked.Add(ref totalSize, size);
});
stopwatch.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"ParallelForDirRun-{files.Length} files, {totalSize} bytes,time:{stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds},Dir:{dir}");
}
从下图对比接口可以看出当循环体内方法执行时间很短时,并行时间反而更长。这块会有更细致的补充。
FormalDirRun------20 files, 255618 bytes,time:0,Dir:E:LearnWallorleans
ParallelForDirRun-20 files, 255618 bytes,time:6,Dir:E:LearnWallorleans我们追加一些延时操作如Thread.Sleep,但这应该不是好好例子...但我只想演示效果就行了。
Thread.Sleep(1000);查看结果得到,当方法内有阻塞延时一秒后,两者速度错了七倍。
FormalDirRun------20 files, 255618 bytes,time:20011,Dir:E:LearnWallorleans
ParallelForDirRun-20 files, 255618 bytes,time:3007,Dir:E:LearnWallorleansParallel.ForEach
为了并行速度的最大化,我们应该尽量减少在并行内对共享资源的访问,如Console.Write,文件日志等...但这里为了显示效果,就用了。
public void ParallelForEachDirRun()
{
long totalSize = 0;
var dir = @"E:LearnWallorleans";//args[1];
String[] files = Directory.GetFiles(dir);
stopwatch.Restart();
Parallel.ForEach(files, (current) =>
{
FileInfo fi = new FileInfo(current);
long size = fi.Length;
Interlocked.Add(ref totalSize, size);
Console.WriteLine($"name:{fi.Name}");
});
stopwatch.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"ParallelForEachDirRun-{files.Length} files, {totalSize} bytes,Time:{stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds}");
} name:.gitignore
name:build.sh
.
.
.
name:TestAll.cmd
ParallelForEachDirRun-20 files, 255618 bytes,Time:17Parallel.For 线程局部变量
public void ParallelForForThreadLocalVariables()
{
int[] nums = Enumerable.Range(0, 1000000).ToArray();
long total = 0;
// Use type parameter to make subtotal a long, not an int
Parallel.For<long>(0, nums.Length, () => 0, (j,loop, subtotal) =>
{
subtotal += nums[j];
return subtotal;
},
(x) => Interlocked.Add(ref total, x)
);
Console.WriteLine("The total is {0:N0}", total);
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exit");
Console.ReadKey();
}结果如下:
The total is 499,999,509,000
每个For方法的前两个参数指定开始和结束迭代值。在此方法的重载中,第三个参数是初始化本地状态的位置。在此上下文中,本地状态表示一个变量,其生命周期从当前线程上的循环的第一次迭代之前延伸到最后一次迭代之后。
第三个参数的类型是Func ,其中TResult是将存储线程本地状态的变量的类型。它的类型由调用泛型For (Int32,Int32,Func ,Func ,Action )方法时提供的泛型类型参数定义,在这种情况下是Int64。type参数告诉编译器将用于存储线程局部状态的临时变量的类型。在此示例中,表达式() => 0(或Function() 0在Visual Basic中)将线程局部变量初始化为零。如果泛型类型参数是引用类型或用户定义的值类型,则表达式如下所示:
() => new MyClass() 这块内容比较繁琐,一句话来说:前两个参数是开始和结束值,第三个是根据For泛型而初始化的值。我其实也没看太懂这块。.net Framework源码如下,.netcore的不知道:
public static ParallelLoopResult For<TLocal>(
int fromInclusive, int toExclusive,
Func<TLocal> localInit,
Func<int, ParallelLoopState, TLocal, TLocal> body,
Action<TLocal> localFinally)
{
if (body == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("body");
}
if (localInit == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("localInit");
}
if (localFinally == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("localFinally");
}
return ForWorker(
fromInclusive, toExclusive, s_defaultParallelOptions,
null, null, body, localInit, localFinally);
}
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="TLocal">本地数据的类型.</typeparam>
/// <param name="fromInclusive">循环开始数</param>
/// <param name="toExclusive">循环结束数</param>
/// <param name="parallelOptions">选项</param>
/// <param name="body">循环执行体</param>
/// <param name="bodyWithState">ParallelState的循环体重载。</param>
/// <param name="bodyWithLocal">线程局部状态的循环体重载。</param>
/// <param name="localInit">一个返回新线程本地状态的选择器函数。</param>
/// <param name="localFinally">清理线程本地状态的清理函数。</param>
/// <remarks>只能提供一个身体参数(即它们是独占的)。</remarks>
/// <returns>A <see cref="T:System.Threading.Tasks.ParallelLoopResult"/> structure.</returns>
private static ParallelLoopResult ForWorker<TLocal>(
int fromInclusive, int toExclusive,
ParallelOptions parallelOptions,
Action<int> body,
Action<int, ParallelLoopState> bodyWithState,
Func<int, ParallelLoopState, TLocal, TLocal> bodyWithLocal,
Func<TLocal> localInit, Action<TLocal> localFinally)
{
.
