1 昨日回顾
继承的耦合度是最高的 因为有父类的完全方法
比聚合还高
2 工厂方法模式(从这里开始就是GOF讲的23种设计模式中的内容了
简单工厂模式违背了开闭原则,
对简单的工厂模式进行改造:
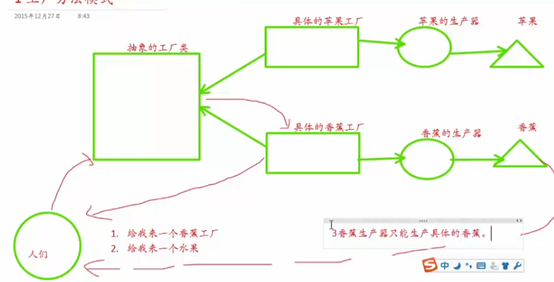
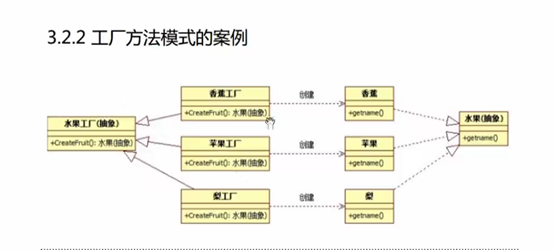
工厂方法模式:

抽象的工厂类:

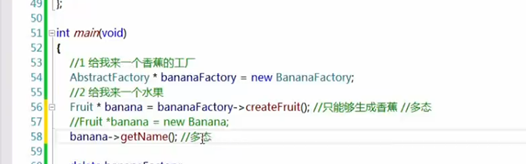
Main函数:

发生了两次多态:

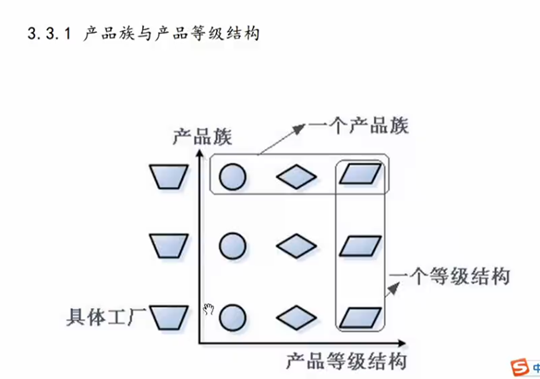
3 抽象工厂方法模式

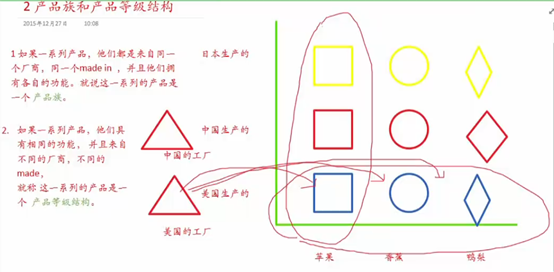
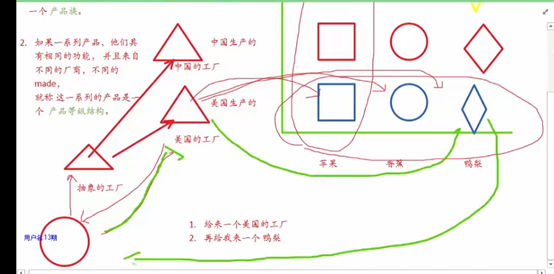

1.添加一个产品族,测试:


2.添加一个产品等级结构

(在添加鸭梨生成器的时候修改了抽象工厂 已经违背了开闭原则了)
结论: 针对产品族进行添加 符合开闭原则
针对产品等级结构添加 不符合开闭原则
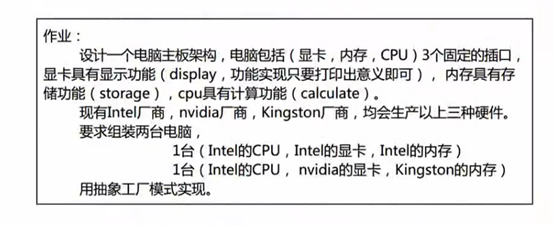
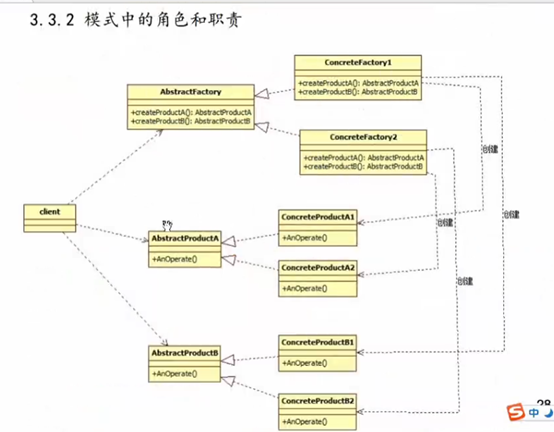
4 抽象工厂方法模式和工厂三兄弟总结








5 单例模式的任务管理器
如果对象是全局唯一的 那么就说它是一个单例
Windows下任务管理器就是单例的 怎么打开都是一个
内部的数据是向操作系统内核发请求得到的
- 如果任务管理器有多个 不停的发请求 会出现 同一时刻 不同的系统参数会给用户带来歧义
- Windows操作系统就给任务管理器类设置为单例类,全局唯一。
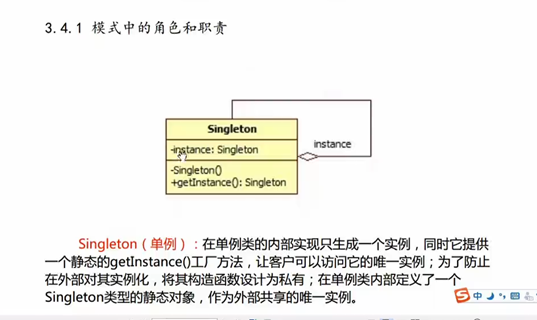
6 单例模式


饿汉式: 在编译时候确定单例对象
懒汉式: 在调用的时候才确定单例对象
当懒汉式遇见多线程
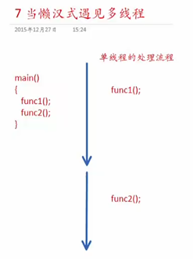
多线程情况:
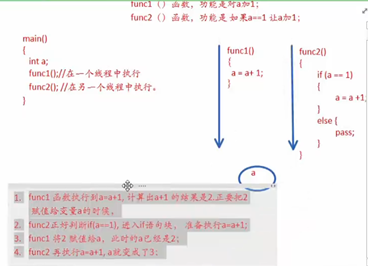
如果a可能回是func1 和func2的竞争资源
应该使用锁 调用前查看是否被锁

使用锁。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/*
一是某个类只能有一个实例
二是它必须自行创建这个实例
三是它必须自行向整个系统提供这个实例
*/
/*
单例模式的使用步骤:
a) 构造函数私有化。 //为了不让在类的外部再创建一个本类的实例。
b) 提供一个全局的静态方法(全局访问点)来获取单例对象。
c) 再类中定义一个静态指针 指向奔雷的变量的静态变量指针。
*/
class Singleton
{
public:
static Singleton * getInstance() {
return instance;
}
private:
// 不让类的外部再创建实例
Singleton() {
}
static Singleton * instance; // 指向本类唯一实例的指针
};
/*
饿汉式 - 在编译期间就已经确定这个唯一的实例了。
*/
// 给静态成员赋值
Singleton * Singleton::instance = new Singleton(); // 类的内部
class Singleton2
{
public:
static Singleton2* getInstance()
{
if (instance == NULL) {
instance = new Singleton2;
}
return instance;
}
private:
Singleton2() {
}
static Singleton2 *instance;
};
// 懒汉式的初始化方式
Singleton2 * Singleton2::instance = NULL;
int main(void)
{
Singleton * s1 = Singleton::getInstance();
Singleton * s2 = Singleton::getInstance();
if (s1 == s2) {
cout << "s1 == s2" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "s1 != s2" << endl;
}
Singleton2 *s3 = Singleton2::getInstance();
Singleton2 *s4 = Singleton2::getInstance();
if (s3 == s4) {
cout << "s3 == s4" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "s3 != s4" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
7 单例模式-打印机案例


