对应慕课视频的连接:https://www.imooc.com/video/5316
1,工厂模式的应用场景
有一组类似的对象需要被创建
在编码时不能预见需要被创建哪种类的实例
在系统需要考虑扩展性的情况下,不应依赖产品类实例如何创建,组合和表达的细节
2,项目中的现状:
在软件系统中经常面临着“对象”的创建工作,由于需求的变化,这个对象可能随之发生改变,但它却拥有比较稳定的接口。
为此我们需要提供一种风专辑之来隔离这个易变对象的变化,从而保持系统中其他依赖对该对象的对象不随着需求变化而改变
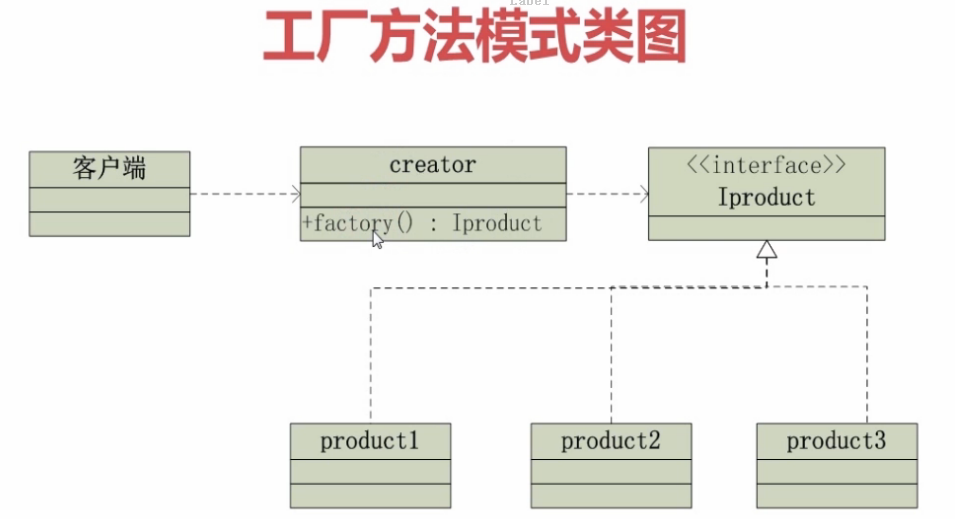
比如说,客户端要求生产苹果,creater就生产苹果,Uproduct就代表水果,他下面的Product1,Product2,Product3就可以表苹果,香蕉,橘子等具体的水果
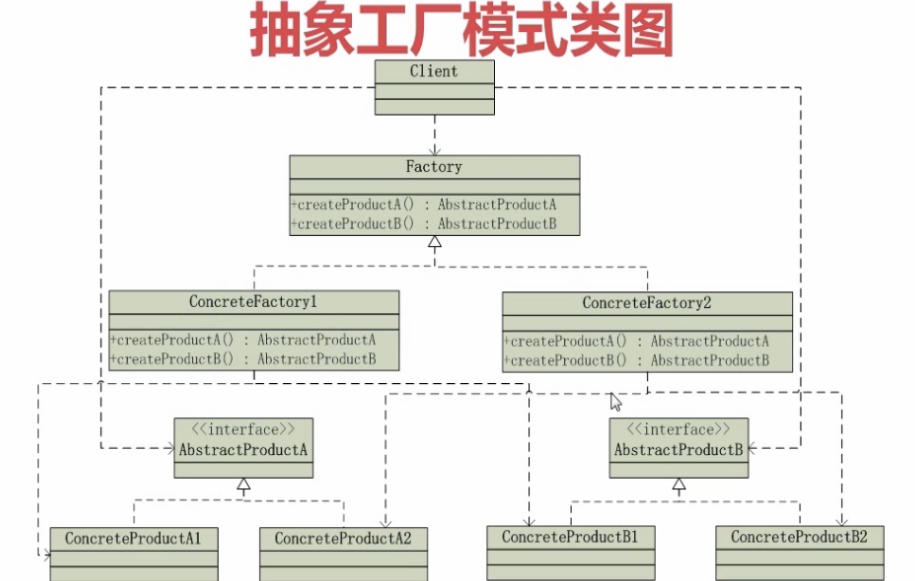
在抽象工厂中呢,用户发出请求,factory生产水果,CreateFactory1,CreateFactory2他两个都可生产两种类型的水果,但是生产的具体产品又各不相同,CreateFactory1,CreateFactory2为两个系列。
一、代码部分(工厂模式实现)
(1)是定义生产头发的接口类
package com.songyan.factory; /** * 生产头发 * @author Administrator * */ public interface Hair { public void draw(); }
(2)定义生产发型的实现类:生产左偏分发型的类,生产右偏分发型的类
package com.songyan.factory; public class LeftHair implements Hair{ @Override public void draw() { System.out.println("left hair"); } }
package com.songyan.factory; public class RightHair implements Hair{ @Override public void draw() { System.out.println("right hair"); } }
(3)编写测试类,生产左偏分发型
package com.songyan.factory; public class Test { public static void test1() { Hair hair=new LeftHair(); hair.draw(); } public static void main(String[] args) { test1(); } }
这种方法生产发型是在客户端生产,不安全------>在工厂中生产发型
(4)定义生产发型的工厂类
package com.songyan.factory; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class HairFactory { public static Hair getHair(String key) { Hair hair=null; if("left".equals(key)) { hair=new LeftHair(); } else if("right".equals(key)) { hair=new RightHair(); } return hair; } }
(5)编写对应的测试类
package com.songyan.factory; public class Test { public static void test1() { Hair hair=new LeftHair(); hair.draw(); } public static void test2() { HairFactory factory=new HairFactory(); Hair hair=factory.getHair("left"); hair.draw(); }public static void main(String[] args) { //test1(); test2(); } }
这种方式,当添加新的发型时,需要在factory中添加新的else if判断(不合理)---->运用反射的技术,通过类名,动态的创建对象
反射的知识点:http://www.cnblogs.com/excellencesy/p/8868567.html
(6)通过反射创建对象
package com.songyan.factory; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class HairFactory { public static Hair getHairByClass(String ClassName) { Hair hair=null; try { hair=(Hair) Class.forName(ClassName).newInstance(); } catch (InstantiationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return hair; } }
