虚拟化数电底层
目前已基本实现函数和结构体的面向对象化。
对象:以数电模块为单位(应该)
内部成员:线路,逻辑门,连接关系。以及虚拟化的输入端(调试用)。
方法:
- 建立线路(Line_create)
- 建立逻辑门(Gate_create)
- 连接输入端(Pin_attach)
- 连接元件(Attach)
- 模块充电(Power_on)
- 模块计算(CST)
- 改变输入(Update)
一.基本操作:
- 建立线路
- 实现框架:
其中:
typedef _line* line; #define line_create(lptr) do { _line_create(&lptr); } while(0) main() { line l; line_create(l);
(...) }typedef struct _LINE {
(...)
} _line; #define MAXN 50000 _line _line__ALLOC_SPACE[MAXN]; _line* LAS_ptr = _line__ALLOC_SPACE; //initial is first address void _line_create(_line **ptr_addr) { //_line's pointer's address *ptr_addr = ++LAS_ptr;
(...)
}效果:申请从内存池中分配一个线路,将指针返回给封装好的line类型。
- 实现框架:
- 建立逻辑门
- 实现框架:
typedef _logic_gate* gate; #define gate_create(gptr, value) do { _logic_gate_create(&gptr, value); } while(0) main() { gate g; gate_create(g, n);
(...) } //n = 1: and gate n = 2: or gate n = 3: not gate其中:
typedef struct _LOGIC_GATE { char gate; //and = 1 or = 2 not = 3 (...) } _logic_gate; _logic_gate _logic_gate__ALLOC_SPACE[MAXN]; _logic_gate* LGAS_ptr = _logic_gate__ALLOC_SPACE; void _logic_gate_create(_logic_gate **ptr_addr, char value) { *ptr_addr = ++LGAS_ptr; (**ptr_addr).gate = value; (...) }
效果:申请从内存池中分配一个逻辑门,将指针返回给封装好的gate类型。
- 实现框架:
- 连接输入端
- 原理:我们把输入端虚拟化,不展开一个对象,而是在line类型中标记,并唯一确定这个line中的电平。
- 实现框架:
#define ATT_NULL 0 #define PIN -1 typedef struct _LINE { (...) BOOL level; //electric level char attach_name; //-1:pin 0:ATT_NULL >0:logic_gate's name(1,2,3....) (...) } _line; BOOL _pin_attach(_line *line_ptr, BOOL pin_value) { (...) (*line_ptr).attach_name = PIN; (*line_ptr).level = pin_value; (...) } #define pin_attach(lptr, value) do { _pin_attach(lptr, value); } while(0) main() { line l; line_create(l); pin_attach(l, BOOL_VALUE);
(...) }效果:l被标记成为连接输入端的线路,并被持续性地赋值为BOOL_VALUE(TRUE或者FALSE)
- 连接元件:
- 连接线路和逻辑门:
- 思路:由于一条线路可以连接多个逻辑门入口,但是一个逻辑门的出口只能连接一个线路,所以可以把每个线路连接的逻辑门入口保存为一个静态链表,而把逻辑门出口和线路简单地一一对应起来。
- 实现框架:
#define attin(gptr, inptr) do { _logic_gate_income_attach(gptr, inptr); } while(0) #define attout(gptr, outptr) do { _logic_gate_outcome_attach(gptr, outptr); } while(0) main() { line l1, l2, l3; gate g; (...) attin(g, l1); attin(g, l2); attout(g, l3); (...) }
其中:
typedef struct _LINE { (...) struct _LOGIC_GATE_LIST* list_head; (...) } _line; typedef struct _LOGIC_GATE { (...) struct _LINE *outcome_ptr; (...) } _logic_gate; typedef struct _LOGIC_GATE_LIST { struct _LOGIC_GATE* gate_ptr; struct _LOGIC_GATE_LIST* next; } _logic_gate_list;
_logic_gate_list _logic_gate_list__ALLOC_SPACE[MAXN]; _logic_gate_list *LGLAS_ptr = _logic_gate_list__ALLOC_SPACE;
