- 深度优先搜索DFS
DFS就是回溯法,用递归的方法是很自然的。那么该如何递归呢?
简单的说就是:1、如果当前节点没有被搜索过,那么处理当前节点,并标记为搜索过;如果当前节点已经被搜索过,退出;
2、递归遍历所有没有被搜索过的临接节点。
注意,第一步的退出条件。递归必须有退出条件,否则会出现死循环。
对任意节点调用上述DFS函数,将搜索到所有和该节点联通的节点。
- 非递归方式实现DFS
递归和栈总是联系在一起的,如果不采用递归,那么就需要自己维护一个栈。
1、从某节点开始,入栈;
2、当栈不为空时,循环3、4;当栈为空时,退出循环;
3、对栈顶节点处理,标记为搜索过;注意,如果该节点的某个临接节点处理完后,会回溯到该节点,注意不要重复处理该节点。
4、对栈顶节点,任意找一个没有搜索过的临接节点,入栈(注意只入栈一个临接节点,DFS就是找到一条路一直走下去,走不通了再回溯);如果发现该栈顶节点所有的临接节点都被搜索过,或者该节点没有临接节点,将该栈顶节点出栈。
- 实现代码
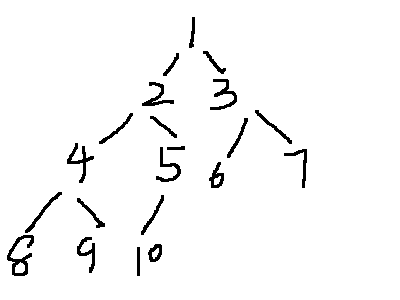
下面是DFS的递归和非递归的代码,C实现。为了简单起见,搜索对象为下图所示的满二叉树,用数组表示。
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<string.h> 3 4 #define true 1 5 #define false 0 6 #define ok 0 7 #define error -1 8 9 #define MAX_LEN 20 10 #define TREE_LEN 10 11 12 typedef struct 13 { 14 int arr[MAX_LEN]; 15 int top; 16 }STACK; 17 18 int is_empty(STACK *s) 19 { 20 if(s == NULL ) 21 { 22 printf("null param. "); 23 return error; 24 } 25 if(0 == s->top) 26 return true; 27 else 28 return false; 29 } 30 31 int is_full(STACK *s) 32 { 33 if(s == NULL ) 34 { 35 printf("null param. "); 36 return error; 37 } 38 if( MAX_LEN == s->top) 39 return true; 40 else 41 return false; 42 } 43 void push(STACK* s,int elem) 44 { 45 if(s == NULL ) 46 { 47 printf("null param. "); 48 return; 49 } 50 51 if(is_full(s)) 52 { 53 printf("is full. "); 54 return; 55 } 56 57 s->arr[s->top++] = elem; 58 } 59 60 void pop(STACK* s) 61 { 62 if(s == NULL ) 63 { 64 printf("null param. "); 65 return; 66 } 67 68 if(is_empty(s)) 69 { 70 printf("is empty. "); 71 return; 72 } 73 74 s->arr[--s->top] = 0; 75 } 76 77 int top(STACK* s) 78 { 79 if(s == NULL ) 80 { 81 printf("null param. "); 82 return error; 83 } 84 85 if(is_empty(s)) 86 { 87 printf("is full. "); 88 return error; 89 } 90 91 return s->arr[s->top-1]; 92 } 93 94 void dfs(STACK* p_stack,int *p_tree,int tree_len) 95 { 96 int visited[tree_len]; 97 int temp = 0; 98 int treeIndex = 0; 99 100 memset(visited,0,sizeof(visited)); 101 102 push(p_stack,p_tree[treeIndex]); 103 while(!is_empty(p_stack)) 104 { 105 temp = top(p_stack); 106 107 if(treeIndex < tree_len && !visited[treeIndex]) 108 { 109 printf("%d->",temp); 110 visited[treeIndex] = true; 111 } 112 113 if(2*treeIndex+1 < tree_len && !visited[2*treeIndex+1]) 114 { 115 push(p_stack,p_tree[2*treeIndex+1]); 116 treeIndex = 2*treeIndex+1; 117 } 118 else if( 2*treeIndex+2 < tree_len && !visited[2*treeIndex+2] ) 119 { 120 push(p_stack,p_tree[2*treeIndex+2]); 121 treeIndex = 2*treeIndex+2; 122 } 123 else 124 { 125 pop(p_stack); 126 treeIndex = (treeIndex-1)>>1; 127 } 128 } 129 printf(" "); 130 } 131 132 133 void dfs_reverse(int *p_tree,int*p_visited,int tree_len,int treeIndex) 134 { 135 int left,right = 0; 136 137 if(treeIndex < tree_len && !p_visited[treeIndex]) 138 { 139 printf("%d->",p_tree[treeIndex]); 140 p_visited[treeIndex] = true; 141 142 left = 2*treeIndex+1; 143 if( left < tree_len && !p_visited[left]) 144 dfs_reverse(p_tree,p_visited,tree_len,left); 145 146 right = 2*treeIndex+2; 147 if( right < tree_len && !p_visited[right]) 148 dfs_reverse(p_tree,p_visited,tree_len,right); 149 } 150 } 151 152 153 int tree[TREE_LEN] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10}; 154 STACK stack ; 155 156 #ifdef REVERSE 157 int main() 158 { 159 int visited[TREE_LEN] = {0}; 160 memset(visited,0,sizeof(visited)); 161 162 dfs_reverse(tree,visited,TREE_LEN,0); 163 } 164 #else 165 int main() 166 { 167 memset(&stack,0,sizeof(stack)); 168 dfs(&stack,tree,TREE_LEN); 169 } 170 #endif
编译运行结果:

可以看出结果是符合预期的。代码中对左右子树的处理,是对临接节点处理的一种特殊情况。