通过传入累的全名,创建对应的对象
(7)对应的测试方法test3()
package com.songyan.factory; public class Test { public static void test1() { Hair hair=new LeftHair(); hair.draw(); } public static void test2() { HairFactory factory=new HairFactory(); Hair hair=factory.getHair("left"); hair.draw(); } public static void test3() { HairFactory factory=new HairFactory(); Hair hair=factory.getHairByClass("com.songyan.factory.LeftHair"); hair.draw(); } public static void main(String[] args) { //test1(); //test2(); test3(); } }
这种方式需要输入复杂的类全名(不合理)----->配置简单的关键字
(8)编写配置文档type.properties
left=com.songyan.factory.LeftHair
right=com.songyan.factory.RightHair
(9)编写配置文档的读取类及方法
package com.songyan.factory; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.Enumeration; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Map.Entry; import java.util.Properties; public class PropertiesReader { public Map<String,String> getProperties() { //定义储存properties的map集合 Map<String ,String> map= new HashMap<String,String>(); //定义properties对象,操作Properties文件 Properties pro=new Properties(); //输入流以行的形式输入 InputStream in=getClass().getResourceAsStream("type.properties") ; try { pro.load(in); Enumeration enu=pro.propertyNames(); while(enu.hasMoreElements()) { // String key =(String)enu.nextElement(); String value=pro.getProperty(key); map.put(key,value); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return map; } }
(10)编写相应的工厂方法
package com.songyan.factory; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class HairFactory { public static Hair getHairByKey(String key) { Hair hair=null; Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<String,String>(); PropertiesReader reader=new PropertiesReader(); map=reader.getProperties(); System.out.println(map); String className=map.get(key); try { hair=(Hair) Class.forName(className).newInstance(); } catch (InstantiationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return hair; } }
(11)编写对应的测试test4()