BOOL _logic_gate_income_attach(_logic_gate *gate_ptr, _line *income_ptr) { LGLAS_ptr++; //allocate new node into the list table "line's logic_gates" (*LGLAS_ptr).gate_ptr = gate_ptr; (*LGLAS_ptr).next = (*income_ptr).list_head; (*income_ptr).list_head = LGLAS_ptr; (...) //income_ptr's list <- gate_ptr } BOOL _logic_gate_outcome_attach(_logic_gate *gate_ptr, _line *outcome_ptr) { (*gate_ptr).outcome_ptr = outcome_ptr; (...) }
- 连接线路和线路:
- 由于线路连起来实质上是把一根线整合到另一根线上面了,所以只需删除整合过去的线路,并将它连接的所有逻辑门都转移到被整合的线路上即可。此外因为我们实现的内存池没有回收功能,所以那个删除的空间就浪费了。但是整体上提高了效率,利大于弊。
- 实现框架:
#define line_merge(lmge, lmged) do { _line_merge(&lmge, &lmged); } while(0) main() { l l1, l2; (...) line_merge(l1, l2); (...) }
其中:
typedef struct _LINE { (...) BOOL remove; //be removed or not? (...) } _line; void _line_free(_line **ptr_addr) { (**ptr_addr).remove = TRUE; //in this case, a space in LAS[] will be wasted, but it worthed } BOOL _line_merge(_line **lineA_ptr_addr, _line **lineB_ptr_addr) { //merge lineB's logic gates into lineA P.S: maybe a gate will connect to a line twice. _logic_gate_list* list_ptr = (**lineB_ptr_addr).list_head; while(list_ptr != GATE_NULL) { _logic_gate_income_attach((*list_ptr).gate_ptr, *lineA_ptr_addr); list_ptr = (*list_ptr).next; //get next logic_gate } _line_free(lineB_ptr_addr); //delete (*lineB_ptr_addr) = (*lineA_ptr_addr); (...) }
注意:
struct _LOGIC_GATE_LIST* GATE_NULL = (struct _LOGIC_GATE_LIST*)987654321; void _line_create(_line **ptr_addr) { //_line's pointer's address (...) (**ptr_addr).list_head = GATE_NULL; //logic_gate_list' head points to GATE_NULL (...) }
从而这样就可以实现静态链表结构。
- 连接线路和逻辑门:
- 模块充电:
- 假设我们已经建立好了一个模块,其中有完整的线路,逻辑门,连接关系,以及虚拟化的输入端。那么一开始模块没有初始化的时候,所有的值都是缺省的。现在我们要做的就是把模块初始化,完成在当前输入端下的模块状态,从而可以实现进一步的计算。
- 具体操作上,考虑一下物理条件下的实际状态。当逻辑门没有供电的时候,无论输入端是什么,输出端都不会有电。当模块开机,逻辑门同时开始供电,由于所有逻辑门同时开始计算,此时模块内部可能会产生很杂乱的数电信号,这种信号没有意义,我们依然将其看作是缺省的。那么我们把可以确定的稳定的信号作为有意义的信息进行计算,最初的信息肯定是从输入端开始的,因为在一定时期中输入端是恒定不变的。
- 于是我们就从输入端开始进行广搜,把所有计算出来的新的线路加入下一轮队列中,那么加入过队列的值由稳定的信号转移过来,就也可以看成稳定的。(这种情况存在一个反例,就是模块中存在环状电路,就有可能产生高频脉冲,无法得出稳定的信号值。然而我们不予以考虑。)广搜足够多的的次数以后,停止广搜。此时模块可以看成初始化完毕。
-
模块计算:
- 数电模块本质上是一个有限状态机,在物理上所有元件在同一时间并行计算,为了模拟物理的并行结构,可以用类似于上面广搜的办法,每一次将模块中所有与线路和逻辑门按照规则计算,实现状态转移。也就是在当前时刻内,扫描所有逻辑门,由逻辑门的入口线路,更新出口线路。
- 优化:有的逻辑门显然不用转移。可以贪心地发现如果当前逻辑门两个入口线路的值在上一个时刻点都没有转移过,那么这个逻辑门也就不用计算了,因为结果显然也不会变。所以就不用更新出口线路,让出口线路的值继续挂着。
- 进而可以实现类似上面广搜的模式:存储上一个时刻点所有更新过的线路,进而计算所有相关的逻辑门。如果逻辑门出口线路的值更新了,则把这个线路存入下一轮广搜队列。
- 模块计算和模块充电的核心代码类似:
void CST() { //Circut_state_transition _line now_line; _logic_gate now_gate; _logic_gate_list* list_ptr; //enumerate all the lines and logic_gates while(!LPS.empty()) { now_line = LPS.pop() //last period's lines list_ptr = now_line.list_head; while(list_ptr != GATE_NULL) { now_gate = *(*list_ptr).gate_ptr; //get now_gate's informations (...) LGPS.push(now_gate) //add this logic_gate into logic_gate stack (...) list_ptr = (*list_ptr).next; //get next logic_gate } } (...) //calcaulate logic_gates in logic_gate stack, answers stored in logic_gate_outcome_update_level //update LPS[]: LPS_clear(); while(!LGPS.empty()) { now_gate = LGPS.pop(); (...) if((*now_gate.outcome_ptr).level != _logic_gate_outcome_update_level) { (*(now_gate.outcome_ptr)).level = _logic_gate_outcome_update_level; LPS_push(now_gate.outcome_ptr); } (...) } }
