一、题目:二叉树中和为某一值的路径
题目:输入一棵二叉树和一个整数,打印出二叉树中结点值的和为输入整数的所有路径。从树的根结点开始往下一直到叶结点所经过的结点形成一条路径。例如输入下图中二叉树和整数22,则打印出两条路径,第一条路径包含结点10、12,第二条路径包含结点10、5和7。
二叉树结点的定义如下:
public class BinaryTreeNode { public int Data { get; set; } public BinaryTreeNode leftChild { get; set; } public BinaryTreeNode rightChild { get; set; } public BinaryTreeNode(int data) { this.Data = data; } public BinaryTreeNode(int data, BinaryTreeNode left, BinaryTreeNode right) { this.Data = data; this.leftChild = left; this.rightChild = right; } }
二、解题思路
2.1 核心步骤
首先,通过下图了解遍历上图中的二叉树的过程:

通过上图可以总结出规律:
(1)当用前序遍历的方式访问到某一结点时,我们把该结点添加到路径上,并累加该结点的值。
(2)如果该结点为叶结点并且路径中结点值的和刚好等于输入的整数,则当前的路径符合要求,我们把它打印出来。如果当前结点不是叶结点,则继续访问它的子结点。
(3)当前结点访问结束后,递归函数将自动回到它的父结点。这里要注意的是:在函数退出之前要在路径上删除当前结点并减去当前结点的值,以确保返回父结点时路径刚好是从根结点到父结点的路径。
2.2 代码实现
public static void FindPath(BinaryTreeNode root, int expectedSum) { if (root == null) { return; } int currentSum = 0; List<int> path = new List<int>(); FindPath(root, expectedSum, path, ref currentSum); } private static void FindPath(BinaryTreeNode root, int expectedSum, List<int> path, ref int currentSum) { currentSum += root.Data; path.Add(root.Data); // 如果是叶结点,并且路径上结点的和等于输入的值 // 打印出这条路径 bool isLeaf = root.leftChild == null && root.rightChild == null; if (isLeaf && currentSum == expectedSum) { foreach (int data in path) { Console.Write("{0} ", data); } Console.WriteLine(); } // 如果不是叶结点,则遍历它的子结点 if (root.leftChild != null) { FindPath(root.leftChild, expectedSum, path, ref currentSum); } if (root.rightChild != null) { FindPath(root.rightChild, expectedSum, path, ref currentSum); } // 在返回到父结点之前,在路径上删除当前结点, // 并在currentSum中减去当前结点的值 path.Remove(root.Data); currentSum -= root.Data; }
三、单元测试
3.1 测试用例
(1)辅助方法的封装

private static void TestPortal(string testName, BinaryTreeNode root, int expectedSum) { if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(testName)) { Console.WriteLine("{0} begins:", testName); } FindPath(root, expectedSum); Console.WriteLine(); } private static void SetSubTreeNode(BinaryTreeNode root, BinaryTreeNode lChild, BinaryTreeNode rChild) { if (root == null) { return; } root.leftChild = lChild; root.rightChild = rChild; } private static void ClearUpTreeNode(BinaryTreeNode root) { if (root != null) { BinaryTreeNode left = root.leftChild; BinaryTreeNode right = root.rightChild; root = null; ClearUpTreeNode(left); ClearUpTreeNode(right); } }
(2)功能、特殊输入测试
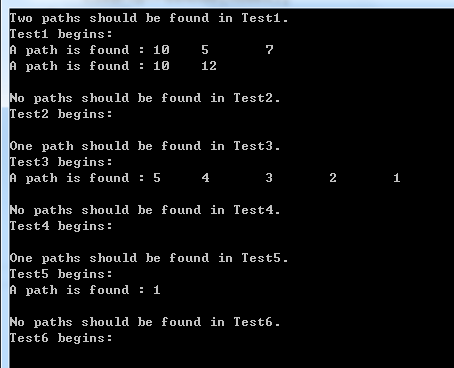
// 10 // / // 5 12 // / // 4 7 // 有两条路径上的结点和为22 public static void Test1() { BinaryTreeNode node10 = new BinaryTreeNode(10); BinaryTreeNode node5 = new BinaryTreeNode(5); BinaryTreeNode node12 = new BinaryTreeNode(12); BinaryTreeNode node4 = new BinaryTreeNode(4); BinaryTreeNode node7 = new BinaryTreeNode(7); SetSubTreeNode(node10, node5, node12); SetSubTreeNode(node5, node4, node7); Console.WriteLine("Two paths should be found in Test1."); TestPortal("Test1", node10, 22); ClearUpTreeNode(node10); } // 10 // / // 5 12 // / // 4 7 // 没有路径上的结点和为15 public static void Test2() { BinaryTreeNode node10 = new BinaryTreeNode(10); BinaryTreeNode node5 = new BinaryTreeNode(5); BinaryTreeNode node12 = new BinaryTreeNode(12); BinaryTreeNode node4 = new BinaryTreeNode(4); BinaryTreeNode node7 = new BinaryTreeNode(7); SetSubTreeNode(node10, node5, node12); SetSubTreeNode(node5, node4, node7); Console.WriteLine("No paths should be found in Test2."); TestPortal("Test2", node10, 15); ClearUpTreeNode(node10); } // 5 // / // 4 // / // 3 // / // 2 // / // 1 // 有一条路径上面的结点和为15 public static void Test3() { BinaryTreeNode node5 = new BinaryTreeNode(5); BinaryTreeNode node4 = new BinaryTreeNode(4); BinaryTreeNode node3 = new BinaryTreeNode(3); BinaryTreeNode node2 = new BinaryTreeNode(2); BinaryTreeNode node1 = new BinaryTreeNode(1); node5.leftChild = node4; node4.leftChild = node3; node3.leftChild = node2; node2.leftChild = node1; Console.WriteLine("One path should be found in Test3."); TestPortal("Test3", node5, 15); ClearUpTreeNode(node5); } // 1 // // 2 // // 3 // // 4 // // 5 // 没有路径上面的结点和为16 public static void Test4() { BinaryTreeNode node1 = new BinaryTreeNode(1); BinaryTreeNode node2 = new BinaryTreeNode(2); BinaryTreeNode node3 = new BinaryTreeNode(3); BinaryTreeNode node4 = new BinaryTreeNode(4); BinaryTreeNode node5 = new BinaryTreeNode(5); node1.leftChild = node2; node2.leftChild = node3; node3.leftChild = node4; node4.leftChild = node5; Console.WriteLine("No paths should be found in Test4."); TestPortal("Test4", node1, 16); ClearUpTreeNode(node1); } // 树中只有1个结点 public static void Test5() { BinaryTreeNode node1 = new BinaryTreeNode(1); Console.WriteLine("One paths should be found in Test5."); TestPortal("Test5", node1, 1); ClearUpTreeNode(node1); } // 树中没有结点 public static void Test6() { Console.WriteLine("No paths should be found in Test6."); TestPortal("Test6", null, 0); }
3.2 测试结果