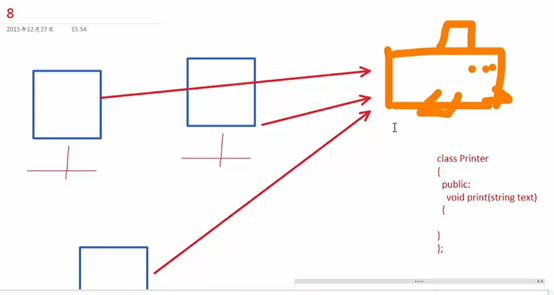
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Printer
{
public:
static Printer * getInstance() {
return instance;
}
void print(string text)
{
cout << "打印的内容是" << text << endl;
sequence++;
cout << "今天已经打印了" << sequence << "条数据" << endl;
}
static int GetCnt() {
return sequence;
}
private:
Printer() {
}
// 垃圾回收工
class Garbo {
private:
~Garbo() {
if (instance != NULL) {
delete instance;
}
}
};
static Garbo garbo; // 在静态区域开辟一个对象,Garbo
// (静态成员在编译的时候就会在静态区开辟 当程序执行完毕的时候 在静态区开辟的内存会开始释放)
static int sequence; // 记录打印机已经打印了多少条数据
static Printer * instance;
};
int Printer::sequence = 0;
// 饿汉式
Printer * Printer::instance = new Printer;
Printer::Garbo Printer::garbo;
// 静态成员在编译的时候就会在静态区开辟 当程序执行完毕的时候 在静态区开辟的内存会开始释放 析构函数中就把instance给删除了
int main(void)
{
// 员工1 获取
Printer *p1 = Printer::getInstance(); // 获取到唯一的打印机实例
p1->print("一份简历");
Printer *p2 = Printer::getInstance();
p2->print("lol 皮肤");
Printer *p3 = Printer::getInstance();
p3->print("离职申请");
system("pause");
return 0;
}

服务器中一般把线程池设计为单例
掌握所有线程
日志模块
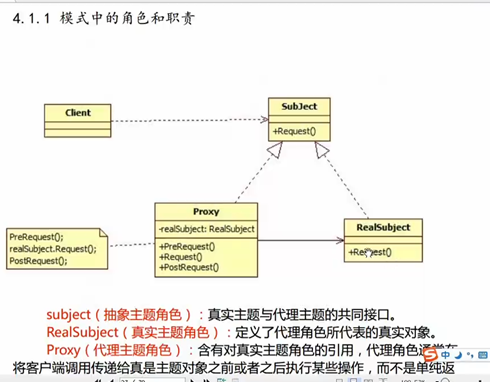
8 代理模式
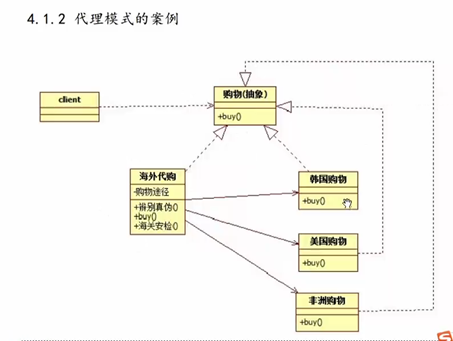
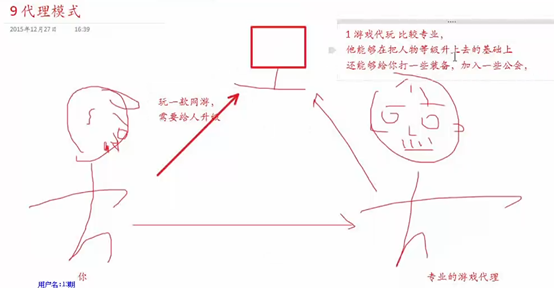
9 代理模式案例