.
.
}Parallel.ForEach线程局部变量
/// <summary>
///
/// </summary>
public void ParallelForEachThreadLocalVariables()
{
int[] nums = Enumerable.Range(0, 1000000).ToArray();
long total = 0;
// First type parameter is the type of the source elements
// Second type parameter is the type of the thread-local variable (partition subtotal)
Parallel.ForEach<int, long>(nums, // source collection
() => 0, // method to initialize the local variable
(j, loop, subtotal) => // method invoked by the loop on each iteration
{
subtotal += j; //modify local variable
return subtotal; // value to be passed to next iteration
},
// Method to be executed when each partition has completed.
// finalResult is the final value of subtotal for a particular partition.
(finalResult) => Interlocked.Add(ref total, finalResult)
);
Console.WriteLine("The total from Parallel.ForEach is {0:N0}", total);
}ForEach的源码如下
/// <summary>
/// Executes a for each operation on an <see cref="T:System.Collections.IEnumerable{TSource}"/>
/// in which iterations may run in parallel.
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="TSource">The type of the data in the source.</typeparam>
/// <param name="source">An enumerable data source.</param>
/// <param name="body">The delegate that is invoked once per iteration.</param>
/// <exception cref="T:System.ArgumentNullException">The exception that is thrown when the <paramref name="source"/>
/// argument is null.</exception>
/// <exception cref="T:System.ArgumentNullException">The exception that is thrown when the <paramref name="body"/>
/// argument is null.</exception>
/// <exception cref="T:System.AggregateException">The exception that is thrown to contain an exception
/// thrown from one of the specified delegates.</exception>
/// <returns>A <see cref="T:System.Threading.Tasks.ParallelLoopResult">ParallelLoopResult</see> structure
/// that contains information on what portion of the loop completed.</returns>
/// <remarks>
/// The <paramref name="body"/> delegate is invoked once for each element in the <paramref name="source"/>
/// enumerable. It is provided with the current element as a parameter.
/// </remarks>
public static ParallelLoopResult ForEach<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource> source, Action<TSource> body)
{
if (source == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("source");
}
if (body == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("body");
}
return ForEachWorker<TSource, object>(
source, s_defaultParallelOptions, body, null, null, null, null, null, null);
}取消 Parallel.ForEach或Parallel.For
通过CancellationTokenSource来获取token
CancellationTokenSource cts = new CancellationTokenSource();
通过ParallelOptions.CancellationToken属性来控制取消状态。
ParallelOptions po = new ParallelOptions();
po.CancellationToken = cts.Token;
通过Parallel.For或Foreach的ParallelOptions值来控制并行内方法的取消。
代码如下:
int[] nums = Enumerable.Range(0, 10000000).ToArray();
CancellationTokenSource cts = new CancellationTokenSource();
// Use ParallelOptions instance to store the CancellationToken
ParallelOptions po = new ParallelOptions();
po.CancellationToken = cts.Token;
po.MaxDegreeOfParallelism = System.Environment.ProcessorCount;
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to start. Press 'c' to cancel.");
Console.ReadKey();
// Run a task so that we can cancel from another thread.
