1. (quiz) spectral resolution光谱分辨率:land set>spot (band 更少)
2. transparency透明性:microwave > visible > NIR
3. Landsat MSS bands
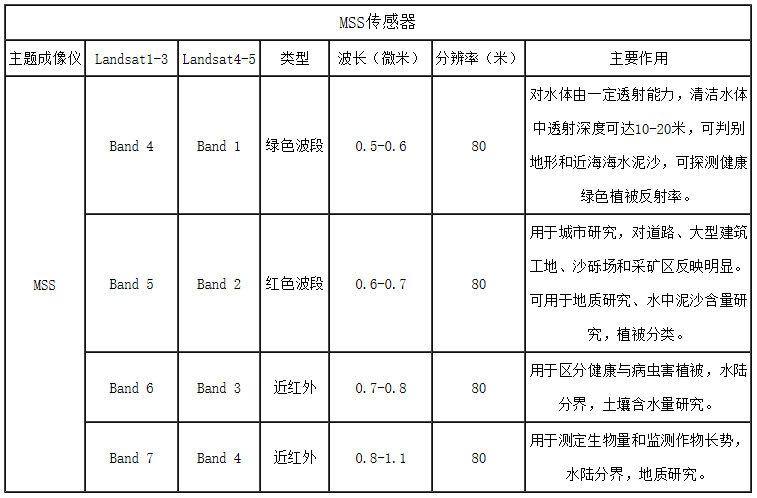
其中band 4应该为蓝色,信号弱
4. amplitude^2=intensity
振幅的平方为强度
c=frequency*波长(真空下,c = 3*10^8m/s)
5. (quiz) polarisation偏振: circular, random, plane, elliptical
circular and random are hard to tell the difference
6. rader 两次 Doppler Effect
7. Vertical structure of the atmosphere大气的垂直结构
Troposphere对流层:from the ground surface to 10 - 17 km
Stratosphere平流层:from 10 - 17 km to about 50 km
Mesosphere中间层:from about 50 km to about 90 km
Thermosphere热层:from about 90 km to 500 km
8. 电磁辐射与大气的相互作用
a. scattering散射
Rayleigh scattering: 当粒子与辐射波长相比非常小时, 如尘埃或氮氧分子的小点(蓝天,日出日落)
Mie scattering: 粒子的大小与辐射的波长几乎相同,如灰尘、花粉、烟雾和水蒸气
Nonselective scattering (water drops > wavelength):粒子比辐射的波长大得多,如水滴和大尘埃( 雾和云呈现白色【蓝+绿+红光=白光】)
b. absorption吸收:
大气中吸收不同波长能量的分子,臭氧、二氧化碳和水蒸气是吸收EMR>atmospheric windows的三种主要大气成分(Ozone, carbon dioxide, and water vapour)
atmospheric windows:相对(但不完全)不受散射和吸收影响的光谱区域,与其他波长的辐射相比,这些区域的电磁辐射通过大气层的变化较小
9. Scattering factors
a. wavelength of the radiation辐射波长
b. abundance of particles or gases粒子或气体的丰度
c. distance the radiation travels through the atmosphere辐射穿过大气层的距离

10. Reflection(R)+Absorption(A)+Transmission(T)= Incident (I)
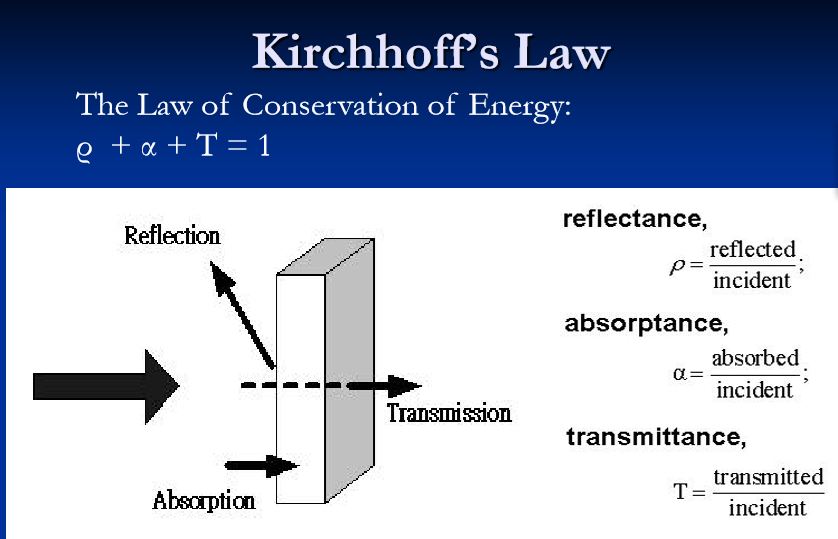
11. Specular Reflection镜面反射
镜面反射是指若反射面比较光滑,当平行入射的光线射到这个反射面时,仍会平行地向一个方向反射出来
12.