#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
// 商品
class Item
{
public:
Item(string kind, bool fact)
{
this->kind = kind;
this->fact = fact;
}
string getKind()
{
return this->kind;
}
bool getFact()
{
return this->fact;
}
private:
string kind; // 商品的种类
bool fact; // 商品的真假
};
// 抽象的购物方式
class Shopping {
public:
virtual void buy(Item *it) = 0; // 抽象的买东西方法
};
// 韩国购物
class KoreaShopping:public Shopping {
public:
virtual void buy(Item *it) {
cout << "去韩国买了" << it->getKind() << endl;
}
};
// 美国购物
class USAShopping :public Shopping
{
public:
virtual void buy(Item *it)
{
cout << "去美国买了" << it->getKind() << endl;
}
};
// 海外代理
class OverseasProxy : public Shopping {
public:
OverseasProxy(Shopping * shopping)
{
this->shopping = shopping;
}
virtual void buy(Item *it) {
// 1 辨别商品的真假
// 2 进行购买()
// 3 通过海关安检,带回祖国
if (it->getFact() == true)
{
cout << " 1 发现正品 要购买" << endl;
// 用传递进来的购物方式去购物
shopping->buy(it);
// 3 安检
cout << "2 通过海关安检, 带回祖国" << endl;
}
else {
cout << " 1 发现假货,不会购买" << endl;
}
shopping->buy(it);
// ...
}
private:
Shopping *shopping; // 有一个购物方式
};
int main(void)
{
// 1 辨别商品的真假
// 2 进行购买()
// 3 通过海关安检,带回祖国
Item it1("nike鞋",true);
Item it2("CET4证书", false);
#if 0
// 想去韩国买一个鞋
Shopping *koreaShopping = new KoreaShopping;
// 1 辨别商品的真伪
if (it1.getFact() == true) {
cout << "1 发现正品,要购物" << endl;
// 2 去韩国买了这个商品
koreaShopping->buy(&it1);
// 3 安检
cout << "2 通过海关安检, 带回祖国" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "3 发现假货,不会购买" << endl;
}
#endif
// 使用代理的方式
Shopping *usaShopping = new USAShopping;
Shopping *OverseaProxy = new OverseasProxy(usaShopping);
OverseaProxy->buy( &it1);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
9 代理模式案例
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class BeautyGirl
{
public:
// 1 跟男人抛媚眼
virtual void MakeEyesWithMan() = 0;
// 2 与男人共度美好的约会
virtual void HappyWithMan() = 0;
};
// 潘金莲
class JinLian :public BeautyGirl
{
public:
// 1 跟男人抛媚眼
virtual void MakeEyesWithMan()
{
cout << "潘金莲抛了一个媚眼" << endl;
}
// 2 与男人共度美好的约会
virtual void HappyWithMan()
{
cout << "潘金莲跟你共度约会" << endl;
}
private:
};
class WangPo :public BeautyGirl
{
public:
WangPo(BeautyGirl* girl) {
this->girl = girl;
}
// 1 跟男人抛媚眼
virtual void MakeEyesWithMan() {
girl->MakeEyesWithMan();
}
// 2 与男人共度美好的约会
virtual void HappyWithMan() {
girl->HappyWithMan();
}
private:
BeautyGirl* girl;
};
// 西门大官人
int main(void)
{
BeautyGirl *jinlian = new JinLian;
WangPo * wangpo = new WangPo(jinlian);
// 想让潘金莲抛一个
wangpo->MakeEyesWithMan();
// 让金莲约个会
wangpo->HappyWithMan();
return 0;
}}
代理:
class Proxy: public BaseClass
{
public:
Proxy(BaseClass * obj)
{
this.obj = obj
}
virtual void ....
virtual void ....
private:
Baseclass * obj
}