Task.Factory.StartNew(() =>
{
var s = Console.ReadKey().KeyChar;
if (s == 'c')
cts.Cancel();
Console.WriteLine("press any key to exit111");
});
try
{
Parallel.ForEach(nums, po, (num) =>
{
double d = Math.Sqrt(num);
Console.WriteLine("{0} on {1}", d, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
po.CancellationToken.ThrowIfCancellationRequested();
});
}
catch (OperationCanceledException e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
finally
{
cts.Dispose();
}
Console.ReadKey();运行结果如下,键盘输入c时,并行取消。
1937.41838537782 on 7
2739.95711645274 on 8
2501.40660429287 on 9
2958.47798707376 on 10
.
.
.
press any key to exit111
The operation was canceled.捕获并行体内的异常
示例方法采用ConcurrentQueue来接收异常集合,最后抛出一个聚合异常AggregateException。
var exceptions = new ConcurrentQueue();
exceptions.Enqueue(e);
外部调用AggregateException.Flatten方法获取异常信息。
这为我以后捕获异常提供了一个好思路。
/// <summary>
/// 捕获并行体内的异常
/// </summary>
public void HandleExceptionParallelLoop()
{
// Create some random data to process in parallel.
// There is a good probability this data will cause some exceptions to be thrown.
byte[] data = new byte[5000];
Random r = new Random();
r.NextBytes(data);
try
{
ProcessDataInParallel(data);
}
catch (AggregateException ae)
{
var ignoredExceptions = new List<Exception>();
// This is where you can choose which exceptions to handle.
foreach (var ex in ae.Flatten().InnerExceptions)
{
if (ex is ArgumentException)
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
else
ignoredExceptions.Add(ex);
}
if (ignoredExceptions.Count > 0) throw new AggregateException(ignoredExceptions);
}
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exit.");
Console.ReadKey();
}
private void ProcessDataInParallel(byte[] data)
{
// Use ConcurrentQueue to enable safe enqueueing from multiple threads.
var exceptions = new ConcurrentQueue<Exception>();
// Execute the complete loop and capture all exceptions.
Parallel.ForEach(data, d =>
{
try
{
// Cause a few exceptions, but not too many.
if (d < 3)
throw new ArgumentException($"Value is {d}. Value must be greater than or equal to 3.");
else
Console.Write(d + " ");
}
// Store the exception and continue with the loop.
catch (Exception e)
{
exceptions.Enqueue(e);
}
});
Console.WriteLine();
// Throw the exceptions here after the loop completes.
if (exceptions.Count > 0) throw new AggregateException(exceptions);
}对微小执行体提速
当Parallel.For循环有一个很快的执行体,它可能比同等顺序循环执行更慢。较慢的性能是由分区数据所涉及的开销和每次循环迭代调用委托的成本引起的。为了解决这种情况,Partitioner类提供了Partitioner.Create方法,该方法使您能够为委托主体提供顺序循环,以便每个分区仅调用一次委托,而不是每次迭代调用一次。
var rangePartitioner = Partitioner.Create(0, source.Length);
/// <summary>
/// 提速
/// </summary>
public void SpeedUpMicroParallelBody() {
// Source must be array or IList.
var source = Enumerable.Range(0, 100000).ToArray();
// Partition the entire source array.
var rangePartitioner = Partitioner.Create(0, source.Length);
double[] results = new double[source.Length];
// Loop over the partitions in parallel.
Parallel.ForEach(rangePartitioner, (range, loopState) =>
{
// Loop over each range element without a delegate invocation.
for (int i = range.Item1; i < range.Item2; i++)
{
results[i] = source[i] * Math.PI;
}
});
Console.WriteLine("Operation complete. Print results? y/n");
char input = Console.ReadKey().KeyChar;
if (input == 'y' || input == 'Y')
{
foreach (double d in results)
{
Console.Write("{0} ", d);
}
}
}源码地址
总结
本篇文章沿着微软官方文档步骤熟悉了第一部分数据并行的用法。
Parallel.For和Parallel.ForEach实现并行。
Parallel.For和Parallel.ForEach线程局部变量。
取消并行ParallelOptions.CancellationToken
捕捉异常ConcurrentQueue累加并行体内的异常,外部接收。
加速Partitioner.Create
感谢观看!