13. spatial resolution = IFOU linear = GSD
GSD is not the same with CGI, CGI is pixed sive which no not have physical meaning, but GSD can be converted to any pixed size
14. rader wavelength < light
15. SLR: Satellite Laser Ranging卫星激光测距
VLBI: Very Long Baseline
Insar: Interferometry Synthetic Aperture Rader干涉测量合成孔径雷达
16. soil before flooding is medium brightness, after flooding is low brightness
17. NDVI= (NIR-R)/(NIR+R)
18. Diffuse Reflection漫反射
从相对粗糙的表面(根据电磁辐射的波长)获得的反射类型,其中反射的光线在各个方向上散射
通常由许多具有彼此相对随机相位的个体反射组成,例如来自天然森林冠层或农业领域,漫反射的反面是镜面反射或相干
19. Roughness vs. wavelength粗糙度与波长
一个特定的目标是反射、漫反射,或者介于两者之间取决于入射辐射的波长与表面的粗糙度相比
如果波长远小于表面变化或构成表面的颗粒大小,漫反射将占主导地位
20. The Rayleigh criteri
h = λ/( 8cosθ )
If h > λ, the surface acts as a diffuse reflector漫反射镜
If h < λ, the surface is specular镜面的
h是s surface irregularity height表面不规则高度
λ is the wavelength
θ是入射角(从垂直于表面的法向[垂直]测量)
21. image是指任何图形表示,无论使用什么波长或遥感设备来检测和记录电磁能
photograph是指被检测到并记录在胶片上的图像
All photographs are images, but not all images are photographs
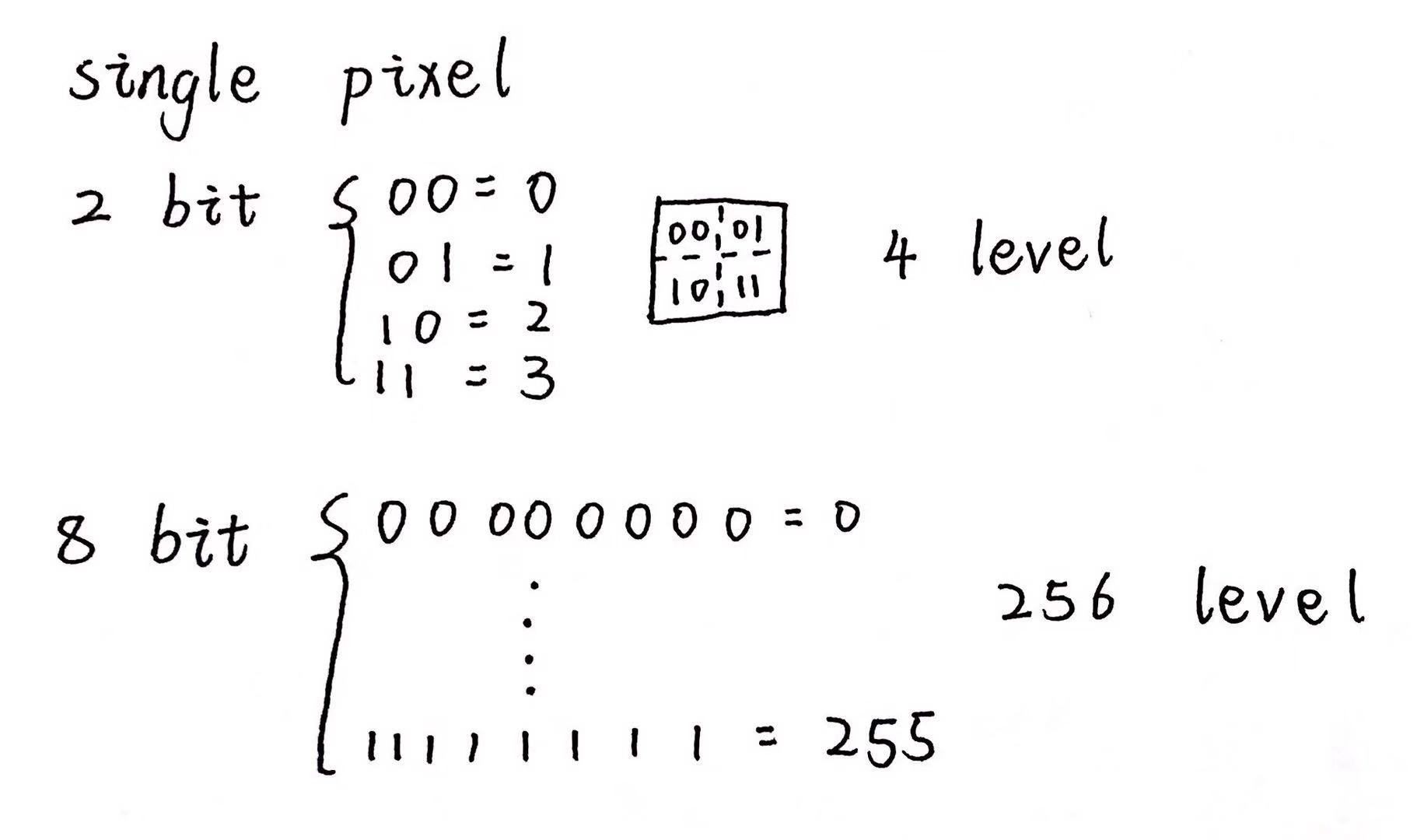
22. 将图像细分为大小相等且形状相同的小区域,称为picture elements or pixels
用数值或数字(计数值)表示每个区域的亮度
23. channel:收集和存储信息的窄波长范围
Data storage: CCT (computer compatible tape), CD, and DVD
来自每个通道的数据被表示为原色(蓝色、绿色和红色)之一,并且根据每个通道中每个像素的相对亮度(即数字值),原色以不同的比例组合以表示不同的颜色