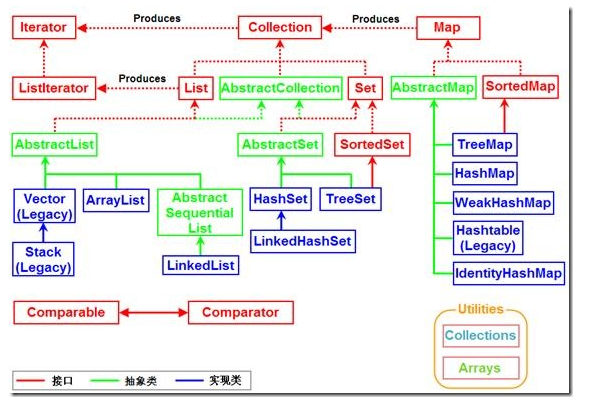
一、arrayList对象创建
当调用无参构造方法来构造一个ArrayList对象时,它会在内部分配一个初始大小为10的一个Object类型数组, 当添加的数据容量超过数组大小的时候,会产生一个新的数组,新的数组大小为原来数组大小的1.5倍+1, 接着把原数组中的数据拷贝到新的素组中,并让原来的引用变量指向这个新数组,参见ArrayList源代码 ;
二、arrayList相关方法:
添加元素:add(E e)
指定位置添加:add(int index, E element)
获取指定位置的元素:public E get(int index)
设置指定位置的元素: public E set(int index, E element) 返回该位置原来存储的元素
删除指定位置的元素 public E remove(int index) 返回被删除的元素
删除指定元素: public boolean remove(Object o) 如果指定元素在集合中存在,返回true 否则返回false
是否包指定元素:public boolean contains(Object o) @return <tt>true</tt> if this list contains the specified element
数组大小: public int size()
list转数组: public Object[] toArray() { return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); }
查找元素在list中的索引值: int indexOf(Object o); 返回此列表中首次出现的指定元素的索引,或如果此列表不包含该指定元素,则返回-1
三、arraylist遍历:
1. for循环
2.foreach
3.迭代器遍历 list实现了 Collection接口,collection接口实现了 Iterable 接口,因此list 可以使用Iterable接口的iterator()方法获得一个迭代器对象
1 package com.iotek.list; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 import java.util.List; 6 7 public class ArrayListDemo { 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 List<String> nlist = new ArrayList<String>(); // 接口的引用变量指向子类对象 11 nlist.add("null"); // 向容器中添加元素 12 nlist.add("lucy"); 13 nlist.add("jack"); 14 nlist.add("tom"); 15 nlist.add("john"); 16 nlist.add("jack"); 17 // foreach遍历 18 for (String s : nlist) { 19 System.out.print(s + " "); 20 } 21 22 nlist.add(1, "jay"); // 将元素“jay”插入到下标1的位置处 23 nlist.set(0, "chengang"); // 将下标0位置处的元素替换成“chengang” 24 25 // 使用迭代器遍历 26 System.out.println(); 27 Iterator<String> it = nlist.iterator(); 28 while (it.hasNext()) { // it.hashNext()判断下一个元素是否为空 29 String name = it.next(); 30 System.out.print(name + " "); 31 } 32 33 System.out.println(); 34 System.out.println("获取下标:" + nlist.indexOf("lucy")); // 输出元素“lucy”的索引值(在容器数组中的下标值) 35 System.out.println("删除元素:" + nlist.remove("jack"));// 删除,如果列表中有这个元素,返回true 36 System.out.println("删除指定位置元素:" + nlist.remove(0)); // 返回被删除位置的元素 37 System.out.println("是否包含某个元素:" + nlist.contains("chengang")); // 已删除该元素,故返回false 38 nlist.clear(); // 清空容器 39 System.out.println("判断容器是否为空:" + nlist.isEmpty()); 40 41 } 42 43 }

四 、indexof(Object o) 以及Contains(Object o)原理:
indexof(Object o) 方法本质上是调用对象o的equals()方法去list里查找,找到了就返回这个元素的下标,没有找到则返回-1;
而equals 本质比较的是两个对象的引用地址,而非对象的内容:
public boolean equals(Object obj) { return (this == obj); }
1 /** 2 * Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element 3 * in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element. 4 * More formally, returns the lowest index <tt>i</tt> such that 5 * <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>, 6 * or -1 if there is no such index. 7 */ 8 public int indexOf(Object o) { 9 if (o == null) { 10 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) 11 if (elementData[i]==null) 12 return i; 13 } else { 14 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) 15 if (o.equals(elementData[i])) 16 return i; 17 } 18 return -1; 19 }
contains方法源码如下,本质上是调用indexof来判断是否包含指定对象的,如果用contains方法判断list里面是否包含自定义的对象,那么也需要重写该对象的类的equals方法
1 /** 2 * Returns <tt>true</tt> if this list contains the specified element. 3 * More formally, returns <tt>true</tt> if and only if this list contains 4 * at least one element <tt>e</tt> such that 5 * <tt>(o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e))</tt>. 6 * 7 * @param o element whose presence in this list is to be tested 8 * @return <tt>true</tt> if this list contains the specified element 9 */ 10 public boolean contains(Object o) { 11 return indexOf(o) >= 0; 12 }
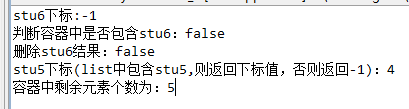
测试示例,不重写对象的equals方法时:
1 package com.iotek.list; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.List; 5 6 public class ArrayListDemo2_1 { 7 8 /** 9 * 用ArrayList容器存放对象数据 10 * 11 * @param args 12 */ 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 List<Student> stuList = new ArrayList<Student>(); // 通过泛型限定数组元素的数据类型为Student 15 Student stu1 = new Student("zhangsan", 10); 16 Student stu2 = new Student("lisi", 20); 17 Student stu3 = new Student("jack", 30); 18 Student stu4 = new Student("mandy", 10); 19 Student stu5 = new Student("mary", 20); // 创建5个Student对象 20 stuList.add(stu1); 21 stuList.add(stu2); 22 stuList.add(stu3); 23 stuList.add(stu4); 24 stuList.add(stu5); // 将5个Student对象添加到容器中 25 Student stu6 = new Student("mary", 20); 26 27 // 如果使用默认的equals方法,由于indexOf(Object 28 // o)方法的实现原理,stu6还未添加到容器中,因此找不到stu6的地址,返回-1 29 System.out.println("stu6下标:" + stuList.indexOf(stu6)); 30 System.out.println("判断容器中是否包含stu6:" + stuList.contains(stu6)); 31 System.out.println("删除stu6结果:"+stuList.remove(stu6)); // 删除stu6,不含stu6,返回false 32 System.out.println("stu5下标(list中包含stu5,则返回下标值,否则返回-1):"+stuList.indexOf(stu5)); 33 System.out.println("容器中剩余元素个数为:" + stuList.size()); 34 } 35 36 } 37 38 class Student { 39 private String name; 40 private int age; 41 42 public Student(String name, int age) { 43 super(); 44 this.name = name; 45 this.age = age; 46 } 47 48 public String getName() { 49 return name; 50 } 51 52 public void setName(String name) { 53 this.name = name; 54 } 55 56 public int getAge() { 57 return age; 58 } 59 60 public void setAge(int age) { 61 this.age = age; 62 } 63 64 }
结果如下:
重写对象的equals方法后:
1 package com.iotek.list; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.List; 5 6 public class ArrayListDemo2_2 { 7 8 /** 9 * 用ArrayList容器存放对象数据 10 * 11 * @param args 12 */ 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 List<Student1> stuList = new ArrayList<Student1>(); // 通过泛型限定数组元素的数据类型为Student 15 Student1 stu1 = new Student1("zhangsan", 10); 16 Student1 stu2 = new Student1("lisi", 20); 17 Student1 stu3 = new Student1("jack", 30); 18 Student1 stu4 = new Student1("mandy", 10); 19 Student1 stu5 = new Student1("mary", 20); 20 stuList.add(stu1); 21 stuList.add(stu2); 22 stuList.add(stu3); 23 stuList.add(stu4); 24 stuList.add(stu5); 25 Student1 stu6 = new Student1("mary", 20);//重复元素 26 System.out.println("stu6下标:" + stuList.indexOf(stu6)); 27 System.out.println("判断容器中是否包含stu6:" + stuList.contains(stu6)); 28 System.out.println("删除stu6结果:" + stuList.remove(stu6)); // 删除stu6,不含stu6,返回false,如果包含,返回该元素 29 System.out.println("stu5下标:" + stuList.indexOf(stu5)); // 删除stu6后再查看,返回-1 30 System.out.println("容器中剩余元素个数为:" + stuList.size()); 31 32 } 33 34 } 35 36 class Student1 { 37 private String name; 38 private int age; 39 40 public Student1(String name, int age) { 41 super(); 42 this.name = name; 43 this.age = age; 44 } 45 46 @Override 47 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 48 if (this == obj) 49 return true; // 如果2个指针指向同一对象,返回true 50 if (obj == null) 51 return false; 52 if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) // 如果2个类型不一样,返回false 53 return false; 54 Student1 other = (Student1) obj; // 接下来将obj转换成Student对象 55 if (age != other.age) // 如果年龄或者姓名有一个不相等,返回false,都相等,返回true 56 return false; 57 if (name == null) { 58 if (other.name != null) 59 return false; 60 } else if (!name.equals(other.name)) 61 return false; 62 return true; 63 } 64 65 public String getName() { 66 return name; 67 } 68 69 public void setName(String name) { 70 this.name = name; 71 } 72 73 public int getAge() { 74 return age; 75 } 76 77 public void setAge(int age) { 78 this.age = age; 79 } 80 81 }
结果如下:

对自定义的类,需要比较该类的两个对象是否相等时,需要比较这两个对象的属性是否相等,(而不是通过比较这两个对象的引用变量,因为2个对象的引用变量的地址永远不相同,除非这两个引用变量指向了同一个对象), 那么此时,需要重写equals方法,默认的Object类中的equals方法比较的是2个对象的地址