1、神经网络的计算通常包括前向传播(foward propagation)步骤和反向传播(backward propagation)的步骤;
2、数据预处理:
- X.shape:[nx,m]--->nx 是特征数,m为样本数
- Y.shape:[1,m]
- W.shape:[nx,1]
- b---->是实数
- X 数据标准化
3、激励函数:
sigmoid(x)=1/(1+e-x)函数:
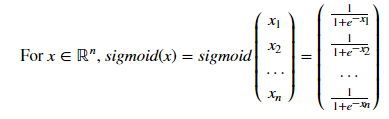
1 import numpy as np 2 def sigmoid(x): 3 """ 4 Compute the sigmoid of x 5 6 Arguments: 7 x -- A scalar or numpy array of any size 8 9 Return: 10 s -- sigmoid(x) 11 """ 12 13 14 s = 1.0/(1+np.exp(-x)) 15 16 17 return s
softmax函数:
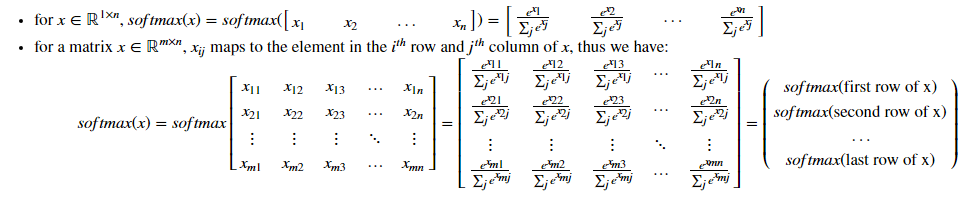
1 def softmax(x): 2 """Calculates the softmax for each row of the input x. 3 4 Your code should work for a row vector and also for matrices of shape (n, m). 5 6 Argument: 7 x -- A numpy matrix of shape (n,m) 8 9 Returns: 10 s -- A numpy matrix equal to the softmax of x, of shape (n,m) 11 """ 12 13 14 # Apply exp() element-wise to x. Use np.exp(...). 15 16 x_exp = np.exp(x) 17 18 # Create a vector x_sum that sums each row of x_exp. Use np.sum(..., axis = 1, keepdims = True). 19 20 x_sum = np.sum(x_exp,axis=1,keepdims=True) 21 22 # Compute softmax(x) by dividing x_exp by x_sum. It should automatically use numpy broadcasting. 23 24 s = x_exp / x_sum 25 26 27 return s
4、二分类(Binary Classification)-Logistic Regression:
Building the parts of our algorithm:
- Define the model structure(such as number of input features)
- Initialize the model's parameters
- Loop:
- Calculate current loss(forward propagation)
- Calculate current gradient(backward propagation)
- Update parameters(gradient descent)
Forward and Backward propagation:
- You get X
- You compute A=σ(wTX+b)=(a(0),a(1),...,a(m−1),
- You calculate the cost function:J=−1/m∑mi=1y(i)log(a(i))+(1−y(i))log(1−a(i))
- Backward propagation:
-
∂J/∂w=(1/m)X(A−Y)T
-
∂J/∂b=1m∑i=1m(a(i)−y(i))
-

1 import numpy as np 2 3 #define sigmoid 4 5 def sigmoid(z): 6 s=1.0/(1+np.exp(z)) 7 8 #Initializing parameters 9 10 def initialize_with_zeros(dim): 11 w=np.zeros((dim,1)) 12 b=0 13 assert(w.shape==(dim, 1)) 14 assert(isinstance(b,float) or isinstance(b,int)) 15 return w,b 16 17 # forward and backward propagate 18 19 def propagate(w,b,X,Y): 20 """ 21 Implement the cost function and its gradient for the propagation explained above 22 23 Arguments: 24 w -- weights, a numpy array of size (num_px * num_px * 3, 1) 25 b -- bias, a scalar 26 X -- data of size (num_px * num_px * 3, number of examples) 27 Y -- true "label" vector (containing 0 if non-cat, 1 if cat) of size (1, number of examples) 28 29 Return: 30 cost -- negative log-likelihood cost for logistic regression 31 dw -- gradient of the loss with respect to w, thus same shape as w 32 db -- gradient of the loss with respect to b, thus same shape as b 33 """ 34 m=X.shape[1] 35 A=sigmoid(np.dot(w.T,X)) 36 cost=(-1.0/m)*np.sum(Y*np.log(A)+(1-Y)*np.log((1-A))) 37 dw=(1/m)*np.dot(X,(A-Y).T) 38 db=(1/m)*np.sum(A-Y) 39 assert(dw.shape==w.shape) 40 assert(db.type==b.type) 41 cost=np.squeeze(cost) 42 assert(cost.shape==()) 43 grads={"dw":dw, 44 "db":db} 45 return grads,cost 46 47 #using gradient descent,The goal is to learn ww and bb by minimizing the cost function JJ . For a parameter θθ , the update rule is θ=θ−α dθ , where αα is the learning rate. 48 49 def optimize(w, b, X, Y, num_iterations, learning_rate, print_cost = False): 50 costs=[] 51 for i in range(num_iterations): 52 grads, cost = propagate(w,b,X,Y) 53 dw = grads["dw"] 54 db = grads["db"] 55 w = w - learning_rate * dw 56 b = b - learning_rate * db 57 if i%100==0: 58 costs.append(cost) 59 if print_cost and i%100==0: 60 print ("Cost after iteration %i: %f" %(i, cost)) 61 params = {"w": w, 62 "b": b} 63 64 grads = {"dw": dw, 65 "db": db} 66 67 return params, grads, costs 68 69 #predict 70 def predict(w,b,X): 71 m=X.shape[1] 72 Y_prediction=np.zeros((1,m)) 73 w=w.reshape(X.shape[0],1) 74 A=sigmoid(np.dot(w.T,X)+b) 75 for i in range(A.shape[1]): 76 Y_prediction[0,i]=np.where(A[0,i]>=0.5,1,0) 77 assert(Y_prediction.shape==(1,m)) 78 return Y_prediction 79 80 #model 81 82 def model(X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test, num_iterations = 2000, learning_rate = 0.5, print_cost = False): 83 w, b = initialize_with_zeros(X_train.shape[0]) 84 parameters, grads, costs = optimize(w, b, X_train, Y_train, num_iterations, learning_rate, print_cost) 85 Y_prediction_test = predict(w, b, X_test) 86 Y_prediction_train = predict(w, b, X_train) 87 print("train accuracy: {} %".format(100 - np.mean(np.abs(Y_prediction_train - Y_train)) * 100)) 88 print("test accuracy: {} %".format(100 - np.mean(np.abs(Y_prediction_test - Y_test)) * 100)) 89 d = {"costs": costs, 90 "Y_prediction_test": Y_prediction_test, 91 "Y_prediction_train" : Y_prediction_train, 92 "w" : w, 93 "b" : b, 94 "learning_rate" : learning_rate, 95 "num_iterations": num_iterations} 96 97 return d