- 改变输入:
- 实际上这一步甚至虚拟化输入端都是多余的,调试的意义大于实际意义。真正开发中输入端会用线路连接起来,而不是虚拟一个输入端。那么在调试的时候我们可能要在模块充电完毕后,模拟各种输入端的值。考虑实际操作中如果输入端是作为”线路“而存在的,那么每一次更新输入端,都会在CST中加入队列,进行计算。所以我们就人工地实现广搜过程中加入队列的操作:
inline void pin_update(line lpin, BOOL value) { //still pin, no need to change name's value if(value != (*lpin).level) { (*lpin).level = value; LPS_push(lpin); //in many situation, this operation will wake-up this circut. } }
- 实际上这一步甚至虚拟化输入端都是多余的,调试的意义大于实际意义。真正开发中输入端会用线路连接起来,而不是虚拟一个输入端。那么在调试的时候我们可能要在模块充电完毕后,模拟各种输入端的值。考虑实际操作中如果输入端是作为”线路“而存在的,那么每一次更新输入端,都会在CST中加入队列,进行计算。所以我们就人工地实现广搜过程中加入队列的操作:
二.进阶操作:
我在VM_basis++.h中封装了一些常用函数,这里列出函数的声明以及用法:
#define and_create(gptr, inptr1, inptr2, outptr) do { (...) } while(0) #define or_create(gptr, inptr1, inptr2, outptr) do { (...) } while(0) #define not_create(gptr, inptr, outptr) do { (...) } while(0) #define line_array_create(array) do { (...) } while(0) void pins_attach(int argn, ...) { (...) } main() { line L[12]; gate og, ag, ng; line_array_create(L); /****************************************************** for(int i = 1; i < sizeof(L)/sizeof(line); i++) line_create(L[i]); ******************************************************/ and_create(ag, L[1], L[3], L[5]); /****************************************************** gate_create(ag, 1); attin(ag, L[1]); attin(ag, L[3]); attout(ag, L[5]); ******************************************************/ or_create(og, L[2], L[4], L[6]); not_create(ng, L[7], L[8]); pins_attach(3, L[9], FALSE, L[10], FALSE, L[11], TRUE); /****************************************************** pin_attach(L[9], FALSE); pin_attach(L[10], FALSE); pin_attach(L[11], TRUE); ******************************************************/ (...) }
三.禁忌&注意事项:
为了提高程序鲁棒性,我在VM_basis++.h中加了一些防爆措施:
- 一个线路有且只能连接到一个元件上(包括逻辑门,线路,输入端)。
- 逻辑门入口数限制:非门为1,与门或门为2;出口数限制:都为1。不允许接入数超出限制。
如果检测到有以上错误,程序会报错,并指出错误类型。
另外还有如下一些不建议使用的方法:
- 与门或门只接入一根线路。(这种情况下会变成一根带延迟的导线,或者中继器)
- 逻辑门没有出口。
如果检测到有以上操作,程序会警告,并指出不建议的类型。
另外还存在这样的一些错误,程序可以运行,但是电路可能紊乱。例如:存在环形脉冲电路。这需要开发者自己意识到这些错误。
此外VM_basis++.h中还提供了开发者选项:
/******* developer options *******/ #define CANCEL_SUCCESS() SHOW_SUCCESS = FALSE void SHOW_CIRCUT() { printf("=============== SHOW CIRCUT =============== "); _line* _line_iterator = _line__ALLOC_SPACE+1; _logic_gate* _gate_iterator = _logic_gate__ALLOC_SPACE+1; while(_line_iterator <= LAS_ptr) { if((*_line_iterator).remove == FALSE) printf("Line: Name:%d Level:%d ", (*_line_iterator).name, (*_line_iterator).level); _line_iterator++; } printf("=============================================== "); }