package com.songyan.factory; public class Test { public static void test4() { HairFactory factory= new HairFactory(); Hair hair=factory.getHairByKey("left"); hair.draw(); } public static void main(String[] args) { test4(); } }
二、工厂模式的应用(抽象工厂)
抽象工厂的代码实现
(1)定义生产男孩子的接口、女孩子接口
package com.songyan.factory; /** * 男孩接口 * @author Administrator * */ public interface Boy { public void drawMan(); }
package com.songyan.factory; /** *女孩接口 * @author Administrator * */ public interface Girl { public void drawWomen(); }
(2)定义新年男孩,圣诞男孩 继承男孩,
定义新年女孩,圣诞女孩 继承女孩,
package com.songyan.factory; /** * 新年男孩 * @author Administrator * */ public class HNBoy implements Boy{ @Override public void drawMan() { System.out.println("新年男孩"); } }
package com.songyan.factory; /** * 圣诞男孩 * @author Administrator * */ public class MCBoy implements Boy{ @Override public void drawMan() { System.out.println("圣诞男孩"); } }
package com.songyan.factory; /** * 新年女孩 * @author Administrator * */ public class HNGirl implements Girl{ @Override public void drawWomen() { System.out.println("新年女孩"); } }
package com.songyan.factory; /** * 圣诞女孩 * @author Administrator * */ public class MCGirl implements Girl{ @Override public void drawWomen() { System.out.println("圣诞女孩"); } }
(3)定义生产男孩女孩的工厂接口
package com.songyan.factory; /** * 生产男孩女孩的工厂接口 * @author Administrator * */ public interface PersonFactory { //生产男孩子 public Boy getBoy(); //生产女孩子 public Girl getGirl(); }
(4)生产
新年
类型的男孩子,女孩子
package com.songyan.factory; /** * 生产新年类型的男孩子,女孩子 * @author Administrator * */ public class HNFactory implements PersonFactory { @Override public Boy getBoy() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public Girl getGirl() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } }
(5)生产圣诞类型的男孩子,女孩子
package com.songyan.factory; /** * 生产圣诞类型的男孩子,女孩子 * @author Administrator * */ public class MCFactory implements PersonFactory{ // @Override public Boy getBoy() { return null; } @Override public Girl getGirl() { return null; } }
(6)编写测试类
package com.songyan.factory; public class Test2 { public static void main(String[] args) { //绘制圣诞女孩 PersonFactory factory=new MCFactory(); Girl girl=factory.getGirl(); girl.drawWomen(); } }
抽象工厂的应用
(1)数据库的链接
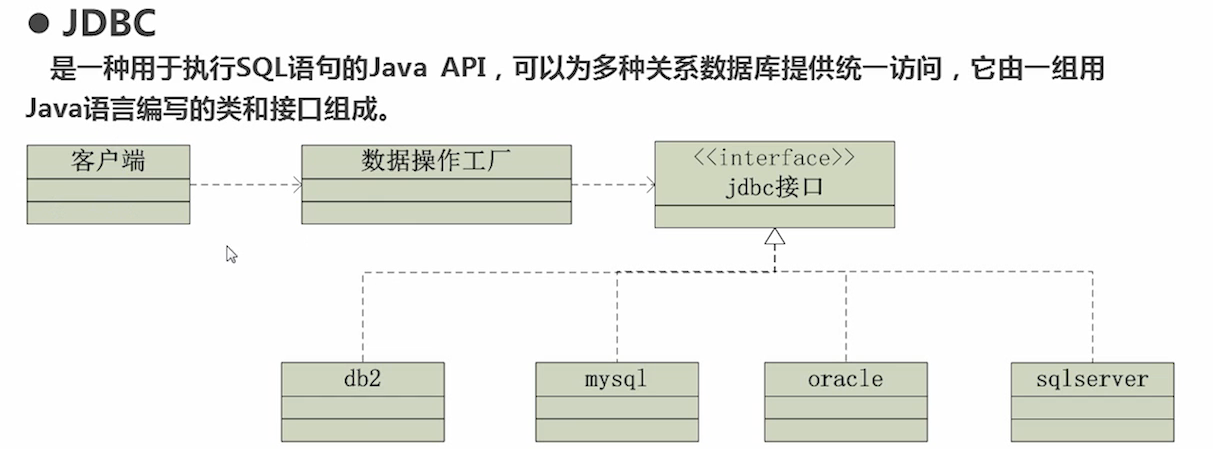
(2)生产bean返回给客户端


三、工厂模式总结