可以在外部调用CANCEL_SUCCESS()函数来取消建立成功提示。
通过SHOW_CIRCUT()函数,可以打印出当前所有线路的值。(其中Name为线路在内存池的下标,或者可以理解为物理层面上真正的线路编号)
四. 具体代码:(按理说头文件不应该定义变量。当然也无所谓)
VM_basis.h:
#include <stdio.h> typedef char BOOL; #define TRUE 1 #define FALSE 0 #define PIN -1 #define ATT_NULL 0 struct _LINE; struct _LOGIC_GATE; struct _LOGIC_GATE_LIST; typedef struct _LINE { BOOL level; //electric level BOOL remove; //be removed or not? struct _LOGIC_GATE_LIST* list_head; int name; //convenience && acculation char attach_name; //-1:pin 0:ATT_NULL >0:logic_gate's name(1,2,3....) } _line; typedef struct _LOGIC_GATE { char gate; //and or not struct _LINE *incomeA_ptr, *incomeB_ptr, *outcome_ptr; //only allow 2 income argvs int name; } _logic_gate; typedef struct _LOGIC_GATE_LIST { struct _LOGIC_GATE* gate_ptr; struct _LOGIC_GATE_LIST* next; } _logic_gate_list; struct _LINE* LINE_NULL = (struct _LINE*)123456789; struct _LOGIC_GATE_LIST* GATE_NULL = (struct _LOGIC_GATE_LIST*)987654321; /******* circut fundamental structures *******/ #define MAXN 50000 //numbers of lines and logic_gates #define MAXM 50000 //numbers of interactions between lines and logic_gates _line _line__ALLOC_SPACE[MAXN]; _line* LAS_ptr = _line__ALLOC_SPACE; _logic_gate _logic_gate__ALLOC_SPACE[MAXN]; _logic_gate* LGAS_ptr = _logic_gate__ALLOC_SPACE; _logic_gate_list _logic_gate_list__ALLOC_SPACE[MAXN]; _logic_gate_list *LGLAS_ptr = _logic_gate_list__ALLOC_SPACE; //change the units' framework structure void _line_create(_line **ptr_addr) { //_line's pointer's address (*ptr_addr) = ++LAS_ptr; (**ptr_addr).level = FALSE; (**ptr_addr).remove = FALSE; (**ptr_addr).name = LAS_ptr-_line__ALLOC_SPACE; //pointer's sub = (addr's D-value)/sizeof(var) (**ptr_addr).attach_name = ATT_NULL; (**ptr_addr).list_head = GATE_NULL; //logic_gate_list' head points to GATE_NULL } void _line_free(_line **ptr_addr) { (**ptr_addr).remove = TRUE; //in this case, a space in LAS[] will be wasted, but it worthed } void _logic_gate_create(_logic_gate **ptr_addr, char value) { (*ptr_addr) = ++LGAS_ptr; (**ptr_addr).gate = value; (**ptr_addr).name = LGAS_ptr-_logic_gate__ALLOC_SPACE; (**ptr_addr).incomeA_ptr = (**ptr_addr).incomeB_ptr = (**ptr_addr).outcome_ptr = LINE_NULL; } //change the units' interaction structure BOOL _logic_gate_income_attach(_logic_gate *gate_ptr, _line *income_ptr) { //Rule:Only allow 2 incomes when gate is or/and gate; Only allow 1 income when gate is not gate. if((*gate_ptr).incomeB_ptr != LINE_NULL || ((*gate_ptr).incomeA_ptr != LINE_NULL) && (*gate_ptr).gate == 3) return FALSE; //attach fail LGLAS_ptr++; //allocate new node into the list table "line's logic_gates" (*LGLAS_ptr).gate_ptr = gate_ptr; (*LGLAS_ptr).next = (*income_ptr).list_head; (*income_ptr).list_head = LGLAS_ptr; if((*gate_ptr).incomeA_ptr == LINE_NULL) (*gate_ptr).incomeA_ptr = income_ptr; else (*gate_ptr).incomeB_ptr = income_ptr; return TRUE; //attach success } BOOL _logic_gate_outcome_attach(_logic_gate *gate_ptr, _line *outcome_ptr) { if((*outcome_ptr).attach_name != ATT_NULL) return FALSE; //line have been attached, attach fail (*outcome_ptr).attach_name = (*gate_ptr).name; (*gate_ptr).outcome_ptr = outcome_ptr; return TRUE; } BOOL _pin_attach(_line *line_ptr, BOOL pin_value) { if((*line_ptr).attach_name != ATT_NULL) return FALSE; (*line_ptr).attach_name = PIN; (*line_ptr).level = pin_value; return TRUE; } //merge lines, lineA <- lineB, including all the logic gates in B BOOL _line_merge(_line **lineA_ptr_addr, _line **lineB_ptr_addr) { if((**lineB_ptr_addr).attach_name != ATT_NULL) return FALSE; //merge lineB's logic gates into lineA P.S: maybe a gate will connect to a line twice. _logic_gate_list* list_ptr = (**lineB_ptr_addr).list_head; while(list_ptr != GATE_NULL) { _logic_gate_income_attach((*list_ptr).gate_ptr, *lineA_ptr_addr); list_ptr = (*list_ptr).next; //get next logic_gate } _line_free(lineB_ptr_addr); //delete (*lineB_ptr_addr) = (*lineA_ptr_addr); //in fact, pysically _lineA and _lineB are the same _line, so there's no need to update attached return TRUE; } /******* units' states && circut transition *******/ BOOL ACCULATE_OPTIMIZATION_FLAG; _line* _line_ptr_stack[MAXN]; //store ptr, acculate copy operations (equels to store names) _logic_gate* _logic_gate_ptr_stack[MAXN]; //LPS -> LGPS -> next LPS -> ... BOOL _logic_gate_outcome_update_level[MAXN]; int LPS_top, LGPS_top; BOOL _logic_gate_vis[MAXN]; //package _line_ptr_stack && line's value operation #define LPS_push(lptr) _line_ptr_stack[LPS_top++] = lptr #define LPS_clear() LPS_top = 0 void CST() { //Circut_state_transition _line now_line; _logic_gate now_gate; _logic_gate_list* list_ptr; //enumerate all the lines and logic_gates while(LPS_top) { now_line = *(_line_ptr_stack[--LPS_top]); list_ptr = now_line.list_head; while(list_ptr != GATE_NULL) { now_gate = (*(*list_ptr).gate_ptr); //get now_gate's informations if(_logic_gate_vis[now_gate.name] == 0) { //LGV[X] == 0: havn't been visited _logic_gate_ptr_stack[LGPS_top++] = (*list_ptr).gate_ptr; //entry ptr _logic_gate_vis[now_gate.name] = TRUE; //mark, in case of gates repeat entry } list_ptr = (*list_ptr).next; //get next logic_gate } } //calcaulate logic_gates int i; for(i = 0; i <= LGPS_top-1; i++) { now_gate = *(_logic_gate_ptr_stack[i]); if(now_gate.outcome_ptr == LINE_NULL) continue; //Warning: no output. no need to calculate if(now_gate.incomeB_ptr == LINE_NULL && now_gate.gate != 3) { //Warning: default input _logic_gate_outcome_update_level[i] = (*(now_gate.incomeA_ptr)).level; continue; } if(now_gate.gate == 1) { if((*(now_gate.incomeA_ptr)).level == TRUE && ((*now_gate.incomeB_ptr).level) == TRUE) _logic_gate_outcome_update_level[i] = TRUE; else _logic_gate_outcome_update_level[i] = FALSE; } if(now_gate.gate == 2) { if((*(now_gate.incomeA_ptr)).level == FALSE && (*(now_gate.incomeB_ptr)).level == FALSE) _logic_gate_outcome_update_level[i] = FALSE; else _logic_gate_outcome_update_level[i] = TRUE; } if(now_gate.gate == 3) { if((*(now_gate.incomeA_ptr)).level == TRUE) _logic_gate_outcome_update_level[i] = FALSE; else _logic_gate_outcome_update_level[i] = TRUE; } } //update LPS[]: LPS_clear(); while(LGPS_top) { now_gate = *(_logic_gate_ptr_stack[--LGPS_top]); if(now_gate.outcome_ptr == LINE_NULL) continue; //Warning: no output. if(ACCULATE_OPTIMIZATION_FLAG == FALSE || (*now_gate.outcome_ptr).level != _logic_gate_outcome_update_level[LGPS_top]) LPS_push(now_gate.outcome_ptr); (*(now_gate.outcome_ptr)).level = _logic_gate_outcome_update_level[LGPS_top]; _logic_gate_vis[now_gate.name] = FALSE; //reset vis[] } }
VM_basis++.h:
#include "VM_basis.h" #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdarg.h> #include <conio.h> /******* package objects and functions *******/ int ERROR_cnt, WARNING_cnt; //package _line & _logic_gate BOOL SHOW_SUCCESS = TRUE; typedef _line* line; typedef _logic_gate* gate; char chs[10][10] = {"", "Or", "And", "Not", "(TRUE)", "(FALSE)"}; #define line_create(lptr) do { _line_create(&lptr); if(SHOW_SUCCESS == TRUE) printf("Create Line ""#lptr""(Name: %d): Succeed ", (*lptr).name); } while(0) #define gate_create(gptr, value) do { _logic_gate_create(&gptr, value); if(SHOW_SUCCESS == TRUE) printf("Create %s Gate ""#gptr""(Name: %d): Succeed ", chs[value], (*gptr).name); } while(0) #define attin(gptr, inptr) do { if(_logic_gate_income_attach(gptr, inptr) == FALSE) { printf(">>>ERROR: Line ""#inptr"" cannot attach to ""#gptr""'s input:"); printf(" ""#gptr""'s input ports is full... "); ERROR_cnt++; } else if(SHOW_SUCCESS == TRUE) printf("Attach Line ""#inptr"" to ""#gptr""'s input: Succeed "); } while(0) #define attout(gptr, outptr) do { if(_logic_gate_outcome_attach(gptr, outptr) == FALSE) { printf(">>>ERROR: Line ""#outptr"" cannot attach to ""#gptr""s output:"); printf(" ""#outptr""have been attached to another unit... "); ERROR_cnt++; } else if(SHOW_SUCCESS == TRUE) printf("Attach Line ""#outptr"" to ""#gptr""'s output: Succeed "); } while(0) #define line_merge(lmge, lmged) do { if(_line_merge(&lmge, &lmged) == FALSE) { printf(">>>ERROR: Line ""#lmged"" cannot attach to ""#lmge"":"); printf(" ""#lmged""have been attached to another unit... "); ERROR_cnt++; } else if(SHOW_SUCCESS == TRUE) printf("Attach Line ""#lmged"" to ""#lmge"": Succeed "); } while(0) #define pin_attach(lptr, value) do { if(_pin_attach(lptr, value) == FALSE) { printf(">>>ERROR: Line ""#lptr"" cannot attach to pin%s", chs[4]); printf(": ""#lptr"" have been attached to another unit... "); ERROR_cnt++; } else if(SHOW_SUCCESS == TRUE) printf("Attach Line ""#lptr"" to pin%s: Succeed ", chs[5]); } while(0) //package gate operation #define and_create(gptr, inptr1, inptr2, outptr) do { gate_create(gptr, 1); attin(gptr, inptr1); attin(gptr, inptr2); attout(gptr, outptr); } while(0) #define or_create(gptr, inptr1, inptr2, outptr) do { gate_create(gptr, 2); attin(gptr, inptr1); attin(gptr, inptr2); attout(gptr, outptr); } while(0) #define not_create(gptr, inptr, outptr) do { gate_create(gptr, 3); attin(gptr, inptr); attout(gptr, outptr); } while(0) //Build lines in a quick way #define line_array_create(array) do { BOOL flag_reg = SHOW_SUCCESS; SHOW_SUCCESS = FALSE; int i, siz = sizeof(array)/sizeof(line); for(i = 1; i < siz; i++) { line_create(array[i]); if(flag_reg == TRUE) printf("Create Line ""#array"[%d]"(Name: %d): Succeed ", i, (*array[i]).name); } SHOW_SUCCESS = flag_reg; } while(0) void pins_attach(int argn, ...) { va_list(pointer); va_start(pointer, argn); line line_buf; BOOL value_buf; int i; BOOL flag_reg = SHOW_SUCCESS; SHOW_SUCCESS = FALSE; for(i = 1; i <= argn; i++) { line_buf = va_arg(pointer, line); value_buf = va_arg(pointer, int); pin_attach(line_buf, value_buf); if(flag_reg == TRUE) printf("Attach Line(name:%d) to pin%s: Succeed ", (*line_buf).name, chs[5-value_buf]); } va_end(pointer); SHOW_SUCCESS = flag_reg; } /******* check && circut power on *******/ #define POWER_ON_TIME 1000 void SHOW_CIRCUT(); void POWER_ON() { //check circut, init circut, insert pins into LPS[] for CST LPS_clear(); _line* _line_iterator = _line__ALLOC_SPACE+1; //_line store from LAS[1]. _logic_gate* _gate_iterator = _logic_gate__ALLOC_SPACE+1; //check lines while(_line_iterator <= LAS_ptr) { if((*_line_iterator).remove == FALSE) { if((*_line_iterator).attach_name == ATT_NULL) { printf(">>>ERROR: Line(name:%d) didn't attached to any unit... ", (*_line_iterator).name); ERROR_cnt++; } if((*_line_iterator).attach_name == PIN) LPS_push(_line_iterator); } _line_iterator++; } //check logic_gates while(_gate_iterator <= LGAS_ptr) { if((*_gate_iterator).outcome_ptr == LINE_NULL) { printf(">>>WARNING: Gate(name:%d) output default... ", (*_gate_iterator).name); WARNING_cnt++; } int cnt = 0, should_be = 2; if((*_gate_iterator).gate == 3) should_be = 1; if((*_gate_iterator).incomeA_ptr != LINE_NULL) cnt++; if((*_gate_iterator).incomeB_ptr != LINE_NULL) cnt++; if(cnt < should_be) { printf(">>>WARNING: Gate(name:%d) input default(now %d, should be %d)... ", (*_gate_iterator).name, cnt, should_be); WARNING_cnt++; } _gate_iterator++; } //tips UI printf("-----------------------------------------------"); printf(" Initializ finished. %d ERRORs, %d WARNINGs. ", ERROR_cnt, WARNING_cnt); if(ERROR_cnt != 0 || WARNING_cnt != 0) { printf(">>>Circut may not work properly. Power_on circut anyway?(Y/N)"); char ans = getch(); while(ans != 'y' && ans != 'Y' && ans != 'n' && ans != 'N') ans = getch(); if(ans == 'n' || ans == 'N') exit(0); } else printf("Circut Power_on... "); /***POWER_ON: a long period of high-level current. To simulate this operate, we cancel the acculate-optimization in CST, calculate every unit in the circut.***/ /***WHY we need to POWER_ON? The reason is when the circut was built, all the levels and values in it is originnaly default(FALSE), so we need to init. ***/ ACCULATE_OPTIMIZATION_FLAG = FALSE; int i; for(i = 1; i <= POWER_ON_TIME; i++) CST(); ACCULATE_OPTIMIZATION_FLAG = TRUE; } /******* (mannul) update circut input *******/ inline void pin_update(line lpin, BOOL value) { //still pin, no need to change name's value if(value != (*lpin).level) { (*lpin).level = value; LPS_push(lpin); //in many situation, this operation will wake-up this circut. } } /******* developer options *******/ #define CANCEL_SUCCESS() SHOW_SUCCESS = FALSE void SHOW_CIRCUT() { printf("=============== SHOW CIRCUT =============== "); _line* _line_iterator = _line__ALLOC_SPACE+1; _logic_gate* _gate_iterator = _logic_gate__ALLOC_SPACE+1; while(_line_iterator <= LAS_ptr) { if((*_line_iterator).remove == FALSE) printf("Line: Name:%d Level:%d ", (*_line_iterator).name, (*_line_iterator).level); _line_iterator++; } printf("=============================================== "); }
顺便再带一个示例程序:
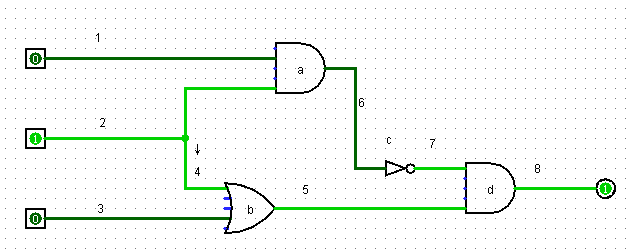
要实现这样一个电路(注:4号线连接在了2号线上面)
我们打这样一个程序:
#include "VM_basis++.h" #define SHOW_SUCCESS_UI_FLAG 1 int main() { if(SHOW_SUCCESS_UI_FLAG != 1) CANCEL_SUCCESS(); line L[9]; gate A, B, C, D; line_array_create(L); pins_attach(3, L[1], FALSE, L[2], TRUE, L[3], FALSE); line_merge(L[2], L[4]); and_create(A, L[1], L[2], L[6]); or_create(B, L[3], L[4], L[5]); not_create(C, L[6], L[7]); and_create(D, L[5], L[7], L[8]); POWER_ON(); SHOW_CIRCUT(); return 0; }
运行结果:
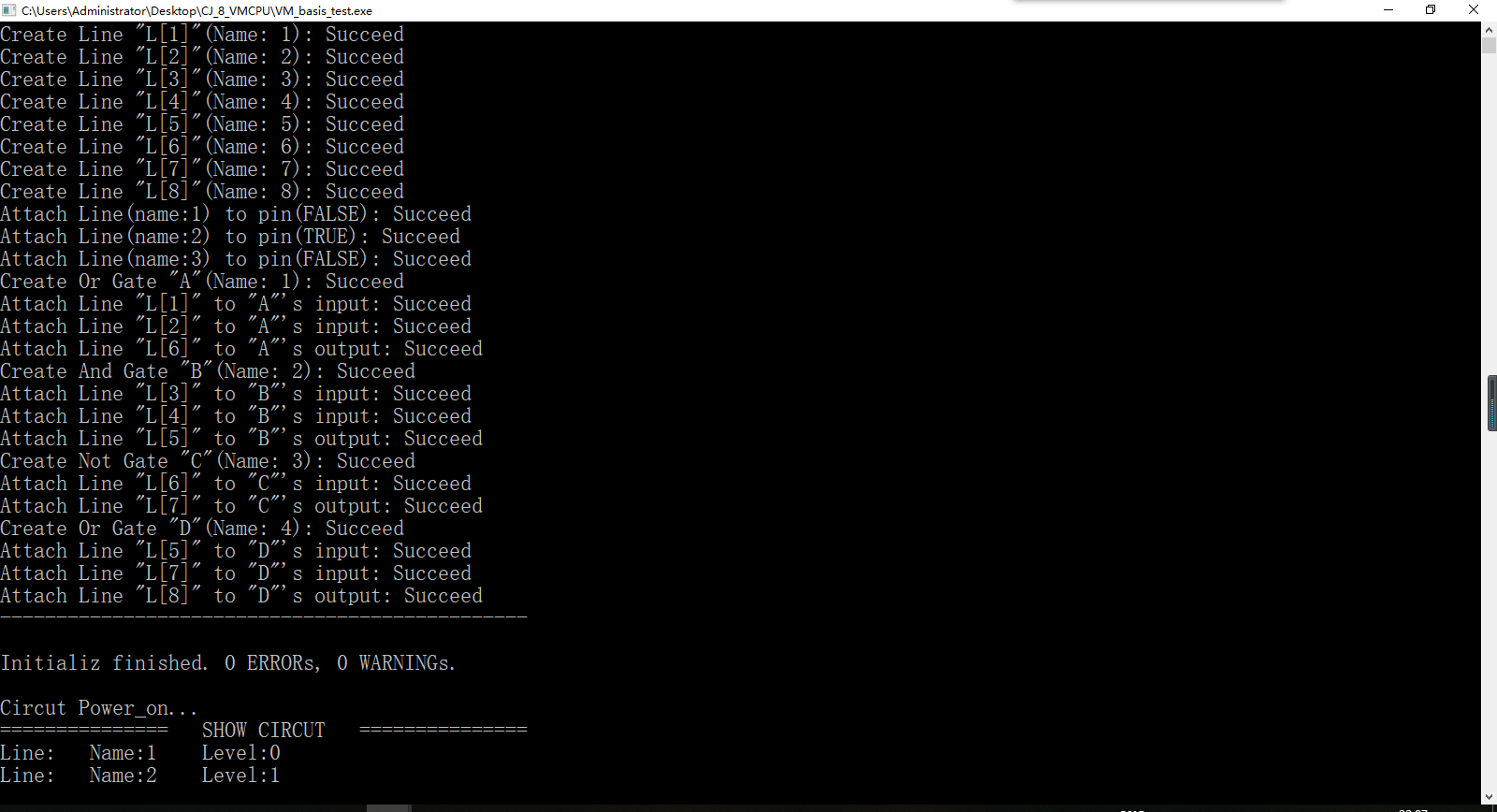
之后,我们改变输入端,造出三个测试数据:
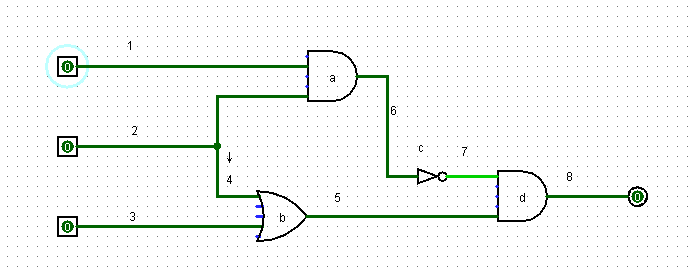
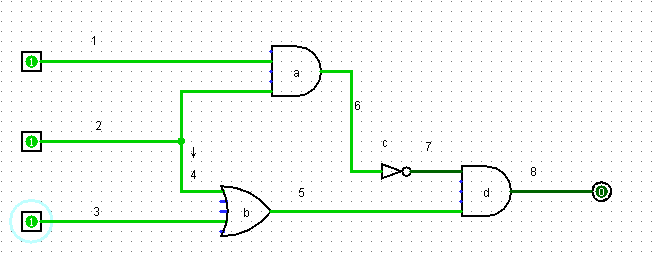

相对应地我们有了如下的代码:
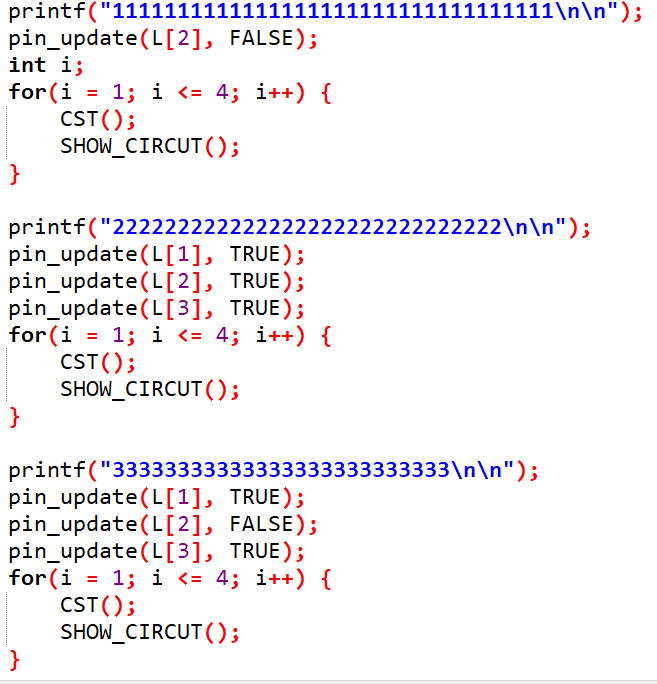
作为对应三组数据的三个输入端电路。我们把计算次数设为4,也就是说对于每一个输入数据,我们把广搜四次的结果作为最终结果。(可以发现数电模块作为一个层次网络的深度只有3,所以广搜4次是显然可行的)
三次结果如下:
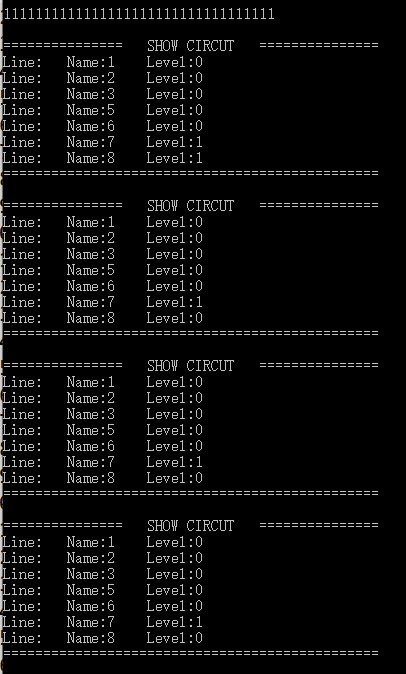
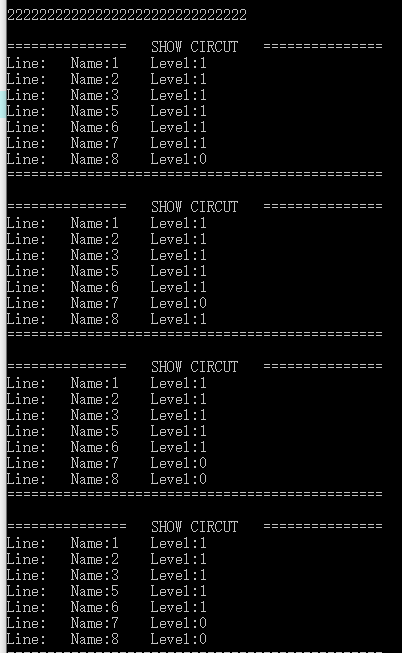
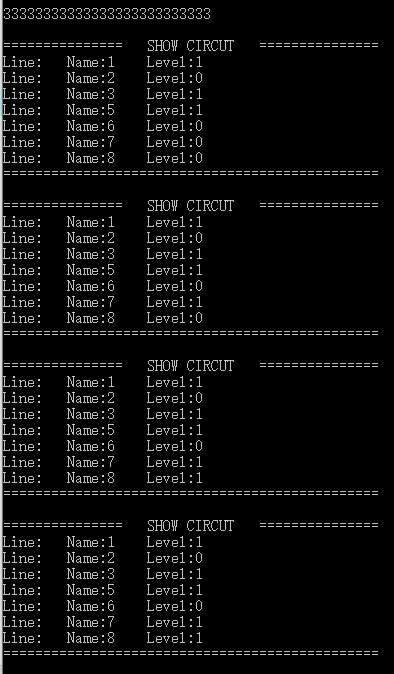
结果完全正确,测试样例通过。
五. 下一层的实现目标:
通过VM_basis++.h,我们已经可以比较方便地建立虚拟化的数电模块,比如锁存器,T触发器等等模块。
下一步的任务是如何在建立完各自的模块之后,将不同模块的接口连接。以及时序控制系统是否可以正常地控制各个模块的计算。